
11+ Training Agenda Templates
It’s always advised to proceed in a systematic way when you are looking to impart a training. If you are…
Jun 29, 2023
The term “internal audit plan or agenda” is the file containing the audit engagements that are managed over a period of time. The most simple form of an internal audit plan is annual audit plan. It is the best way to develop your internal audit plan that depends on the structure of your organization, industry-oriented requirements and other regulations. In such big organizations, there are often designations such as chief audit executive who is responsible for interviewing key employees and audit committee.


 labqualityconfab.com
labqualityconfab.com iia.nl
iia.nl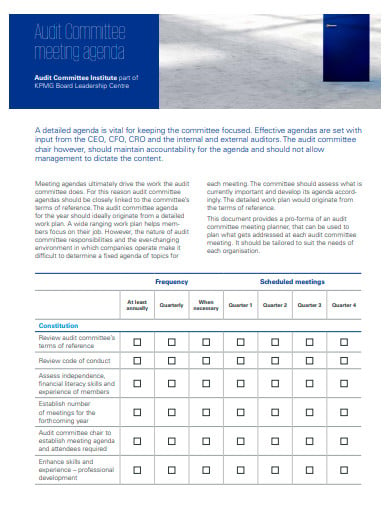 assets.kpmg
assets.kpmg armadale.wa.gov.au
armadale.wa.gov.au southdowns.gov.uk
southdowns.gov.uk eportal.mountsinai.ca
eportal.mountsinai.ca angus.gov.uk
angus.gov.uk rother.gov.uk
rother.gov.uk oag.treasury.gov.za
oag.treasury.gov.za thegrid.org.uk
thegrid.org.uk threerivers.gov.uk
threerivers.gov.ukThe internal audit agenda is planning and figuring out the ways to identify the value of or improving organizational operations. The agenda helps the organization to fulfill the objectives by bringing on the systematic, disciplined approach to evaluate and see the effectiveness of risk management. It prefers to work on the control and governance process. Some steps are discussed below to understand this broad area of internal auditing.
The identification of the areas that operate by using the policies and procedures documented by the organization or by the regulatory bodies. The area includes the manufacturing processes or as simple as the accounting procedure.
The frequency of the auditing must be determined as some areas need the annual auditing while others need quite a frequent auditing. The manufacturing process needs daily audits for quality control purposes.
While you plan on internal auditing, it is kept in mind that a structured and systematic approach can ensure the functions get completed. Scheduling the audits will ensure that it is done in a systemized way.
The scheduled audits are for every organization where the audit is going to take place priorly informing them. With the information to the organization, staff members and employees can assemble all the necessary documents.
The internal audit plan or agenda must be priorly prepared and arranged. And with the preparation comes the responsibilty and duty to assemble all the important and necessary documents required by the audt team.
What is the purpose of the internal audit agenda?
The main aim and objectives of interviewing and speaking with the employees are to be aware of the disturbed areas. In addition to it, the core members of the audit team should pay attention to risk factors that their interviewees see for the organization. When you see the minimal change in regulations of which managers are aware, it is necessary to know about on a huge scale since staff members should be properly trained or know about the risk of getting dinged for noncompliance by an authorized body.
There are penalties that require an official plan to be instituted to bring the organization up to the mark or could incur heavy fines. Another example where staff members must be able to suggest for changing software systems that could pose a cybersecurity problem. Higher-level of management is not aware of things that deal with these systems on a daily might observe.
For making the plan of internal audit, you need the validation and approval of the board members. The internal audit committee has established that work on the complete process of auditing. The audit plan covers the financial, operational, system and risk management control.
With the planning for the internal audit comes the duty and responsibility of creating the internal audit team. The committee is set up by the director of the internal audit that will look into the adequacy and effectiveness of the internal controls. And they monitor and evaluate the different risk factors in the internal administration. It is the job to look after the accomplishment of the aims and objectives of the internal body members.
The internal audit is done through the selected members to safeguard the assets and tasks within the organization. It is their core duty to find out the ways of using them in achieving favorable consequences.
There are plenty of the differences between internal and external audit plans and they both work differently. The audit plans are for the evaluation and assessment of the various activities and operations within the organization. The audit committee is established within the members of the organization that especially look into the planning and execution of internal or external audits.
The internal audit is independent in nature but evaluates and gives assurance that an organization’s internal management process is operating effectively or not. Whereas, the external audit is the process conducted by an independent accountant or an external auditor. At the end of the process, the result is put forward by the auditor through the audit report.

It’s always advised to proceed in a systematic way when you are looking to impart a training. If you are…

An agenda is really important when one has to conduct a program- be it a meeting or conference or an…

A complete cycle of sales process includes many factors like quantity and volume of the product, sales price, commission, trade…

The term “internal audit plan or agenda” is the file containing the audit engagements that are managed over a period…

In simple terms, the purpose of meeting agendas is to provide a proper outline of all the main topics that…

Just like any other staff meetings, church staff meetings are towards the edge of being engaging. Only because these are…

While planning any church meeting, you need to think of all the details about what will interest the church members…

The church nursery schedule is made, keeping in mind the various things as in Christianity along with the religious teaching…

Would you like to sit for hours at a meeting that is dragging on without any actual point being made?…