
11+ Remuneration Policy Templates in PDF | Ms Word
Arrangements on a remuneration policy are significant reports made by associations crosswise over different fields for giving standards to moral…
Sep 13, 2023
A written statement of policy on fraud suggests that the battle against fraud is embraced and sponsored at the highest level within your company. Organizations may want to ensure that all workers are mindful of a zero tolerance approach towards criminal infringements of corporate practices that can be reported police. Any workers, vendors and suppliers should be told of the fraud policy statement.


 ntpc.co.in
ntpc.co.in isaca.org
isaca.org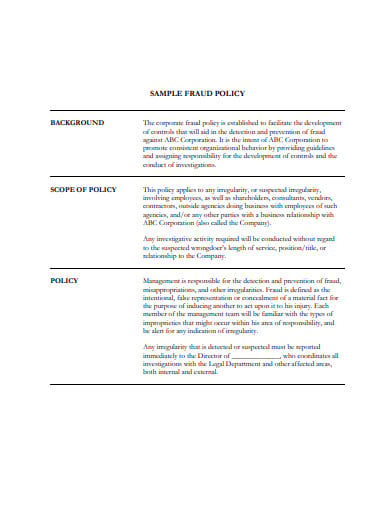 acfe.com
acfe.com coalindia.in
coalindia.in ed.ac
ed.ac indiafirstlife.com
indiafirstlife.com tdic.ae
tdic.ae hrw.org
hrw.org oxfordshire.gov
oxfordshire.gov bradford.gov
bradford.gov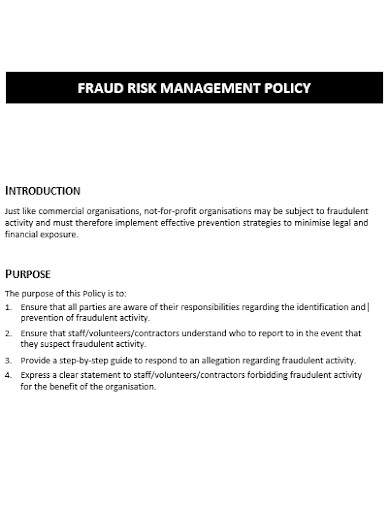 communitydirectors.com
communitydirectors.comEvery company is susceptible to fraud, with only the particular risks associated varying across organizations. Therefore, fraud risk assessment is an important first step in the development of an active prevention programme. The basic process of building a plan involves assigning responsibility to a supervisor or managers, who will then include if appropriate more people in the company to guarantee that all elements of the organization’s operations are tested for fraud risks. Keep in mind that real fraud might still happen, so that a constant tracking and evaluation component is required for the broad process to track effectiveness.
Once a plan for fraud prevention has been in place, communicating it to everybody in the company, from top to bottom, is crucial. This may require preparation or research; however, it will better inform everyone on the firm’s concept of fraud and standards on how it should be handled by employees. Because fraud is a secret risk the corporate risk assessment strategy should include both identification and preventive efforts. Where strong preventive measures are in place, however, managers can get both a boost in identification and prevention. Training on the fraud risk prevention program, for example, may not only discourage any fraud but may also enable honest workers to disclose what they know about fraud.
Fraud prevention controls generally differ from company to company depending on the company protocols and requirements. However, some practices can be used irrespective of the organization it is being used for:
Among the most efficient ways of avoiding fraud is the practice of excluding those who are at higher risk for fraud. Organizations will screen potential workers, employees considered for important new positions, and as far as possible outsourced suppliers or partners.
Training is critical as has already been said. This helps make the organization’s policies clear to set expectations and establish awareness of enforcement actions. No employee should be excluded from this training at any level.
A popular finding in organizational fraud research is that fraud is committed by generally trustworthy people. Often because of their treatment, they rationalize their behavior, e.g. by being passed on for a promotion or a boost. The incentive-based payment systems sometimes lure individuals to pad or cut corners. Evaluations of performance must be correct, equitable and conveyed.
Staff individuals who leave may have information that can help in both prevention and identification for whatever cause.
It’s a well-known concept fundamental for the prevention of fraud. It involves dividing the tasks and responsibilities among the employees so that no single individual has access to too much information.
Preventive measures are specific checks conducted on the individuals who are authorized to approve an action, as well as policies on access to data.
Internal management breaches are a common cause of fraud. Policies will encourage constant monitoring of enterprise-wide transactions to detect illegal or suspicious activities immediately.
All external and internal investigations can help to control fraud. Since Sarbanes-Oxley points strongly to the upgrading of professional standards making fraud prevention an important part of audits.
The following items may be used to create the fraud policy of your organization:
One more principle to remember is reinforcing the program after it has been signed by the employees. By stressing clear and decisive action against criminals, the company will demonstrate the value of the policy and the company’s zero-tolerance for fraud. A few common and standard actions are taken against fraud by organizations:
Not doing something is entirely unacceptable, as it illustrates, among other items, an emptiness in corporate ethics, theoretically undermines bond coverage, and paves a way for other workers to impunity perpetrate wrongdoings. However, then there is the question as to whether the case should be terminated and finished or pursued with legal action. Auditors and investigators almost always want legal action to go forward. Nevertheless, they also hit the administrative challenge or Legal foregoing prosecution of a lawsuit because they assume litigation would be too costly in comparison to any profit the business would derive from the litigation. That’s both short-sided and wrong.

Arrangements on a remuneration policy are significant reports made by associations crosswise over different fields for giving standards to moral…

Grooming policy is the rule or the protocol that an employee has to follow when he becomes the employee of…

A dress code policy is defined as a set of guidelines to make it easy for the employees to know…

A sales commission policy fulfills the policy of establishing responsibilities for setting commission rates and to define the point at…

A confidentiality policy implies individual correspondence or data identifying with an association’s business that is obscure to general society and…

The dividend policy is a financial decision that indicates the balance of the firm’s wages to be paid out to…

The payment policy is the set of rules or directions that guides a customer to make the bill payment templates.…

Bonus Policy can be referred to as the protocol formulated in an organization based on which the employees are given a…

Recruitment policy is the practice that a company exhibits while hiring employees. It a statement that outlines the rules and…