
40+ Monthly Management Report Templates in PDF | Google Docs | Excel | Apple Pages
Managers usually write reports, and they have to be submitted every month to the higher authorities of a company. These…
Sep 16, 2023
An investment evaluation report refers to the dual task of managing financial risk against expected return. You can project the sources and applications of funds for the upcoming periods while evaluating an investment emphasis that should be laid on the question about whether the expected return justifies the risk. Some of the commonly used methods of investment evaluation are payback period, internal rate of return along with the net present value.


 service.gov.uk
service.gov.uk health.gov.au
health.gov.au worldbank.org
worldbank.org norfund.no
norfund.no employment.gov.au
employment.gov.au socialvalueuk.org
socialvalueuk.org eib.org
eib.org adb.org
adb.org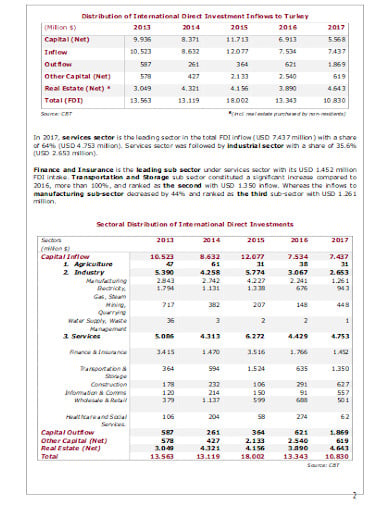 yased.org.tr
yased.org.tr afdb.org
afdb.org allenandclarke.co.nz
allenandclarke.co.nz ohchr.org
ohchr.orgThe evaluation of the projects is generally based on their cash flows. Project evaluation will be based upon their cash flows. We’ll compare the cash invested and the project cash generated. Therefore there will be no accounting or related features that can affect the decision.
The investor considers the cash flows that are driven by the project to evaluate a project. For example, if the project uses the available staff who would not be fired in the absence of a project, this cost should not be included in the project. In comparison, if the project sales result in a decrease in the sales of another product this side effect should be taken into account.
A dropped cost refers to an element created by the project, regardless of whether to continue with it or not. For example, the costs involved with several project evaluation studies like market research, product design, etc, that will always be borne by the client regardless of the final project decision. In such cases, the related dropped costs should not be included in the project calculation.
The project runs for a given period. The more common criteria for establishing this time horizon is the economic life of the investment’s major component, but other criteria can be used as per the features of the project.
If the project has a limited life, the distribution of assets and the recognition of work capital balances will have to take place at the end of the project, their actual cash flows being. Nevertheless, the value of asset sales must be calculated. And taking a conservative view, the disposal of assets will take place in the year after the last operating cash flow happens or the operating activity is completed.
The project data can be prepared on the assumption of zero inflation (real prices) or consideration of a given price development scenario and its impact on project outputs and inputs. The latter is more popular in projects that are developed in countries with high and particularly unpredictable inflation, whereas the former is more widely used. The real price method creates additional problems in the valuation process concerning the estimation of the discount rate: this has to be determined to take into account the potential scenario of zero inflation.
While there are numerous individual ways to evaluate stocks, industries, and economies, a study of investment can be separated into a few different categories.
Investors may use a bottom-up approach to investment valuation or a top-down approach when making investment decisions. Bottom-up investment research includes the study of individual stocks for their qualities, such as price, management skills, pricing power, and other particular stock and underlying business characteristics. A bottom-up investment evaluation may not focus on economic cycles or any market cycles for capital allocation decisions that do not focus firsthand on economic cycles or market cycles. Rather, it aims to find the best companies and stocks, irrespective of the overarching macro-trends in the economy, market or particular industry.
The macroeconomic strategy is a trademark of a study of top-down investment evaluation. Before making a more concentrated investment decision to allocate capital to specific companies, it emphasizes economic, market and industry trends. As a result, the investor determines that overweight financials and underweight sectors will be the investment portfolio. We then continue to find the best financial-sector stocks. On the opposite, a bottom-up investor may have considered a manufacturing company making for a good investment and allocating a large amount of capital to it despite the negative outlook for its wider industry.
Other methods of investment evaluation include basic analysis and technical analysis. The fundamental analysis stresses both the evaluation of corporate financial health and economic outlooks. Fundamental analytics practitioners are searching for stocks that they believe the market has mispriced trading at a price lower than that justified by the intrinsic value of their businesses. Such investors will often assess the financial validity of a firm, future business prospects, profit potential, and economic moat to decide whether they will make appropriate investments, encompassing bottom-up research.
The technical evaluation stresses the assessment of stock price patterns and statistical parameters, through computer-calculated charts and graphs. Like fundamental analysts who seek to measure the intrinsic value of a commodity, technical analysts rely on market movement patterns, trading signals and numerous other analytical charting methods to determine the strength or weakness of security. Day traders frequently make use of technical evaluation in defining their approaches and timing the entries and exits of their positions.

Managers usually write reports, and they have to be submitted every month to the higher authorities of a company. These…

Have you ever tried sending a Report Outline for corrective action to a company about bad food, product, or service?…

Crafting an event report is an essential step in analyzing the success and impact of any event, whether it’s a…

A report card is one of the crucial elements of recording the results of an evaluation of a leaner. Many…

Getting ready with your inspection report? Not satisfied with your report’s format? Don’t you worry? We have here an array…
Every organization must be careful while creating a daily or weekly activity report as it is with the help of…

The audit report is the ending result of an audit and can be utilized by the receiver person or organization…

Audit committee reports present a periodic and annual picture of the financial reporting method, the audit process, data on the…

Timely reports are vital for any logistics industry as data is essential to help make decisions. Plus, the industry’s scope…