![How To Create Meeting Minutes in Google Docs [Template + Example]](https://images.template.net/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/How-To-Make_Create-Meeting-Minutes-in-Google-Docs-Template-Example-788x443.png)
How To Create Meeting Minutes in Google Docs [Template + Example]
Meeting minutes Play a vital role in the recording of meeting information and details. In any kind of meeting, there is always…
Apr 20, 2023
Review of Systems or ROS is a special fillable tool that plans to learn more about the condition of one’s life. Known as the very first document to fill out before visiting a clinic, it is paramount for the review of systems to ask the right set of questions for clinical protocol purposes.

Review of systems is a medical document that healthcare professionals use to inquire about a patient’s symptoms, medical history, or overall health.
A review of systems or systems inquiry refers to a document that enlists a range of close-ended questions related to symptoms and signs of a patient’s health.
A review of systems is presented either as a questionnaire or a checklist that is used to evaluate a patient’s organ systems. From the eyes, ears, constitutional symptoms, respiratory system, cardiovascular system, integumentary system, and many more, the ROS covers at least 14 systems to assess a person’s HPI (history of present illness) or medical history. The review of systems basically has a whole inventory of categorized body systems for profiling.
Documentation is important for software development when it comes to coding and analyzing the software development life cycle. Besides patient health, a review of systems for software development is used to boost business productivity, improve software projects, or update files. So be sure to track the software development life cycle by referring to the ROS list.
Not all ROS documents are in paper form because you can also go for a digitized version. By keeping a soft copy and coding ROS data online, you can simply achieve that with a digital review of systems template. Make sure to prepare an official database for your company to house these digital records without losing them.
The review of systems is a helpful tool to record an adult or child’s medical history. The history taking and review of systems can aid you with any form of historical health records. Be sure to keep your own copy of the ROS in case it will be asked as proof by your employer or anyone from the management team.
A disorganized and hard-to-follow review of systems will only make your experience more difficult to achieve. You may still go for a complex route such as making a hybrid ROS with charting, meeting minutes, learning articles, statistics, and other data. However, everything should make sense and must be organized in a way where you can call the ROS a comprehensive review of systems.
The medical review of systems is the most known type of ROS since ROS itself covers medical information or health-driven data. Body symptoms, disease signs, and medical timelines are the common targets to determine here. Medical professionals refer to the review of systems in checking what symptoms a patient is or not experiencing.
The general review of systems is the most versatile type of ROS. It can be the screening tool you use for business health assessments, organizational performance checkups, architecture student reviews, and even association diagnostics tests. Just make sure the review of systems you use is properly curated and relevant for its purpose.
Professional nurses and college nursing students can practice screening the health of patients through a careful assessment done via the nursing review of systems. Whether the purpose is for educational or official use, the nursing ROS won’t let you down for effective health assessments. The data written inside may help health experts recognize critical facts and signs about a patient’s health that shouldn’t be overlooked.
The review of systems can either be a problem pertinent, extended, or complete health screening test. Nonetheless, each of these is still considered an assessment review of systems. The assessment process is basically done by finishing the ROS digitally or in print before a clinical visit while the health provider reviews the document.
The sample review of systems is a dependable guide for you to familiarize the format, content, layout, or overall graphic design of the ROS document. Samples make your time worthwhile because you won’t have to design things out of scratch. As long as you have the complete parts of the TOR from the title down to the notes section, you’re good to go.
There is no need to stick to one format or design of your ROS because the editable review of systems exists to accommodate your customization needs. Whether you want the ROS in PDF version or you wish to add a chart, diagram, extra points, and other applicable resources, editable ROS templates won’t fail you. Take this opportunity to personalize the review of systems in the best way possible.
The review of systems isn’t your average type of checklist because its bits of information are carefully planned out. In fact, you’ll appreciate the content and quality of this type of document when you learn its significance and the reasons it is so important in health documentation.
Don’t assume that a review of systems asks random questions because everything is planned and curated. To gather intel on the HPI efficiently, there is a standardized guide regarding the appropriate body system conditions to ask as well as the overall flow of the test. A careful review ensues to measure just how healthy or not a person is.
Quality is guaranteed when the 14 important organ systems are categorized in the whole review of systems. That is because the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services follow the 14 categories in any standard review of systems. So if you are looking for the right type of review of systems for general use, opt to incorporate the 14 systems right into your document.
Upon running an evaluation or health test on a patient, the review of systems is an effective reference to use because it is easy to follow. The questions asked during checkups are usually read from head to toe of the document. Thus, just follow the outline of the document and you’re definitely good to go.
Besides the close-ended questions prepared as a list in the review of systems, there is also some space to write additional notes. There may be instances where other observations not predicted from the review of systems would come up yet are still crucial to know about one’s health. Therefore, write those notes in detail in the free space provided.
The entire review of systems document can be your cheat sheet as to how a proper review of systems should look as well as your main reference in checking patients efficiently from now on. In other words, health conditions can be tracked and monitored appropriately with the help of this document. In conclusion, a review of systems is just as essential as any SOAP note (subjective, objective, assessment, and plan) or physical exam document.
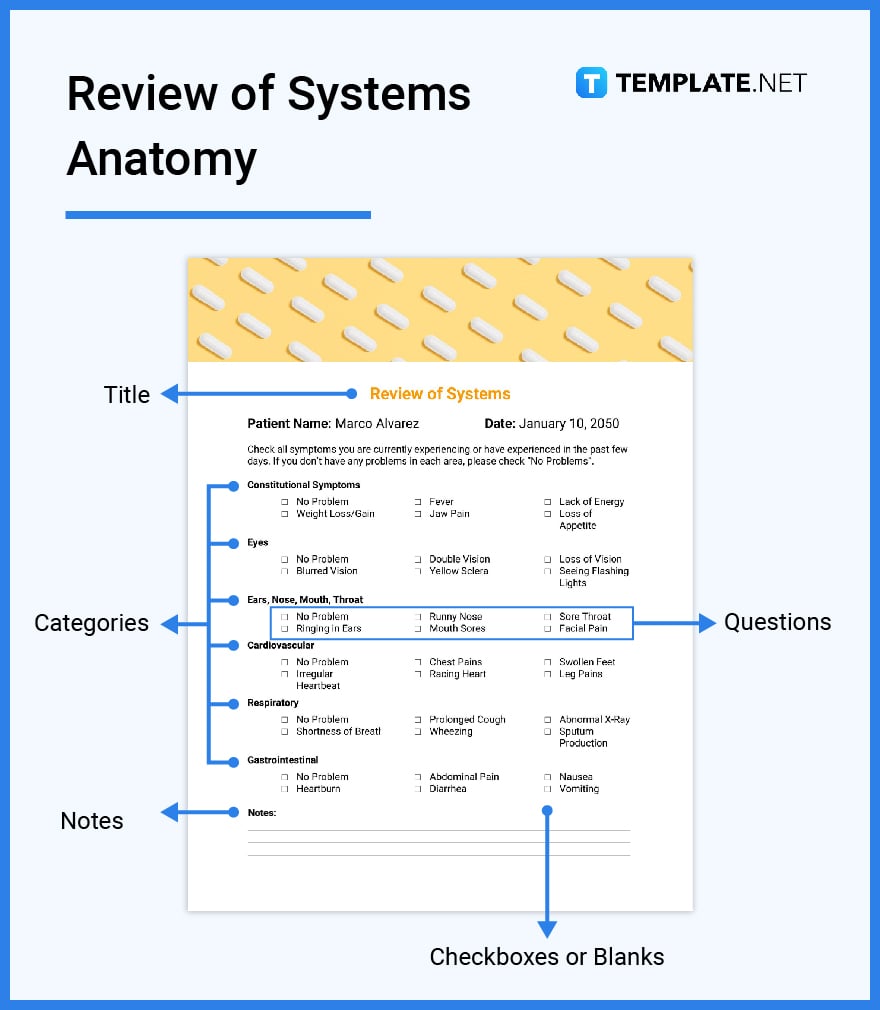
The title of your document should be self-explanatory; this is the part where you write the title “Review of Systems.” It is often inputted in bold capital letters and found on the top-center part of the review of systems.
The 14 body system categories mark as the main meat of your entire review of systems document. These categories are the constitutional symptoms, eyes, ENT (ears, nose, mouth, throat), cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, genitourinary, respiratory, musculoskeletal, neurological, integumentary, endocrine, psychiatric, hematologic/lymphatic, and allergic/immunologic.
Like a questionnaire, each category has its own list of questions. These are basically close-ended queries about body conditions or symptoms that either apply or do not to the patient being assessed.
When you already have the list of categories and proper questions, never forget about where to input answers in the review of systems. You could have multiple choices to encircle answers or basically a set of checkboxes or blanks to mark answers with on the document.
Whether the review of systems is a print document or a soft copy to be kept for blockchain or digital database, never forget to include a section specifically for notes in the document. This part provides further information that may need to be expounded about a patient’s health condition.
1. Figure out the best Review of Systems Size for your document
2. Identify the main purpose of making the ROS
3. Pick a decent Review of Systems Template to work with
4. Edit the template and add the parts of the review of systems
5. Download your ROS template and publish it

A review of systems refers to a predefined screening document that evaluates the different organ systems of a patient.
An assessment is any action form of estimation or evaluation to gauge not only a patient’s health but all sorts of aspects such as business, manufacturing, school, and a lot more.
A review of systems is the standard document used to elicit medical symptoms, signs, and histories of a patient.
A physical exam is a systematized examination that concerns the physical aspects and conditions of a person.
Routine tests refer to regular evaluations that check how reliable products or test subjects are during and after manufacturing.
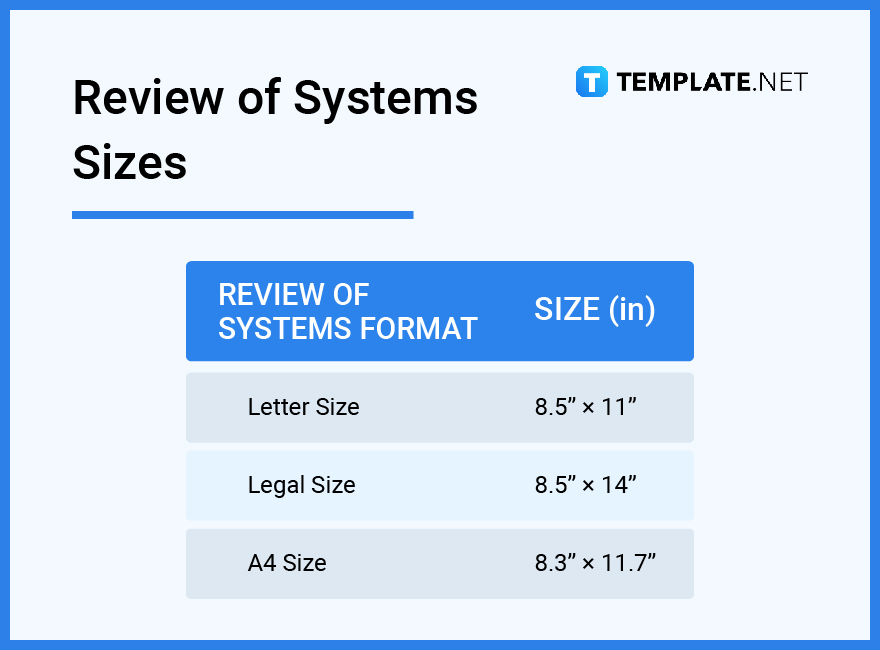
Whether your review of systems has around 10 or up to 14 points, it is essential to note that these documents are not that different from the standard document sizes. A typical review of systems sizes would be the letter, legal, and A4 dimensions.
The review of systems is useful for many reasons, meaning it also has a lot of potentials to offer when it comes to the many examples you can benefit from. Get introduced to some interesting reviews of systems ideas and take inspiration from each example.
The review of systems document should have a title, the 14 categories, questions, checkboxes/blanks, and notes.
These are the complete, extended, and problem pertinent reviews of systems.
Yes, a review of systems is necessary medically.
The ROS provides nurses with potential health issues, ongoing diseases, or conditions that lead to HPI.
It helps understand the chief concern of a person’s health and eventually know what recommended physical therapy fits best for the patient.
The ROS should have around 10 to 14 points.
It is both because the ROS records the patient’s subjective symptoms while the health expert observes the objective signs.
It goes under the subjective-objective assessment part of a SOAP note.
The ROS is like a medical quiz where it’s important to uncover what is wrong with the patient and help determine what appropriate clinical solutions to give afterward.
These consist of the constitutional, eyes, ENT, cardiovascular, respiratory, gastrointestinal, genitourinary, musculoskeletal, integumentary, neurological, psychiatric, endocrine, hematologic/lymphatic, and allergic/immunologic symptoms.
![How To Create Meeting Minutes in Google Docs [Template + Example]](https://images.template.net/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/How-To-Make_Create-Meeting-Minutes-in-Google-Docs-Template-Example-788x443.png)
Meeting minutes Play a vital role in the recording of meeting information and details. In any kind of meeting, there is always…
![How To Make/Create a Manual in Google Docs [Templates + Examples] 2023](https://images.template.net/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/How-To-Make-Create-a-Manual-in-Google-Docs-788x443.png)
Manuals are essential instructional and reference guides. They help direct and inform an individual’s actions and also explain how to…
![How To Make/Create a Manual in Microsoft Word [Templates + Examples] 2023](https://images.template.net/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/How-To-Make-Create-a-Manual-in-Microsoft-Word-788x443.png)
Creating a manual can be a time-consuming and tedious task. However, manuals and other reference guides are necessary for organizations…
![How To Create a Legal Document in Google Docs [Template + Example]](https://images.template.net/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/How-To-Make_Create-a-Legal-Document-in-Google-Docs-Template-Example-2023-788x443.png)
When creating a legal document, there are a lot of things a person has to consider, and one of which is the…
![How To Make/Create a Contract in Microsoft Word [Template + Example] 2023](https://images.template.net/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/How-To-Make_Create-a-Contract-in-Microsoft-Word-Template-Example-2023-1-788x443.png)
Contracts can come in different forms and for different reasons but the most common thing is that when a company does business with…
![How To Create a Contract in Google Docs [Template + Example]](https://images.template.net/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/How-To-Make_Create-a-Contract-in-Google-Docs-Template-Example-2023-Step-788x443.png)
Contracts are an important part of any company or business, especially those that work with different companies or businesses. Companies…
![How To Make/Create a Report in Google Docs [Templates + Examples] 2023](https://images.template.net/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/How-To-Create-a-Report-in-Microsoft-Word-788x443.png)
A report is a comprehensive document that covers a wide array of topics from finance, research, incidents, feasibility studies, and…
![How To Make/Create a Report in Microsoft Word [Templates + Examples] 2023](https://images.template.net/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/How-To-Make_Create-a-Report-in-Microsoft-Word-Templates-Examples-20232-788x443.png)
A report is a document that contains information, data, analysis, finding, and other relevant information based on a specific topic.…
![How to Make/Create a Notebook in Google Docs [Templates + Examples] 2023](https://images.template.net/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/How-to-Make_Create-a-Notebook-in-Google-Docs-Templates-Examples-2023-788x443.png)
Notebooks always come in handy in writing important information or expressing our thoughts through written words. When we need a…