
32+ Sample Baptism Certificate Templates
Baptismal record is important to any person being given an initiation in becoming a member of their selected religion. Baptism…
Jun 23, 2020
A certificate of deposit is a certificate issued by a bank to the individual depositing money at a defined rate of interest for a specified period of time. It is a time deposit or a financial product that is typically sold by banks, credit unions and thrift institutions. Such certificates are similar to savings accounts in that they are “bank money” insured and therefore practically risk-free, up to the local insured deposit cap.

 uel.ac.uk
uel.ac.uk dtcc.com
dtcc.com alightfinancialsolutions.com
alightfinancialsolutions.com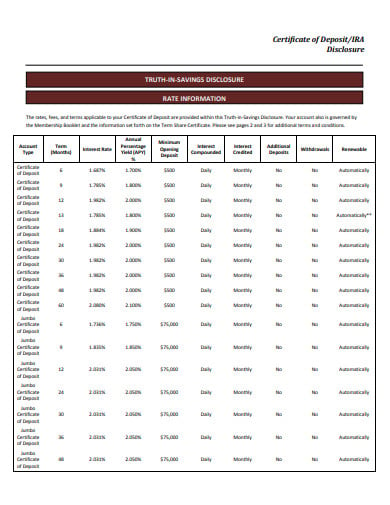 trumarkonline.org
trumarkonline.org raymondjames.com
raymondjames.com ccilindia.com
ccilindia.com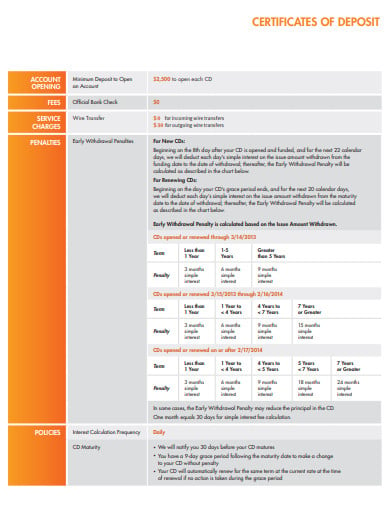 discover.com
discover.com fraser.stlouisfed.org
fraser.stlouisfed.org forms.in.gov
forms.in.gov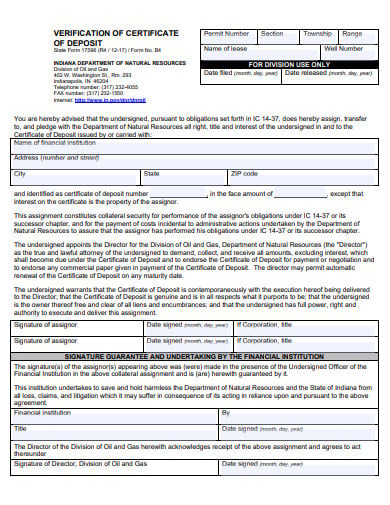 forms.in.gov
forms.in.gov vtf.org
vtf.orgSuch certificates usually require a minimum deposit, and higher rates may be available for larger deposits. The highest rates are usually provided on “Jumbo CDs,” with a minimum of $100,000 deposits. Jumbo certificate of deposits is typically bought by large institutional investors who are interested in low-risk and stable investment options, such as banks and pension funds.
The terms and conditions for certificates of deposits vary widely. If the initial issuing entity has combined with another organization, or if the purchaser exits the CD early, or there is some other problem, the purchaser will have to refer to the terms and conditions agreed upon to ensure that the withdrawal is handled according to the original contract terms.
The first advantage of a CD is safety. In other words, you can be assured of the safety of your funds. The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation insures up to $250,000 worth of CDs. The government ensures that you will never lose your principal. This is why they are less risky than shares, commodities or other more risky assets, for that reason.
Secondly, they deliver rates of interest than account deposits and interest-bearing banking.
Thirdly, you have the option of buying the best rate. Small banks are offering better rates, as they need the funds. Online-only banks will be offering higher rates than brick and mortar banks because they have lower costs.
The main downside is that the duration of the certificate is tied to your income. If you need to withdraw your money before the term is up you pay a penalty.
The second downside is that while your money is tied up you will miss out on investment opportunities that arise.
The third issue is that the CDs are not charged enough to keep up with the inflation rate. When you just invest in CDs, over time you will lose your living standards. Investing in stocks is the best way to keep ahead of inflation but that is risky. You could lose your investment entirely.

Baptismal record is important to any person being given an initiation in becoming a member of their selected religion. Baptism…

Certificates help prove the authenticity of any achievement, completion, award, design, and other professional creations. Our Word certificate templates may…

On completion of a certain task or project, usually, a certificate is awarded to acknowledge it. It is a recognition…

For any insurance company, they can take the insurance certificate template to be presented in their clients as the copy…

You finally became parents. After filling out the birth certificate template given to you, what is the next step? Christening…

A death certificate is a document certifying a person’s passing, documented by a medical practitioner and issued by the county…

Retirement appreciation certificate is the certificate that is presented to a retired person or the person who will be retiring…

Feeling that you want to further your studies and you do not know where to get financial assistance. You can…

These formats are considered to be more formal than the unpopular formats. A good Diploma certificate templates has to mention…