Table of Contents
- 1. System Audit Frame Work Template
- 2. Technical System Audit Template Download
- 3. System Audit Management Report Example
- 4. Printable System Audit Checklist Template
- 5. Internal Audit System Download
- 6. Simple Audit of Online System
- 7. System Focusing Audit Aspects Example
- 8. Basic System Based Audit
- 9. Accounting System Audit Layout
- 10. Information System Audit Scope
- 11. System Audit Report Format
- 12. Independent System Audit Report
- What Do You Understand By System Audit?
- What are the Objectives of System Audit?
- How Will You Conduct a System Audit (5 Steps)
- What Do You Understand by Information System Audit?
- State the Methodology of Information System Audit?
System Audit
The process of system management is one of the effective and important management tools to achieve the objective that is set by the policies of the organization. It is a disciplined and regulated approach that an organization uses to evaluate and improve the effectiveness of the organization. In simple terms, it can be said that the system audit is through evaluation and reviewing of the information system of an organization.

1. System Audit Frame Work Template
 sebi.gov.in
sebi.gov.in2. Technical System Audit Template Download
 kb.icai.org
kb.icai.org3. System Audit Management Report Example
 audit.wa.gov.au
audit.wa.gov.au4. Printable System Audit Checklist Template
 mga.org.mt
mga.org.mt5. Internal Audit System Download
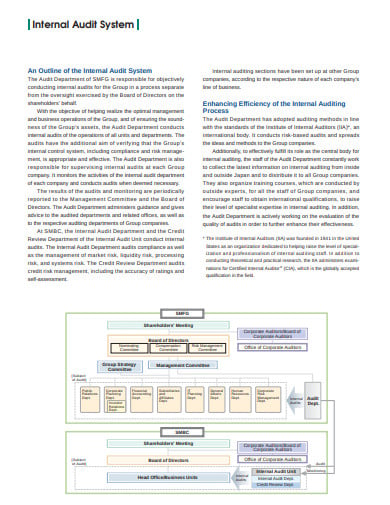 smfg.co.jp
smfg.co.jp6. Simple Audit of Online System
 raw.rutgers.edu
raw.rutgers.edu7. System Focusing Audit Aspects Example
 roger-odenthal.de
roger-odenthal.de8. Basic System Based Audit
 finance.gov.mk
finance.gov.mk9. Accounting System Audit Layout
 dcaa.mil
dcaa.mil10. Information System Audit Scope
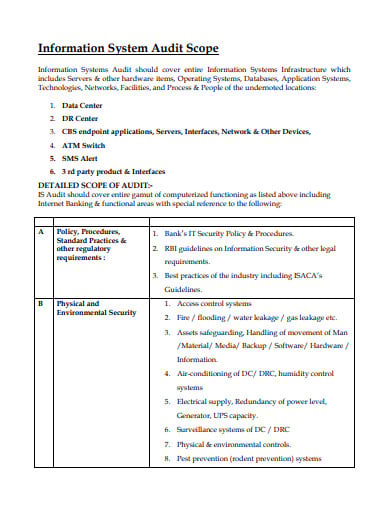 municipalbankmumbai.com
municipalbankmumbai.com11. System Audit Report Format
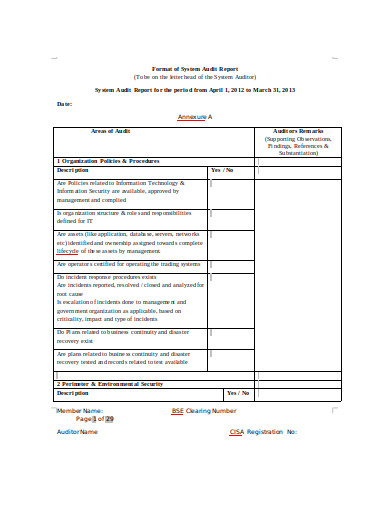 bhavcopy.net
bhavcopy.net12. Independent System Audit Report
 ec.europa.eu
ec.europa.euWhat Do You Understand By System Audit?
System Audit can be defined as the approach of systematic and independent examination of the activities and the result of these activities. It is the evaluation of whether the activities and their results satisfy the planned arrangements. The system audit also checks if those arrangements are implemented effectively to achieve the desired objectives.
System Audit can also be defined as the systematic, independent and documented process to obtain the audit evidence and to determine the extent to which it has satisfied the audit criteria.
What are the Objectives of System Audit?
- The evaluation of the system of the organization against the set standard systems.
- To confirm the presence of system elements with specified requirements.
- To determine whether the system that has been implemented meet the objectives set for the organization.
- Offering opportunities for improvement in the system.
- Meeting the statutory and regulatory requirements.
How Will You Conduct a System Audit (5 Steps)
-
Step 1: Reviewing
This is the stage where the auditor assimilates details of the management practices and the various functioning that are used at the multiple levels of the IT hierarchy. The tasks that are included such as observing the installation procedures, interviewing the installation staff, and reviewing the installation documentation.
-
Step 2: Assessing the Vulnerabilities of the System
This means conducting the assessment of the different systems and identifying the most vulnerable one. The systems and computers that are vulnerable are the ones most used for abuse. Therefore the protocols of quality controls are to be reviewed.
-
Step 3: Identification of the Threats
The chances of the information system getting threatened by the internal and the external users are quite high. The user range from programmer, system analysts, cyber security specialists, etc. Therefore it is extremely necessary that you identify the threats that can posses great harm to the data and the confidential information.
-
Step 4: Analyzation of the Internal Controls
In this step, the system auditor determines the usefulness of the information system’s internal controls and whether they are working or not as should. The auditor should also check any kind of missing in the internal control in the system.
-
Step 5: Final Evaluation
In this step, there are different evaluations that are carried out for the various components of the internal control system. The purpose of the test is to identify any future loss in the information system. This includes identification of the processing, data quality, finding inaccurate data, etc.
What Do You Understand by Information System Audit?
The information system audit also termed as the information technology audit is the examination of the internal controls within the information technology infrastructure. It is the process conducted by the organization to collect and evaluate the information system, practices, and operations.
State the Methodology of Information System Audit?
Phase 1: Planning the Audit
The information system is prepared to adhere to the objectives of the audit as specified by the organization what observes the law and the professional standards. The first thing is to get the audit charter or the document that lists the purpose of the audit. This will help you to know the responsibilities you have as the auditor, the specific areas that the auditor will audit, the accountability that the auditor will hold towards the audit performed.
Phase 2: Assessment of the Risk
Risk is a factor that can pose a threat to the organization and the information system. The risk can also exploit the vulnerabilities of the information system that can cause the loss of the asset of information and confidential data. Therefore it is imparative that risk assessment is conducted to mitigate the risk causing factor and lessen the magnitude of its impact. The types of risks are:
- Inherent Risk: It is the type of risk that the audited area is prone to. This is the risk that occurs due to the omission or error of data conducted by factors outside the internal control.
- Control Risk: This is the risk that can arise in the audited area due to mismanagement and is not timely prevented, detected or corrected by the internal control system.
- Detection Risk: This is the risk that the auditor fails to identify or detect. This can exist significant and either exist individually or in combination with other errors.
Phase 3: Performance of the Audit Work
The Information system audit work requires to provide supervision, gather audit evidence, and documenting the audit source. This objective is achieved by:
- An internal review process is established where the work one person is reviewed by another person preferably someone who is senior.
- Sufficient and reliable evidence is gathered through processes such as observation, inquiry, confirmation and so on.
- The work is documented as done and is supported by the evidence gathered by the auditor.






