
40+ Monthly Management Report Templates in PDF | Google Docs | Excel | Apple Pages
Managers usually write reports, and they have to be submitted every month to the higher authorities of a company. These…
Sep 20, 2023
A paper with the formal results of an audit is referred to as an internal audit report. It is utilized by the internal auditor to determine what was reviewed, highlighting positives, negatives, and outcomes so that the organization’s management knows what is going properly and what needs to be developed. The report must be prepared thoroughly. Have a look at the internal audit report templates provided down below and choose the one that best fits your purpose.


 portseattle.org
portseattle.org barnet.moderngov.co.uk
barnet.moderngov.co.uk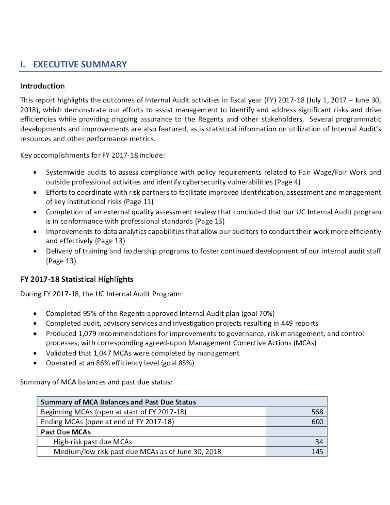 ucop.edu
ucop.edu drc.ngo
drc.ngo trs.texas.gov
trs.texas.gov apps.who.int
apps.who.int hhs.texas.gov
hhs.texas.gov okcommerce.gov
okcommerce.gov okcommerce.gov
okcommerce.gov uthscsa.edu
uthscsa.edu vicroads.vic.gov.au
vicroads.vic.gov.auInternal audits assess an organization’s internal controls, including its corporate governance and accounting methods. They guarantee agreement with laws and regulations and assist to manage specific and timely financial reporting and information collection.

Managers usually write reports, and they have to be submitted every month to the higher authorities of a company. These…

Have you ever tried sending a Report Outline for corrective action to a company about bad food, product, or service?…

Crafting an event report is an essential step in analyzing the success and impact of any event, whether it’s a…

A report card is one of the crucial elements of recording the results of an evaluation of a leaner. Many…

Getting ready with your inspection report? Not satisfied with your report’s format? Don’t you worry? We have here an array…
Every organization must be careful while creating a daily or weekly activity report as it is with the help of…

The audit report is the ending result of an audit and can be utilized by the receiver person or organization…

Audit committee reports present a periodic and annual picture of the financial reporting method, the audit process, data on the…

Timely reports are vital for any logistics industry as data is essential to help make decisions. Plus, the industry’s scope…