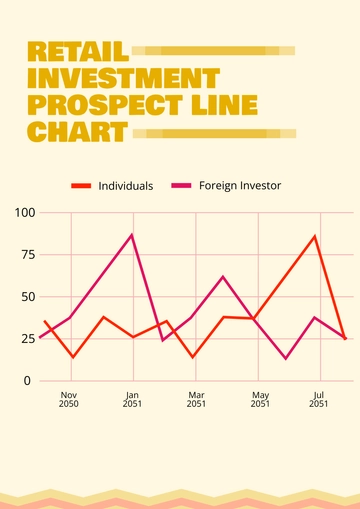
Free Financial Investment Protocol

Introduction
This Financial Investment Protocol Document serves as a comprehensive guide outlining our structured approach to financial investment management. Its purpose is to provide a clear, consistent framework for making informed investment decisions that align with our strategic goals and risk appetite.
Scope and Applicability
The guidelines and principles outlined in this document are applicable to all investment activities undertaken by our organization. They are designed to be relevant across various asset classes, market conditions, and investment horizons. This protocol is intended for use by our investment committee, portfolio managers, and any other stakeholders involved.
Statement of Investment Beliefs
We believe in a disciplined investment approach that emphasizes rigorous research, strategic asset allocation, and active risk management. Our philosophy is grounded in the belief that long-term value creation is achieved through a balance of innovative investment strategies and prudent financial stewardship. We are committed to investing responsibly, with an understanding that our investment decisions can have a broader impact.
Investment Goals
Our short-term investment objectives focus on capital preservation and achieving stable returns that outperform our benchmarks on a yearly basis. We aim to capitalize on market inefficiencies and tactical opportunities to generate competitive short-term gains while maintaining a risk-aware approach.
For the long term, our goal is to achieve sustainable growth of our investment capital. We aim to build a diversified portfolio that delivers robust returns over a 5-10 year period. Our long-term strategy involves investing in assets with strong potential for appreciation and income generation, aligned with our broader investment themes and market outlook.
Risk Tolerance and Return Expectations
We adhere to a moderate risk tolerance framework, recognizing the need to balance potential returns with the risk of capital loss. Our risk tolerance is calibrated to accommodate market volatility, economic shifts, and changes in our investment landscape.
For short-term investments, we aim for returns that consistently outpace inflation and benchmark indices. In the long term, we seek to achieve higher returns commensurate with the risks taken, focusing on capital appreciation and income generation.
Governance and Oversight
In this section, we outline the governance structure and oversight mechanisms that underpin our investment process. Effective governance is essential for ensuring accountability, transparency, and alignment with our investment objectives and ethical standards.
Investment Committee
Position | Responsibilities | Authority Level |
Chairperson of the Committee | Leads the committee, sets meeting agendas, and oversees discussions. | High-level decision-making and oversight. |
Chief Investment Officer | Develops investment strategies, oversees portfolio management. | Strategic planning and execution. |
Portfolio Managers | Implement investment strategies, manage specific asset portfolios. | Asset allocation and selection. |
Risk Management Officer | Identifies, assesses, and mitigates investment risks. | Risk evaluation and mitigation strategies. |
Compliance Officer | Ensures investment activities comply with laws and regulations. | Monitoring compliance and ethical conduct. |
ESG Specialist | Integrates ESG factors into investment decisions. | ESG analysis and integration. |
Decision-making Process and Authority
Investment Decisions: Made collectively by the investment committee based on comprehensive analysis and due diligence. Key decisions require a majority vote.
Strategic Decisions: High-level strategic decisions, such as changes in investment policy or significant asset allocation shifts, are approved by the chairperson in consultation with senior committee members.
Operational Decisions: Day-to-day operational decisions, including trade execution and portfolio adjustments, are delegated to portfolio managers within predefined guidelines.
Asset Allocation and Diversification Strategy
This section addresses our approach to asset allocation and diversification, fundamental components in constructing a well-balanced and resilient investment portfolio. Our strategy is designed to optimize returns while managing risk through careful selection and distribution of assets.
Asset Classes and Their Roles in the Portfolio
Asset Class | Role in Portfolio | Typical Allocation Range |
Equities | Growth and capital appreciation | 40-60% |
Fixed Income | Income generation and risk mitigation | 30-50% |
Real Estate | Hedge against inflation | 5-15% |
Commodities | Diversification | 5-10% |
Alternative Investments | Higher return potential | 5-10% |
Cash and Equivalents | Liquidity and safety | 2-5% |
Strategic Asset Allocation Guidelines
Long-term Focus: Our asset allocation is based on long-term investment horizons, aligning with our overall risk tolerance and return objectives.
Flexibility: While we adhere to our strategic allocation, flexibility is maintained to adjust to changing market conditions and opportunities.
Alignment with Objectives: Asset allocation decisions are aligned with our short-term and long-term investment objectives, ensuring a balanced approach between growth, income, and capital preservation.
Diversification Tactics
Across Asset Classes: We diversify across different asset classes to reduce the risk associated with any single asset class underperforming.
Geographic Diversification: Investments are spread across various global markets to mitigate the impact of regional economic fluctuations.
Sector Diversification: We invest in a range of sectors to avoid overexposure to any single industry's risks.
Risk Management Framework
In this section, we outline our comprehensive risk management framework, essential for identifying, assessing, and mitigating various investment risks. Effective risk management is crucial to protect our assets and ensure the stability and success of our investment strategy.
Potential Risks | Assessment Tools | Strategies |
Market Risk | Statistical analysis, volatility measurements, beta coefficients. | Diversification, hedging strategies, tactical asset allocation. |
Credit Risk | Credit ratings, default probabilities, spread analysis. | Credit analysis, diversification in bond holdings, credit default swaps. |
Liquidity Risk | Cash flow projections, liquidity ratios. | Maintaining a cash reserve, investing in liquid assets, lines of credit. |
Operational Risk | Internal audits, process reviews, risk control self-assessments. | Robust internal controls, staff training, disaster recovery plans. |
Interest Rate Risk | Duration analysis, yield curve assessment. | Duration matching, fixed-to-floating rate instruments, interest rate swaps. |
Geopolitical Risk | Geopolitical analysis, scenario planning. | Geographic diversification, political risk insurance, continuous monitoring. |
Regulatory Risk | Legal reviews, compliance monitoring. | Staying informed of regulatory changes, legal counsel, compliance training. |
Currency Exchange Risk | Currency exposure analysis, forward exchange rates. | Currency hedging strategies, currency diversification, currency futures. |
Inflation Risk | Inflation trends, purchasing power analysis. | Inflation-protected securities, real asset investments, variable-rate loans. |
Investment Selection and Criteria Process
This section elucidates our methodical approach to selecting individual investments, which is critical for achieving our investment objectives. Our process is characterized by stringent criteria, thorough due diligence, and ongoing monitoring to ensure each investment aligns with our strategic goals.
Criteria for Selecting Individual Investments
Does the investment meet our risk-return profile and investment goals?
Is there strong potential for growth or income in the market or sector of the investment?
Does the entity show strong financial performance and stability?
Is the entity's management team experienced and credible?
Does the investment have a sustainable competitive advantage in its market?
Is the investment priced attractively relative to its intrinsic value?
Can the investment be readily bought or sold without a significant price concession?
Is the investment compliant with relevant regulations and laws?
Does the investment meet our environmental, social, and governance criteria?
Due Diligence Process
Assess investment against the selection checklist.
Conduct detailed financial, operational, and strategic analysis.
Evaluate specific risks associated with the investment.
Ensure regulatory and legal compliance.
Engage external experts for specialized assessments, if necessary.
Present findings to the investment committee for deliberation.
Approval or rejection of the investment proposal.
Ongoing Monitoring and Review Procedures
Regularly measure investment performance against benchmarks and expectations.
Continuously monitor market and economic conditions for potential impacts on the investment.
Periodically reassess the risks associated with the investment.
Ensure ongoing regulatory compliance of the investment.
Provide regular updates to stakeholders on the investment's performance and any significant changes.
Performance Monitoring and Reporting
In this section, we detail our approach to measuring and reporting investment performance, an essential practice for evaluating the success of our investment strategies. Accurate performance measurement and transparent reporting are key to maintaining accountability and making informed investment decisions.
KPIs and Benchmarks
KPI | Description | Benchmark Used |
Return on Investment (ROI) | Measures the gain or loss generated on an investment relative to the amount invested. | Specific market index, sector benchmark. |
Alpha | Indicates the performance of an investment relative to the risk-adjusted expected returns. | Market index. |
Beta | Measures the volatility of an investment compared to the overall market. | Market index. |
Sharpe Ratio | Assesses the performance of an investment by adjusting for its risk. | Risk-free rate, such as a 3-month Treasury bill rate. |
Total Expense Ratio (TER) | The total cost of managing and operating the investment. | Industry average. |
Frequency and Format of Performance Reports
Report Type | Frequency | Format |
Compliance Report | Annually | Summary of compliance status and any issues encountered. |
Risk Assessment Report | Bi-annually | Evaluation of investment risks and mitigation measures. |
Process for Reviewing and Evaluating Investment Performance
Gather performance data and relevant market information.
Evaluate against KPIs and benchmarks.
Consider the impact of market & economic factors on performance.
Assess whether the performance aligns with set investment objectives.
Identify any significant deviations from expected performance.
Discuss findings with the investment committee.
Propose changes or adjustments to the investment strategy, if necessary.
Prepare and disseminate performance reports to relevant stakeholders.
Liquidity Management
This section outlines our approach to liquidity management, a key aspect of financial stability and operational efficiency. Effective liquidity management ensures we have sufficient cash flow to meet our investment commitments and respond to opportunities or challenges as they arise.
Liquidity Requirements and Cash Management Strategies
Liquidity Needs Assessment: Regular analysis of short-term and long-term liquidity needs based on our investment commitments and operational expenses.
Cash Reserves: Maintaining an adequate level of cash reserves to meet unexpected outflows without disrupting investment strategies.
Asset Liquidity Evaluation: Continual assessment of the liquidity profile of our assets, prioritizing investments that can be readily converted to cash if needed.
Use of Credit Facilities: Establishing lines of credit or other short-term borrowing options as a backup for unforeseen liquidity needs.
Procedures for Handling Liquidity Crises
Crisis Identification: Early detection of potential liquidity shortfalls through continuous monitoring of cash flow projections and market conditions.
Contingency Plans: Activation of pre-established contingency plans, including liquidation of certain assets and utilization of credit lines.
Stakeholder Communication: Transparent communication with stakeholders regarding the situation and our response strategy.
Post-Crisis Review: Analyzing the crisis to improve future liquidity risk management and updating contingency plans as necessary.
Tax Considerations
In this section, we discuss the importance of considering tax implications in investment decision-making, as taxes can significantly impact investment returns. Our approach aims to maximize after-tax returns while ensuring compliance with tax laws and regulations.
Impact of Taxes on Investment Returns
Capital Gains Tax: Capital Gains Tax is levied on the profit from the sale of an investment or asset. The impact on investment returns depends on the rate of the tax and the holding period of the asset.
Short-Term Capital Gains: For assets held for less than a year, gains are typically taxed at a higher rate, similar to the investor's income tax rate. This can significantly reduce the net profit from short-term investments.
Long-Term Capital Gains: Assets held for more than a year usually qualify for a lower tax rate. This incentivizes long-term investing, as the effective tax rate is reduced, thereby retaining more of the gains.
Dividend Taxation: Dividends received from investments in stocks or mutual funds are subject to dividend taxation. The impact varies based on the type of dividend and the investor's tax bracket.
Qualified Dividends: Generally taxed at a lower rate (similar to long-term capital gains). Investors in higher tax brackets benefit more from this lower rate, improving the after-tax return on investments that pay qualified dividends.
Non-Qualified Dividends: Taxed at the investor's ordinary income tax rate, which can be significantly higher than the rate for qualified dividends. This reduces the net income received from such dividends, especially for investors in higher tax brackets.
Interest Income Taxation: Interest income from investments like bonds, CDs, and savings accounts is typically taxed as ordinary income.
Regular Taxation: Interest income is added to the investor's total income for the year and taxed according to their income tax bracket. This can substantially lower the net return from fixed-income investments, especially for those in higher tax brackets.
Municipal Bonds: As an exception, interest from municipal bonds is often exempt from federal income tax and, in some cases, state and local taxes. This makes municipal bonds a more attractive option for investors in high tax brackets, as the tax-exempt status can result in higher after-tax returns compared to taxable fixed-income investments.
Strategies for Tax-Efficient Investing
Tax-Loss Harvesting: Utilizing investment losses to offset capital gains taxes.
Asset Location Strategy: Placing investments in tax-advantaged accounts (like IRAs and 401(k)s) or taxable accounts based on their tax efficiency.
Utilization of Tax-Exempt Investments: Investing in tax-exempt bonds and other securities to reduce taxable income.
Tax-Deferred Growth Investments: Utilizing investments that offer tax-deferred growth, such as certain retirement accounts, to optimize long-term returns.
Amendment and Review Procedures
Process for Updating and Reviewing the Investment Protocol
Reviews are initiated either as part of the scheduled process or in response to significant changes in the market, regulatory environment, or organizational objectives.
Gather feedback and suggestions for improvements from all relevant stakeholders, including the investment committee, portfolio managers, and compliance officers.
Analyze the need for changes or updates in the investment protocol considering the latest market trends, investment performance, and regulatory changes.
Proposed amendments are drafted and documented with a clear rationale for each change.
The draft amendments are reviewed by the investment committee and other key stakeholders. Amendments require formal approval before implementation.
Approved changes are formally documented, and the updated protocol is disseminated to all relevant parties.
Schedule for Regular Reviews and Updates
A comprehensive review of the entire investment protocol is conducted annually to ensure alignment with our strategic objectives and compliance with regulatory standards. A less formal, quarterly review is conducted to monitor the effectiveness of the protocol and identify any immediate areas for adjustment. In addition to scheduled reviews, ad hoc reviews are conducted in response to significant market events, major regulatory changes, or major shifts in our investment strategy.
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
The Financial Investment Protocol Template from Template.net offers an innovative solution for managing investment strategies. Fully editable and customizable in our AI Editor tool, this template provides a structured approach to developing clear investment protocols. Tailored to meet diverse financial needs, it ensures thoroughness and precision in investment planning. A vital resource for professionals, it simplifies complex investment processes.