
11+ School Counselor Lesson Plan Templates in PDF | Word
Empowering the youth to become the best can be such a fulfilling task to accomplish. But, school counselors proved that…
Mar 23, 2021
An external audit plan summarizes the approach to the audit of the financial statements and the value for money conclusion. This plan also highlights some of the most significant audit risks and the staff will be able to discuss their report and answer any detailed questions arising from it. It helps the auditor to minimize the risks, improve audit efficiency, and also in meeting its objective at the minimum effort.

 ilo.org
ilo.org democracy.aylesburyvaledc.gov.uk
democracy.aylesburyvaledc.gov.uk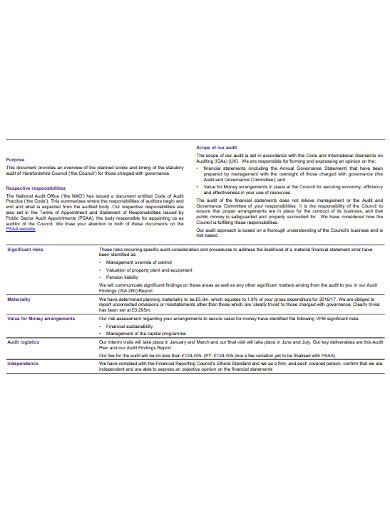 councillors.herefordshire.gov.uk
councillors.herefordshire.gov.uk wokingham.moderngov.co.uk
wokingham.moderngov.co.uk cne-siar.gov.uk
cne-siar.gov.uk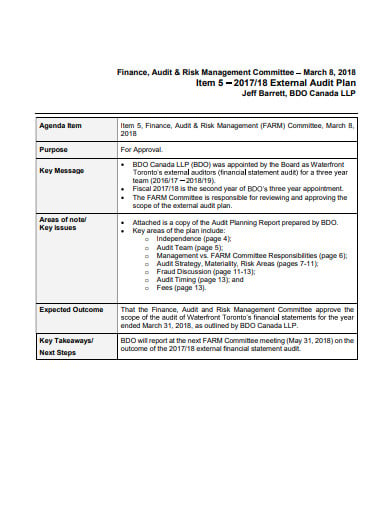 waterfrontoronto.ca
waterfrontoronto.ca democracy.gloucester.gov.uk
democracy.gloucester.gov.uk sestran.gov.uk
sestran.gov.uk democracy.cambridge.gov.uk
democracy.cambridge.gov.uk council.lancashire.gov.uk
council.lancashire.gov.ukThere is no standard length in the process of external audits as the audit goes on until the external auditors have finished. The external audit begins at the end of the company’s fiscal year as it is that this time when the accounting books are closed and financial statements for the year are prepared. The external auditors may even communicate with the internal auditors when any questions arise during the process, but the external auditors are not much influenced by the internal auditors.
The process of an external audit commonly looks at the various financial statements and accounting records and other departments in the company can also be audited during an external audit. For instance, the department that handles information systems might have an external audit that focuses only on technology or an operations department audit that may analyze the internal management structure.
Certain activities need to be completed before the external auditor begins. The external auditor must first meet the management of the company to determine in case any procedures or other factors have affected the company record keeping and reporting. These factors may include in the industry regulations, changes in the company structure and operations, and legal matters.
The reporting phase is considered to be the main part of the external audit. It is done on-site at the company that is being audited. In this particular phase, the auditors examine the company’s ability to record and process the data properly in the reports such as in financial statements. This is usually done by going through the records that are used to create the statement or other documents, and also re-create them to see if they were created correctly or not.
Lastly, the external auditors prepare and deliver a summary report to the company. The summary report lays out all of the findings from the audit. This also includes some differences that are found in the reporting as well as non-compliance of rules and regulations. The findings of the auditor offer the company a way to correct any differences and become compliant before a regulatory body notices.
There is one main reason why organizations hire external auditors, i.e to have an objective assessment of the organization’s financial standing. As there is not any developed relationship between the external auditors and the organization that they are reviewing, they are not biased in any way. This means that they can be objective throughout their audit.
When external auditors are hired by the organizations, they ensure that he or she is not a relative or a friend of the owner, manager or employee. These auditors who are reviewing publicly traded organizations or companies should not hold stock in them or have any kind of equity stake in any of their holdings.
The principal difference between external and internal auditors is the one that employs them. An independent auditor usually works for an organization but he is not employed by it. An organization appoints an external auditor and will work on a particular project basis although some organizations will employ the services of external editors that they have used in the past. On the other hand, an internal auditor generally works for the organization that he reviews.
Both these types of auditors provide similar services as they evaluate the business operations, financial statements as well as the organization’s compliance with relevant laws. They also help organizations in identifying irregularities in their departments and also make recommendations on how to address them properly.
The in-house internal audit team cannot provide impartiality but an external audit is capable of doing that. There are usually no concerns over repercussions for the external auditor if the organization is unhappy with their report. While internal auditors cannot help but be personally invested in the outcome of their findings. This difference is hugely important for reinforcing the credibility of a company’s financial statements and general financial health.
With an external auditor on board, the business stakeholders, relevant revenue and other committees can be assured of a thorough investigation into an organization’s finances and accounting processes. This reliability is particularly important to small and start-up companies or companies that may have suffered a data breach.
Employing an external auditor is believed to strengthen company practice within the scope of government compliance. An external auditor’s job is to identify areas of non-compliance along with the issues with fraud or abuse within the organization.
External auditors also provide some important and valuable understanding of the information that exists within an organization. The findings they make and the audit processes give the business or any organization, confidence, and reassurance that their information and the way they conduct business is suitably decent.

Empowering the youth to become the best can be such a fulfilling task to accomplish. But, school counselors proved that…

A compensation plan is the detailed plan of an employee’s wages, salaries, benefits and the terms of payment. The plan…

As there is a saying that ” with big positions comes the big responsibilities”. It is the huge duty to…

The student recruitment plan is one of the most important and essential parts of educational institutions. The strategy interacts with…

The recruitment and retention are two different terms explaining the thing that is inter-related. Recruitment is the process of identifying,…

A College Recruitment Plan is the designed plan or a strategy that is developed to recruit the employees of a…

A Recruitment Action Plan is a strategy that is designed for putting the recruiting process into action. This is the…

A recruitment business plan is one of the necessities for a company. It does not just help you to map…

Clinical trial recruitments are considered to be very essential to the success of any clinical study and it is often…