
40+ Monthly Management Report Templates in PDF | Google Docs | Excel | Apple Pages
Managers usually write reports, and they have to be submitted every month to the higher authorities of a company. These…
Nov 27, 2024
Technical reports are detailed documents designed to communicate specific technical information or findings to stakeholders, clients, or team members. They often include in-depth research, methodologies, data analysis, and conclusions to address complex problems or convey essential information. Their structured approach ensures accuracy and clarity, making them a crucial resource for decision-making and strategic planning in various industries. You can allso see on Project Report

A brief summary of the report (100-200 words), including key objectives, methodology, results, and conclusions. Avoid technical jargon or detailed data.
Lists all sections and sub-sections with page numbers. Include figures, tables, and appendices if applicable.





It is a formal document requiring a comprehensive but concise statement of what has been done and discovered from your research; with its format you will know what should and not to be included in the simple report template to prevent any lengthy statements or unnecessary information.

ittc.ku.edu

gvsu.edu

niso.org

projectmesa.org

idrc.ca

niap-ccevs.org
wrap.org.uk

sfwater.org
If you have any DMCA issues on this post, please contact us! You can also see more templates like technical report letters in word, pdf, google docs and apple pages in our official website template.net.

Writing a technical report involves presenting technical information in a clear, structured, and concise manner. It is designed to inform or document findings, processes, or data for specific audiences such as engineers, managers, or researchers. Here’s a step-by-step guide to crafting an effective technical report:
A typical technical report includes the following sections:

Technical reports play a crucial role in various fields such as engineering, science, business, and technology. They are essential for communicating complex technical information clearly and effectively. Here are the key reasons why writing a technical report is important:
1. Effective Communication of Information
2. Decision-Making Support
3. Record-Keeping and Knowledge Preservation
4. Enhancing Professionalism
5. Facilitating Collaboration
A technical report typically includes a title page, abstract, introduction, methodology, results, and conclusion. Additional sections like recommendations and references are often added. Visual aids like charts and tables may be included. Each section serves a specific purpose in delivering information. The structure ensures clarity and flow.
The audience for technical reports includes professionals like engineers, scientists, and managers. It may also include stakeholders, clients, or academic reviewers. The tone and complexity depend on the audience’s expertise. Clear and precise writing ensures the report is accessible. Tailoring content to the audience is key.
A technical report focuses on practical technical findings and their applications. A research paper emphasizes academic studies and theoretical discussions. Reports are often prepared for industries, while papers target academic circles. Reports may include recommendations, unlike papers. Both follow formal writing but differ in scope.
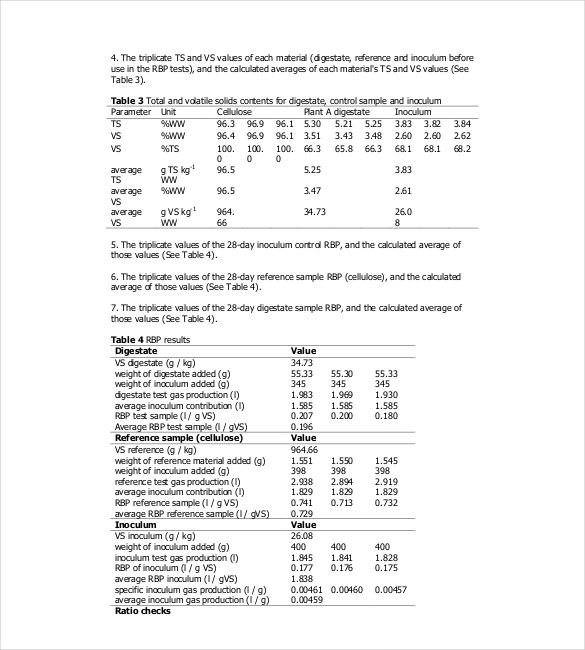
Use visuals like charts, graphs, and diagrams to complement written content. Ensure visuals are clear, labeled, and referenced in the text. Use high-quality images and maintain consistency in style. Avoid clutter by using only relevant visuals. Visuals should enhance understanding, not overwhelm readers.
Ethical considerations include ensuring data accuracy and avoiding plagiarism. Present findings honestly without manipulation or bias. Properly credit all sources and collaborators. Maintain confidentiality for proprietary or sensitive information. Ethical writing builds trust and enhances the report’s value.

Managers usually write reports, and they have to be submitted every month to the higher authorities of a company. These…

Have you ever tried sending a Report Outline for corrective action to a company about bad food, product, or service?…

Crafting an event report is an essential step in analyzing the success and impact of any event, whether it’s a…

A report card is one of the crucial elements of recording the results of an evaluation of a leaner. Many…

Getting ready with your inspection report? Not satisfied with your report’s format? Don’t you worry? We have here an array…
Every organization must be careful while creating a daily or weekly activity report as it is with the help of…

The audit report is the ending result of an audit and can be utilized by the receiver person or organization…

Audit committee reports present a periodic and annual picture of the financial reporting method, the audit process, data on the…

Timely reports are vital for any logistics industry as data is essential to help make decisions. Plus, the industry’s scope…