
12+ HR Fresher Resume Templates
Writing an eye-grabbing Resume Format for someone who has no working experience in the field or any industry somehow sounds…
Jun 23, 2020
A research assistant pertains to an individual who is often recruited by a university, research institute or private organization on a temporary contract to help with academic or private research. These people are not independent and accountable to a manager or lead researcher and are not usually directly accountable for the research results.


 ac.uk
ac.uk usf.edu
usf.edu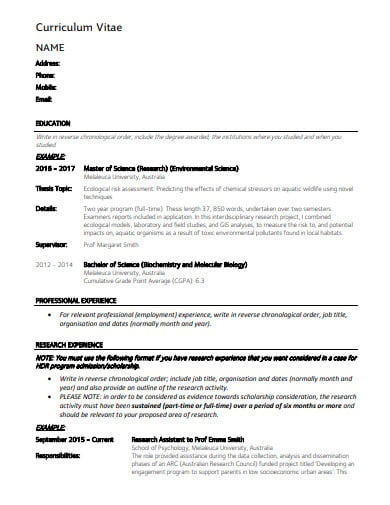 griffith.edu
griffith.edu smith.edu
smith.edu dayjob.com
dayjob.com carleton.edu
carleton.eduResearch assistants are individuals who are there to aid professionals such as researchers and scientists, who are carrying out experiments of different types, who collect data, and/or analyze data and information. Typical employers comprise of research centers for medical purposes, think tanks, consultancies, public benefit groups, universities, polling agencies, and market research companies. Tasks can vary greatly depending on the type of study they’re employed in. However, there are a few basic roles and responsibilities that need to be fulfilled:
Research assistants are generally supervised by key researchers or investigators who lead research projects. They are accountable for supporting the key researcher or investigator in a variety of tasks that facilitate the tasks of research. Such activities differ based on the type of work being carried out and the field in which they are.
Research assistants are generally needed to have at least one bachelor’s degree in the research area in which the study is based. Training varies considerably from field to field.
Prior work experience is not always necessary to be a research assistant, but for scientific research, it is often necessary to have prior experience working in a laboratory, even during school.
A good research assistant must have the skills and qualities as mentioned below:
Research assistants are very often told to gather and assess data and maintain and update existing databases. They could also be asked to undertake reviews of the literature or field studies.
Research assistants might need machinery and tools for the establishment and operation of a laboratory.
Research assistants must be capable of working extremely reliably, pay close attention to detail and keep records of their work.
It is important to be able to meet project deadlines when working with data and statistics and to control your time to achieve your goals.
Generally, research assistants are supposed to work in laboratories and offices, but some may do fieldwork related to a research project.
Research assistants can work part-time or full time. Generally, their employers decide their working hours including the sector in which they will be working, but they generally work within normal business hours.
CVs differ from each other based on the job you are making for. You must start by providing your personal information whilst making such a CV. You need to explain to the receiver who you are in the first paragraph itself. Keep in mind that one recruiter is likely going through a hundred CVs a day. If you do not present yourself adequately at the beginning of the document, your curriculum vitae could easily get lost. The general things that you need to include are your name, address, and contact details.
Your educational qualifications will come next in the CV. Generally, for the position of a research assistant, the individual needs to have at least a Bachelor’s Degree in the field of study or any other related field. Without this, an applicant is deemed unsuitable for the job. In the CV, include the degree or diploma you have received, the college from which it was awarded, the year of graduation, the marks or grades you have obtained and the courses or subjects included when you provide the education information. All this information must be presented in the reverse chronological order.
The purpose or objectives you insert in your curriculum vitae refer to the reason you first write the curriculum vitae. If you want your CV to be considered, you’ll need to create good expectations for your CV. Since you are making the CV for the position of research assistant, your objectives would need to explain all that you want to do and all that you can do in that specific work environment. For instance, if you are applying to work for an experimental physicist, you can provide objectives related to experimental Physics.
This is the part of the curriculum vitae where you get the chance to brag about yourself. Typically what people do is just list all of their abilities and achievements. However, that is not the best way to advertise yourself if you want to get your CV approved. Begin by telling yourself what goals you had in mind, and then proceed to describe what you have done and how you have done it to meet those goals. Keep in mind to adapt your expertise and achievements to a specific job position such as operations.
Contrary to popular belief, extracurricular activities matter a lot when it comes to applying for a job role. For instance, the main role of a research assistant is to provide support to the lead researcher in his or her. However, the assistant might be required to do other things as well such as fieldwork and analyze data and produce results. This is the CV segment where, apart from your main task, you have to tell the recipient how good you are at other tasks. What separates you from the other candidates is your extracurricular activities, by showing you as a whole, well-rounded individual.
When writing a CV, people tend to get carried away no matter the kind of program it is for. That could contribute to more than five or six pages of your CV. And that is not what is needed. No one wants to go through a long and tedious CV, or even has the time. That’s why you should remember to keep the curriculum vitae as clear as possible. It is advisable to adhere to the necessary points only and not use too many details about something or too long descriptions.
Proofreading the CV is the final step in making the CV. Once all of the details have been written, check to see whether you missed any data. Then check to see if you made grammatical or spelling errors of any kind. If any modifications are needed, do the necessary. Once you have done that, go over the document once again. If you are satisfied with the draft, you can send it out to the person you are looking for or you can have a hard copy printed out.

Writing an eye-grabbing Resume Format for someone who has no working experience in the field or any industry somehow sounds…

Graduating from college means you are now ready to enter the world of professional employment, but the only problem is…

Nurses work in a lot of different departments, for example, the operating room, oncology, critical care, ER, or labor and…

When writing a resume, whether you are applying for the position of a bookkeeper, auditor, or cashier, you need to…

Hospitals will never be a caring place without doctors and nurses; they are the primary health care provider that provides…

Many fresh graduates find themselves staring at a blank screen as they try and piece together their sample resumes. Those…

A resume format serves as the blueprint for showcasing your skills, experience, and qualifications effectively to potential employers. Choosing the…

Appear more credible by highlighting your internship and professional experience, technical skills, and other student achievements in your CV with…

The computer science industry presents a bustling career scene today which is even speculated to grow by 15 percent by…