Table of Contents
- 11+ Audit Confirmation Templates in DOC | Excel | PDF
- 1. Audit Confirmation Letter
- 2. Audit Confirmation Template
- 3. Audit Confirmation Request Form
- 4. Audit Confirmation Letter Process
- 5. Group Meeting Agenda Audit Confirmation
- 6. Electronic Audit Confirmation Template
- 7. External Audit Confirmation Template
- 8. Frequently Asked Question Audit Confirmation Report
- 9. Audit Confirmation Process
- 10. Audit Confirmation Request
- 11. Audit Confirmation Letter in PDF
- 12. End of Audit Confirmation Independence Letter
- What is Positive and Negative Confirmation in Auditing?
- What are the Steps to the Traditional Audit Confirmation Methods?
- What is a Positive Confirmation Request?
- What is Negative Confirmation?
- What is External Confirmation in Auditing?
- What is an Audit Inquiry?
- What is an Audit Procedure?
- What are the Goals of the Audit?
11+ Audit Confirmation Templates in MS Word | Excel | PDF
The audit confirmation includes the balance due by the client or owed to the supplier on the audit client’s balance sheet date. The client or supplier can verify, partly confirm or reject the balance by signing the letter and giving it back to the accounting firm in a self-addressed return envelope. Have a look at the audit confirmation templates provided down below and choose the one that best fits your purpose.

11+ Audit Confirmation Templates in DOC | Excel | PDF
1. Audit Confirmation Letter
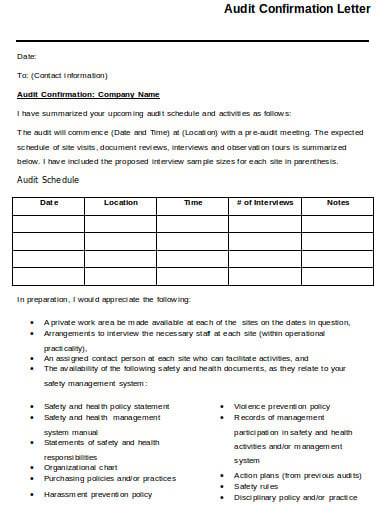 safemanitoba.com
safemanitoba.com2. Audit Confirmation Template
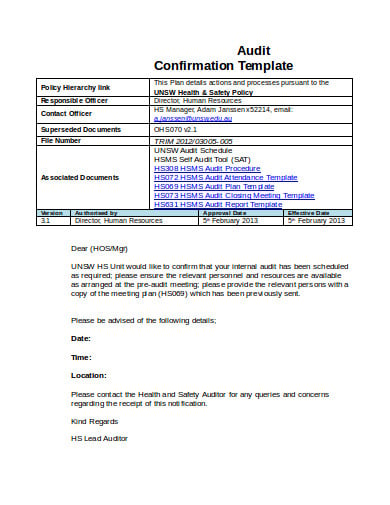 safety.unsw.edu
safety.unsw.edu3. Audit Confirmation Request Form
 hsbc.co.th
hsbc.co.th4. Audit Confirmation Letter Process
 bba.org
bba.org5. Group Meeting Agenda Audit Confirmation
 pcaobus.org
pcaobus.org6. Electronic Audit Confirmation Template
 nacva.com
nacva.com7. External Audit Confirmation Template
 ifac.org
ifac.org8. Frequently Asked Question Audit Confirmation Report
 dbs.com.sg
dbs.com.sg9. Audit Confirmation Process
 butterfieldgroup.com
butterfieldgroup.com10. Audit Confirmation Request
 fhlb.com
fhlb.com11. Audit Confirmation Letter in PDF
 reginfo.gov
reginfo.gov12. End of Audit Confirmation Independence Letter
 nrc.gov
nrc.govWhat is Positive and Negative Confirmation in Auditing?
A positive confirmation is an interrogation made by an auditor to a third party that needs a response. A positive confirmation is deemed to signify a higher quality of proof than a negative approval since the auditor obtains explicit proof from the third party.
What are the Steps to the Traditional Audit Confirmation Methods?
The standard audit confirmation method includes multiple manual actions and normally requires the following five steps:
1. The audit customer gives the accounting firm exportation of their consumers and suppliers including the accounts receivable and payable balances from their accounting method. It is imperative that the accounting firm get accurate accounts receivable and payable data from the audit customer’s documents.
2. The accounting firm chooses a representative sampling from the audit client’s export and produces the audit confirmations with the guidance of the mail merge features standard in different word processing devices. The resulting audit confirmations include as a least the client or supplier, the amount in question, the balance sheet date and a confirmation request.
3. The accounting firm sends the audit confirmations to the audit client’s consumers and suppliers both by post or electronically as an e-mail attachment.
4. It is responded by the audit client’s consumers and suppliers back to the audit confirmation by utilizing a self-addressed and imprinted envelope or by returning the individual email sent by the accounting firm. This step can usually need various manual reminders in order to obtain an acceptable response rate.
5. The accounting firm records the answers separately as they come in and forms the final audit evidence for the accounting sector. The accounting firm most frequently registers the audit confirmations manually, which raises the risk for data entry mistakes particularly when trading with various currencies and many customers and suppliers.
What is a Positive Confirmation Request?
What is Negative Confirmation?
What is External Confirmation in Auditing?
What is an Audit Inquiry?
What is an Audit Procedure?
What are the Goals of the Audit?
- Investigating the inner system.
- Verifying the authenticity and efficacy of transactions that are done.
- Analyzing arithmetical exactness of books of accounts, casting, balancing, etc.
- Establishing the present value of assets and obligations.

