![How To Create Meeting Minutes in Google Docs [Template + Example]](https://images.template.net/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/How-To-Make_Create-Meeting-Minutes-in-Google-Docs-Template-Example-788x443.png)
How To Create Meeting Minutes in Google Docs [Template + Example]
Meeting minutes Play a vital role in the recording of meeting information and details. In any kind of meeting, there is always…
Mar 30, 2023
A bibliography gives credit to all the author’s hard work that was consulted in someone’s research. This list is usually found on the last portion or on the last page of books and/or magazines, most of which can be academic.

A bibliography is defined as a list of works that are written by an author or written by different authors and is typically printed as an appendix.
It can also be referred to as a database of descriptive or critical notes of writing that can relate to a particular subject, author, or period.
A bibliography refers to a list of books, scholarly articles, private records, and any other forms of written material that are cited as references during a study or research, which can be cultural or which can serve a different discipline. Its main purpose is to give credit to the authors whose work was consulted during the research process. It’s usually written at the end part of documents such as school books, research articles, science magazines, and so on.
Sustainable development refers to the type of development that meets the needs of the present generation without compromising the needs of the future generation. Its concept originated from a series of reports such as the Brundtland Report. Further studies relating to this topic can be neatly sorted by cataloging them into a sustainable development bibliography.
A type of bibliography that can be used in an academic setting is a school project bibliography. This is especially common on college projects that require lots of research. Having a bibliography in a school project will improve its credibility when it gets scrutinized by the teacher or by a panel of teachers.
When you start to conduct your research process about a particular topic, especially one that’s unfamiliar to you, a good practice will be compiling a list of resources that you may have to use throughout the entire research. This is known as a preliminary bibliography. In other words, it’s an outline of all the sources that may be used to support your research arguments (such as the internet, various cultural books, and so on).
Another example of a bibliography in the academic setting is an elementary bibliography. This type of bibliography is for students that are still in their elementary level of learning. Additionally, an elementary bibliography is usually made by students who are still learning the ropes of writing one and properly citing the sources they’ve used.
Bibliographies can cite different sources, such as the internet, newspaper articles, magazines (either entertaining or academic), journals, research articles, and so on. Additionally, bibliographies can also cite different books, and a bibliography for books is one type that’s mainly used when books are being used as a source. When a book is being quoted, the book itself is the title of the bibliography’s container, and when there are more than two authors present, et al should be used, which means “and others”.
Bibliographies can also be written for a project such as a simple assignment or a school research project. When this is the case, sources need to be cited to make the final output credible, and the type of bibliography that’s best suited for this will be a bibliography for projects. Depending on the school project, different citation styles may also be used, such as the APA style (American Psychological Association), the MLA style (Modern Language Association), or the Chicago style of citation.
Disaster management refers to a process of effectively preparing for and responding to disasters, and it usually involves strategically organizing resources to reduce the harm that disasters can cause. To effectively prepare for different scenarios, reports may usually have to be generated based on past events so one can learn from them, and the sources used for those reports are usually cited in a disaster management bibliography. The sources cited here usually involve disaster preparedness guides, self-sufficiency guides, survival stories based on previous disasters, and so on.
Another type of bibliography that’s used in an academic setting is a high school bibliography. As the name states, this type of bibliography is prevalent among high school students and is used for their different research projects or assignments. Similar to a project bibliography, this may also use different citation styles, such as the MLA style for high school research that involve English or humanities, the APA style for research topics involving behavioral and social sciences, and Turabian for historical studies.
Annotations can also be added to a bibliography, and a type of bibliography that contains these is called an annotated bibliography. This type of bibliography is a list of books and other works/resources that have descriptive and evaluative comments/quotations about the sources that have been cited in the paper. It’s also known by the short term “annotated bib”, and usually consists of two components which are the citation and the annotation.
A bibliography for students is a type of bibliography that’s most commonly used by students for various academic projects such as research projects. When this type of bibliography is used for school projects, regardless of the style of citation, the sources need to be in alphabetical order, as is the case with all types of bibliographies. They can also be annotated or not.
It’s common knowledge that every book or written material that is academic should have a bibliography section at the very end. This document is still important whether or not it is a mandatory requirement for the entire creation and management of a research project. Here are some other reasons why this document is important.
When one writes a bibliography, they allow themselves to create the best possible versions of all their sources of information. This applies to whether the sources are primary sources or secondary sources. Having a bibliography also enables a reader to determine the recency and authority of the cited work.
Plagiarism is defined as presenting someone else’s work as your own with or without their consent by incorporating it into your work without full acknowledgment. It’s a serious issue nowadays and will always be taken as a form of cheating. By citing sources in a bibliography, the fair practice of crediting someone’s work is practiced and plagiarism can be avoided.
Books and magazines can be great sources of information for readers. And when the writer of a book or a magazine includes their source of information in the work they’ve written, they allow the readers to check how accurate it is or not. This is particularly the case when a random obscure fact is inserted. When a source of that fact is cited at the end of the book, the accuracy is then not questioned by the reader.
Whenever a bibliography is included at the end of a paper, the reader has the opportunity to check and cross-examine the information that is written down in the paper. This, in turn, elevates the value of the paper in question since it shows to the reader that the author has devoted a lot of time and effort to complete the research. Whenever a bibliography is not included in a work, there is a great chance that the paper will only be dismissed as inaccurate and full of hearsay.
A bibliography also allows the reader to keep track of all the sources that were used during the research. This can be important since there will be times that the reader/evaluator will want to cross-reference the facts that are listed, and the bibliography section will allow them to do so. It also acts as a simple yet systematic database of all the information related to the topic of the research.
The bibliography needs to contain the name of the author of the cited source, which can be one or more than one, and may also contain the name of the editors or translators, if applicable.
The next component that should be included in a bibliography is the title of the source, and should also include the edition, the volume, and the book title if the source being cited is a chapter or article in a book.
This part of the bibliography states the names and locations of the companies that published the sources being cited and may also include the page numbers that were consulted and the URL, if applicable.
This part of the bibliography states the publication date of the sources being cited.
This part of the bibliography is included when online resources are cited.

1. Select a Bibliography Size
2. Decide how or where to use the bibliography
3. Pick a Bibliography Template
4. Modify the structure of the template according to your purpose
5. Decide on the citation style to use
6. Finalize and download

A bibliography contains all the sources that have been used in creating the paper, even if they are directly cited or not, and may also provide works for background or further reading and may also include descriptive notes.
A references list (or simply references) includes sources that have been directly cited in the paper and usually contains writings that specifically support the ideas, claims, and concepts in a paper.
A bibliography is an alphabetized list of sources referred to in a body of work and primarily serves as a reference point for readers who wish to read further into the statements made in a body of work.
Literature refers to a collection of work (such as physical novels and oratory works) which can refer to writings that are specifically considered to be an art form such as poetry and drama and its etymology comes from the Latin word literatura which originally means “writing formed with letters”.
A biography is a type of literary genre that simply involves a detailed description of a person’s life, such as their life story or their more intimate details.
Bibliography documents need to follow a certain format, and that includes adhering to the right size. As for the more frequently used sizes, here are the standard bibliography sizes that one should keep in mind.
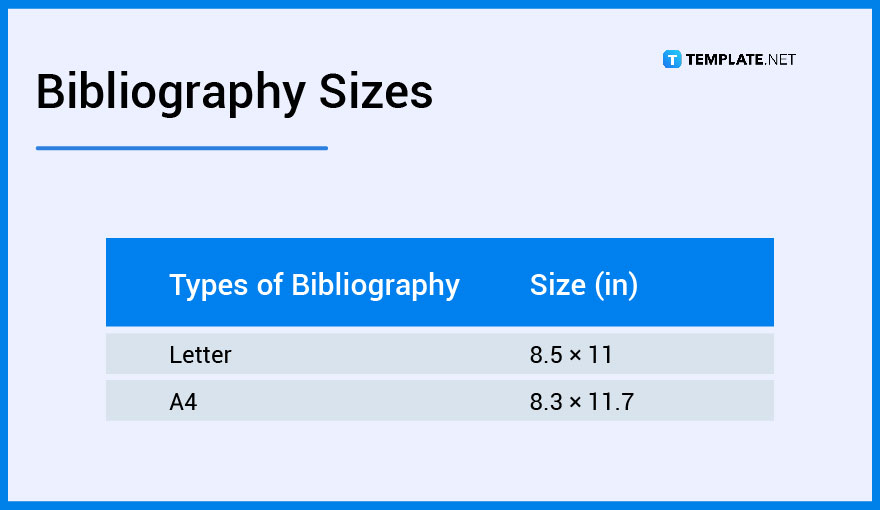
Bibliographies should be relatively simple to make when one knows what they are doing. However, there are times when it can get confusing, and should that occur, here is a list of bibliography ideas and examples that may be of great help.
Bibliography in research refers to a list of books and other source material that have been used in preparing a research paper.
To add the bibliography to a table of contents section in a word processing program (in this case, LibreOffice), right-click the bibliography entry, select Edit, and set the title to nothing, after which you can add the title above the bibliography in the ‘Heading 1’ style so it will then show up in the table of contents section.
A correct bibliography should have the author’s name, the title, and date of publication, the place of publication, the publishing company, the volume number, and a page number.
The four resources of a bibliography can include personal papers, legal notices and records, photographs, and online websites.
The methods of preparing a bibliography include the APA method, the MLA method, the Turabian method, and the Chicago method.
The method of the bibliography was invented and its use began in the early 20th century.
The branches of bibliography are the enumerative bibliography, the analytical bibliography, the descriptive bibliography, the textual bibliography, and the historical bibliography.
A bibliography in a college project refers to a list of source materials that have been used or referred to during the college project.
To format each reference in a bibliography, it should have the author’s full name (starting with the last and followed by the first name), observe proper capitalizations when citing the titles of the sources, italicize titles of larger works or database and website names, include page numbers whenever possible, and add URLs or accessed dates for online resources.
Bibliographic documentation refers to the list of works cited in different formats, such as a reference list for APA format and works cited for MLA format.
A bibliography citation (or a bibliographic citation) includes information on the author and publisher, as well as a brief synopsis of the text, which is commonly referred to as the abstract.
![How To Create Meeting Minutes in Google Docs [Template + Example]](https://images.template.net/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/How-To-Make_Create-Meeting-Minutes-in-Google-Docs-Template-Example-788x443.png)
Meeting minutes Play a vital role in the recording of meeting information and details. In any kind of meeting, there is always…
![How To Make/Create a Manual in Google Docs [Templates + Examples] 2023](https://images.template.net/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/How-To-Make-Create-a-Manual-in-Google-Docs-788x443.png)
Manuals are essential instructional and reference guides. They help direct and inform an individual’s actions and also explain how to…
![How To Make/Create a Manual in Microsoft Word [Templates + Examples] 2023](https://images.template.net/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/How-To-Make-Create-a-Manual-in-Microsoft-Word-788x443.png)
Creating a manual can be a time-consuming and tedious task. However, manuals and other reference guides are necessary for organizations…
![How To Create a Legal Document in Google Docs [Template + Example]](https://images.template.net/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/How-To-Make_Create-a-Legal-Document-in-Google-Docs-Template-Example-2023-788x443.png)
When creating a legal document, there are a lot of things a person has to consider, and one of which is the…
![How To Make/Create a Contract in Microsoft Word [Template + Example] 2023](https://images.template.net/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/How-To-Make_Create-a-Contract-in-Microsoft-Word-Template-Example-2023-1-788x443.png)
Contracts can come in different forms and for different reasons but the most common thing is that when a company does business with…
![How To Create a Contract in Google Docs [Template + Example]](https://images.template.net/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/How-To-Make_Create-a-Contract-in-Google-Docs-Template-Example-2023-Step-788x443.png)
Contracts are an important part of any company or business, especially those that work with different companies or businesses. Companies…
![How To Make/Create a Report in Google Docs [Templates + Examples] 2023](https://images.template.net/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/How-To-Create-a-Report-in-Microsoft-Word-788x443.png)
A report is a comprehensive document that covers a wide array of topics from finance, research, incidents, feasibility studies, and…
![How To Make/Create a Report in Microsoft Word [Templates + Examples] 2023](https://images.template.net/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/How-To-Make_Create-a-Report-in-Microsoft-Word-Templates-Examples-20232-788x443.png)
A report is a document that contains information, data, analysis, finding, and other relevant information based on a specific topic.…
![How to Make/Create a Notebook in Google Docs [Templates + Examples] 2023](https://images.template.net/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/How-to-Make_Create-a-Notebook-in-Google-Docs-Templates-Examples-2023-788x443.png)
Notebooks always come in handy in writing important information or expressing our thoughts through written words. When we need a…