
40+ Word Checklist Templates
Due to limited memory and attention, we humans often forget to do tasks which we were supposed to perform. Our…
Aug 25, 2023
A safety audit is a systematic mechanism by which knowledge is gathered about the performance, efficacy, and durability of the overall health and safety management system of an organization. Such audits are conducted in all kinds of organizations and institutions. A school safety audit checklist lists the tasks that need to be performed to conduct such an audit properly.


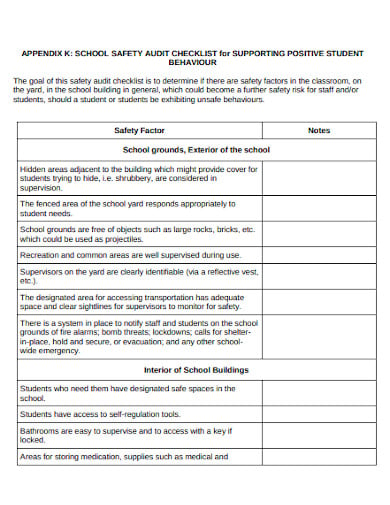 pvnccdsb.on.ca
pvnccdsb.on.ca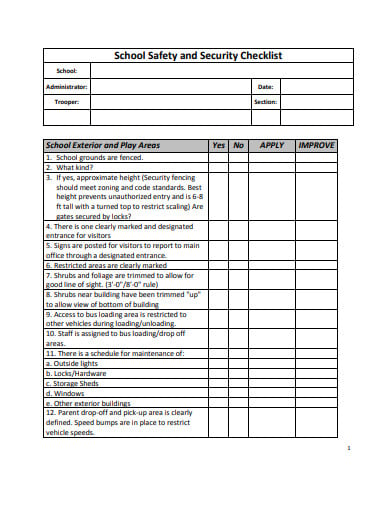 louisianabelieves.com
louisianabelieves.com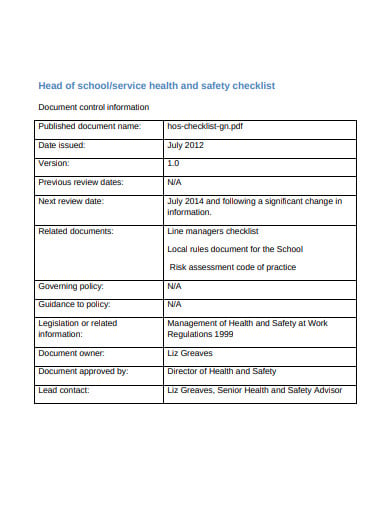 bristol.ac.uk
bristol.ac.uk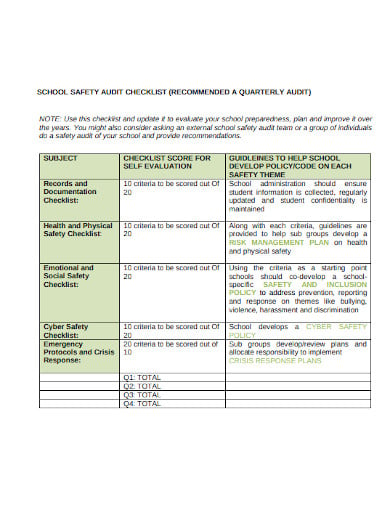 aanganindia.org
aanganindia.org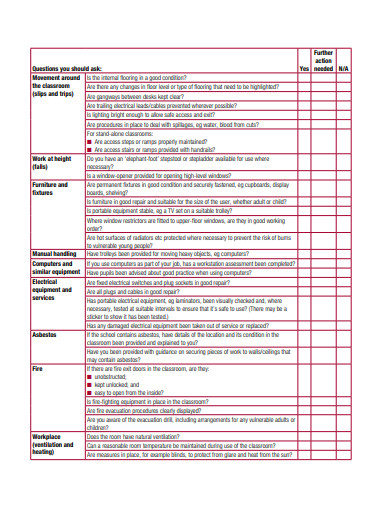 hse.gov.uk
hse.gov.uk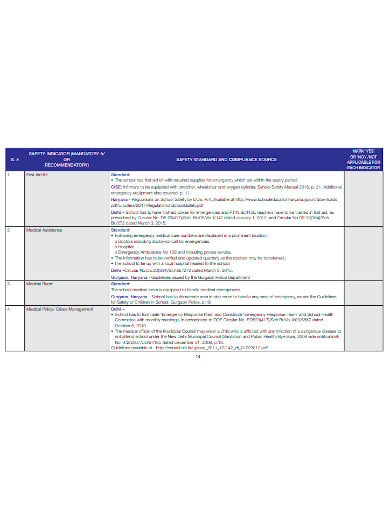 ficci.in
ficci.in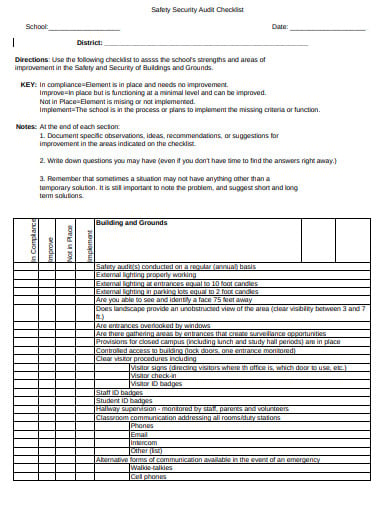 cloudfront.net
cloudfront.net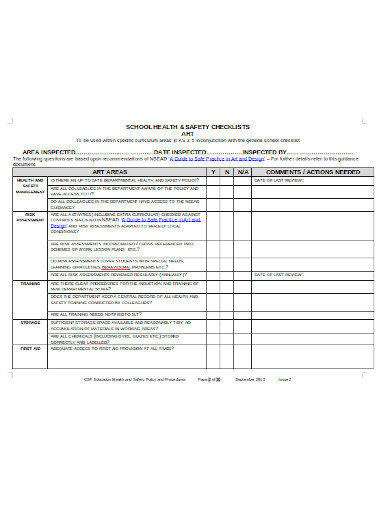 thegrid.org.uk
thegrid.org.uk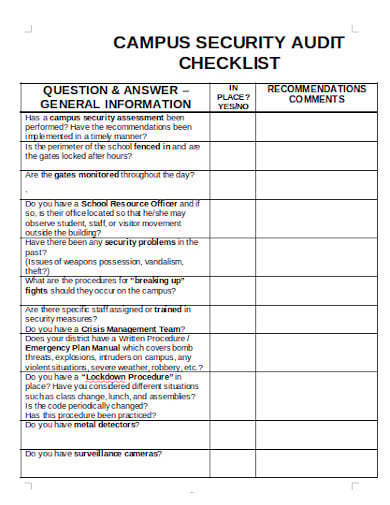 scsba.org
scsba.org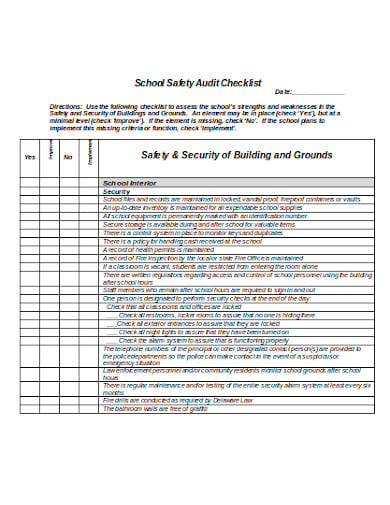 doe.de.us
doe.de.us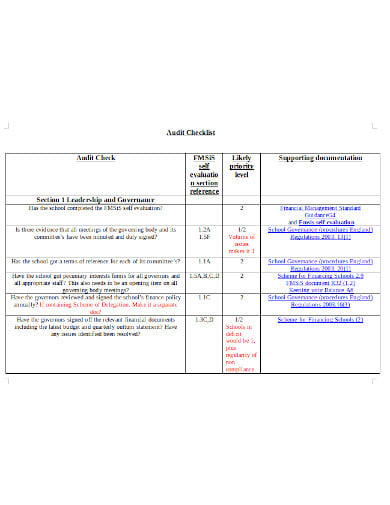 webfronter.com
webfronter.comConducting just one safety audit per year can have the adverse effect of making protection and security seem like a routine target that needs to be accomplished once a year instead of a continuous requirement. There may be a “ramping up” atmosphere created by managers and supervisors working to ensure compliance ahead of the audit as the date of an annual audit approaches which might lead to discouragement. A better way of approach is to schedule specific safety audits on an 11-month sample schedule throughout the year.
A security audit can only be as effective as the experts that carry out it, so it helps to entrust the procedure to those with the requisite knowledge and experience. To guarantee such expertise, some companies choose to hire outside consultants or security professionals, but many prefer to keep the operations in-house. Businesses should create security audit teams consisting of three to five employees who are well versed in current safety standards when using the latter method. You can also see more on Audit Checklist in Word.
The experience should be prepared for both those conducting the audit and those being audited. The company should inform all affected managers and supervisors at least a week before a workplace safety audit that they must have all records, documents and procedures ready and available when the audit starts. At least a week before a workplace safety audit, the employer will advise all concerned managers and supervisors that they must have all reports, paperwork, and processes ready and available at the start of the examination.
Exhaustive sample reports are a protection assessment prerequisite and target. A compliance audit team will review all relevant incident reports for the segment they are auditing to determine which potential problem issues are most likely to exist. Competent records of accidents allow auditors to extend limited attention to known problem areas better.
The protection evaluation teams need to sift through the gathered information after reviewing all records, written plans, processes, work practices, and facilities and generate a comprehensive basic report detailing all activity fields. Any statements, suggestions and corrective actions on safety audits will address whether the audited printable plan meets any criteria for legislative and appropriate industry practice, whether those standards are being followed, and whether there is documented evidence of enforcement.
The use of state-of-the-art management systems makes it much easier to ensure that all the above-stated safety audit standards are met. Modern technology enables safety auditors to test and verify the compliance status of the workplace more easily and effectively. You can also see more on Safety Checklist.
The following lists some steps that need to be followed if you want to ensure that the audit is conducted properly;
Before you can conduct a safety audit, the first that needs to be done is an inspection of the general environment. Similarly, when an auditor comes to conduct a safety audit, the inspection of the general work environment is one of the first things they will do. Each review will provide a complete overview of what to do. Besides, any common areas, for example, parking lots, storage areas, breakrooms, bathrooms, must also be checked for potential risks. You can also see more on Construction Safety Checklist Templates.
The next step is to enquire about and evaluate the work areas of the organization or the institution. This refers to the auditor carrying out a physical inspection of those areas. This evaluation should be carried out efficiently and effectively. The auditor can request a workplace map so that they can specify where they are going to start and finish and ensure that they cover all areas. The problems are recorded to be worked on later. You can also see more on School Checklist Templates.
The auditor needs to work in each area with the immediate supervisors to gather knowledge about the tasks, roles, and responsibilities of the different members of that institution or organization. For example, if the audit is being conducted in a school, the work and tasks of the teachers and the professors would need to be documented. Once the listing is provided to the auditor, their job is to look for potential job-related injuries that might occur in these functions. You can also see more on Audit Checklist in Pages format.
The auditor’s final task is to recommend a course of action after the findings and their results have been reported, which should be taken to eliminate any risks, mitigate potential dangers and otherwise correct any defects in the workplace. For example, if the organization has old worn-out equipment that could pose a risk to workers, the auditor should record these things in their reports to either fix or remove them. You can also see more on Training Checklist Templates.

Due to limited memory and attention, we humans often forget to do tasks which we were supposed to perform. Our…

A facility maintenance checklist is a priceless defense means to keep a building reliable and safe by periodical planning, checkups,…
A Recruitment Checklist is the to-do-list where you list down all the important details that you need to do or…

Logistics Performance Index indicates that America is one of the leading logistics industries in the globe. Its networks coordinate with…

The best way you can make sure that all cleaning go as planned is to have a cleaning checklist samples.…

A Resume Screening Checklist is a checklist that is prepared by the recruiter to list all the important points based…

HR Compliance Checklist is the tool that is used by HR professionals to make the preparations for the HR tools.…

A retirement party is the opportunity to celebrate the retiree’s past achievements as well as their future efforts. The party…

The mortgage business has gone through a lot of chapters in the industry, combating business challenges every year. According to…