Financial Cost Management Protocol
I. Cost Analysis and Identification
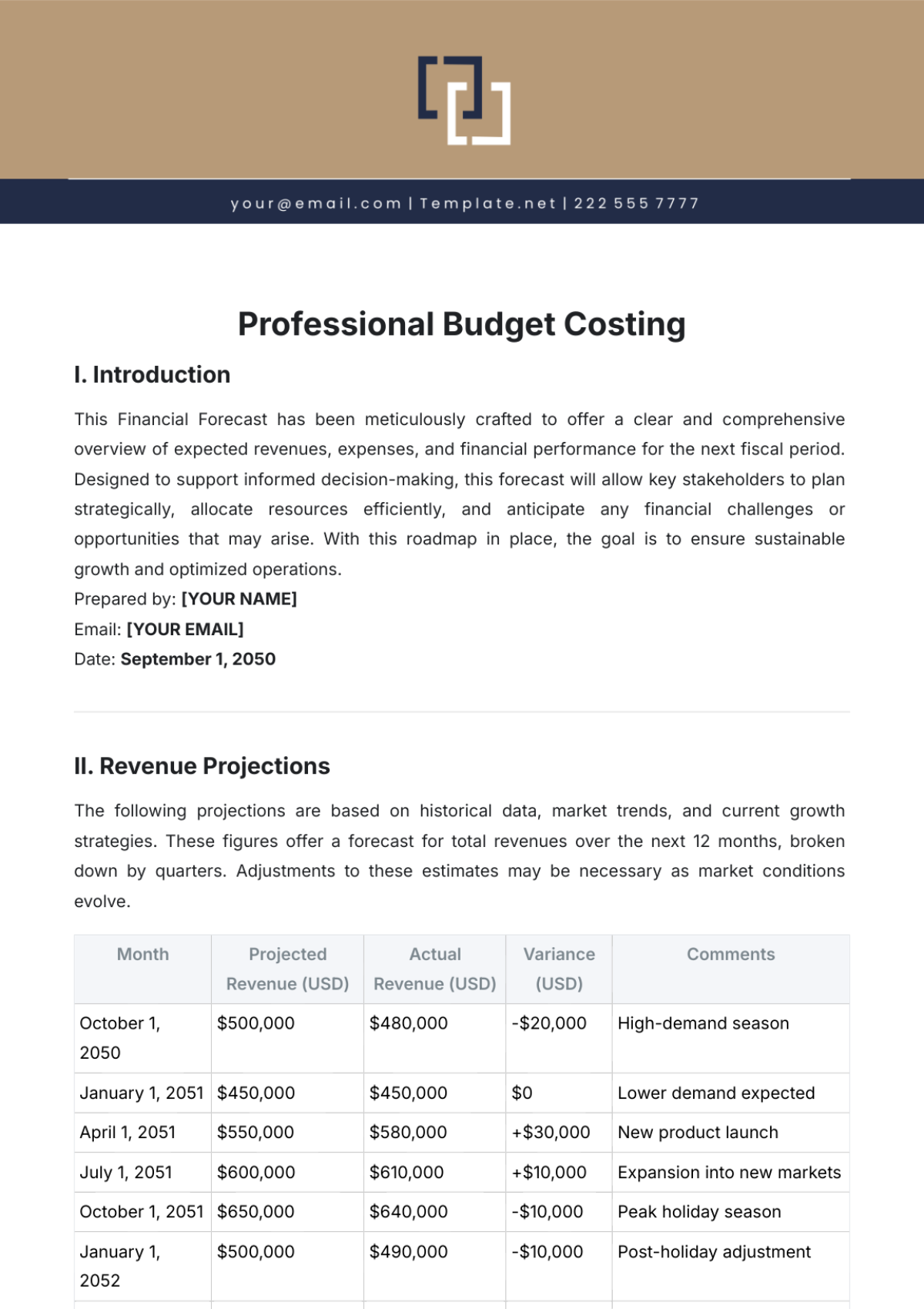
Comprehensive Review of Current Expenses
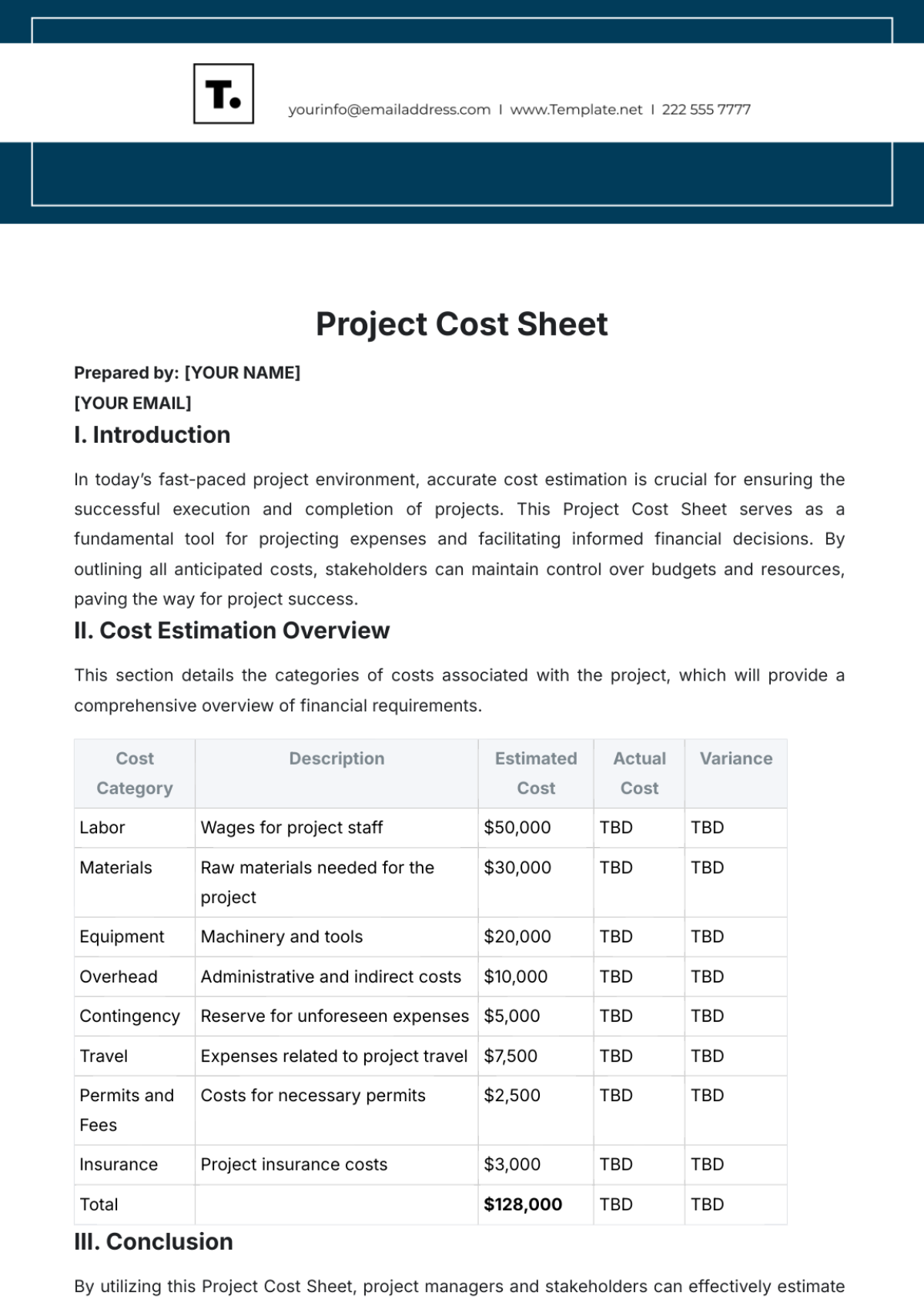
At [Your Company Name], our financial team meticulously reviews all expenditures to create a comprehensive financial landscape. We delve into various categories such as utilities, employee salaries, raw material purchases, technology upgrades, and marketing campaigns. For instance, last quarter's review revealed that marketing expenses accounted for a significant portion of our budget, primarily due to our new product launch campaign. This kind of detailed expense mapping is crucial for identifying potential areas for cost optimization and ensuring efficient allocation of resources.
Identification of Fixed and Variable Costs
Our approach to identifying fixed and variable costs involves categorizing expenses based on their nature and behavior. For example, rent payments for our main office and salaries for permanent staff are classified as fixed costs, as they remain constant regardless of business activity. In contrast, costs like utility bills and raw material purchases are categorized as variable, fluctuating based on production volume and operational demand. This classification is essential for accurate budgeting and financial planning, enabling us to predict cash flow needs more accurately and make informed strategic decisions.
Analysis of Direct and Indirect Costs
In analyzing direct and indirect costs, we focus on how each expense directly or indirectly contributes to our product output and service delivery. Direct costs include expenses like manufacturing supplies and direct labor, directly tied to production volume. Indirect costs, such as administrative salaries and building maintenance, support overall operations but are not tied to any specific product or service. This analysis helps us in determining product pricing, assessing cost centers, and improving overall profitability. For example, a recent analysis highlighted that indirect costs in our administration department were disproportionately high, prompting a strategy review for more efficient resource utilization.
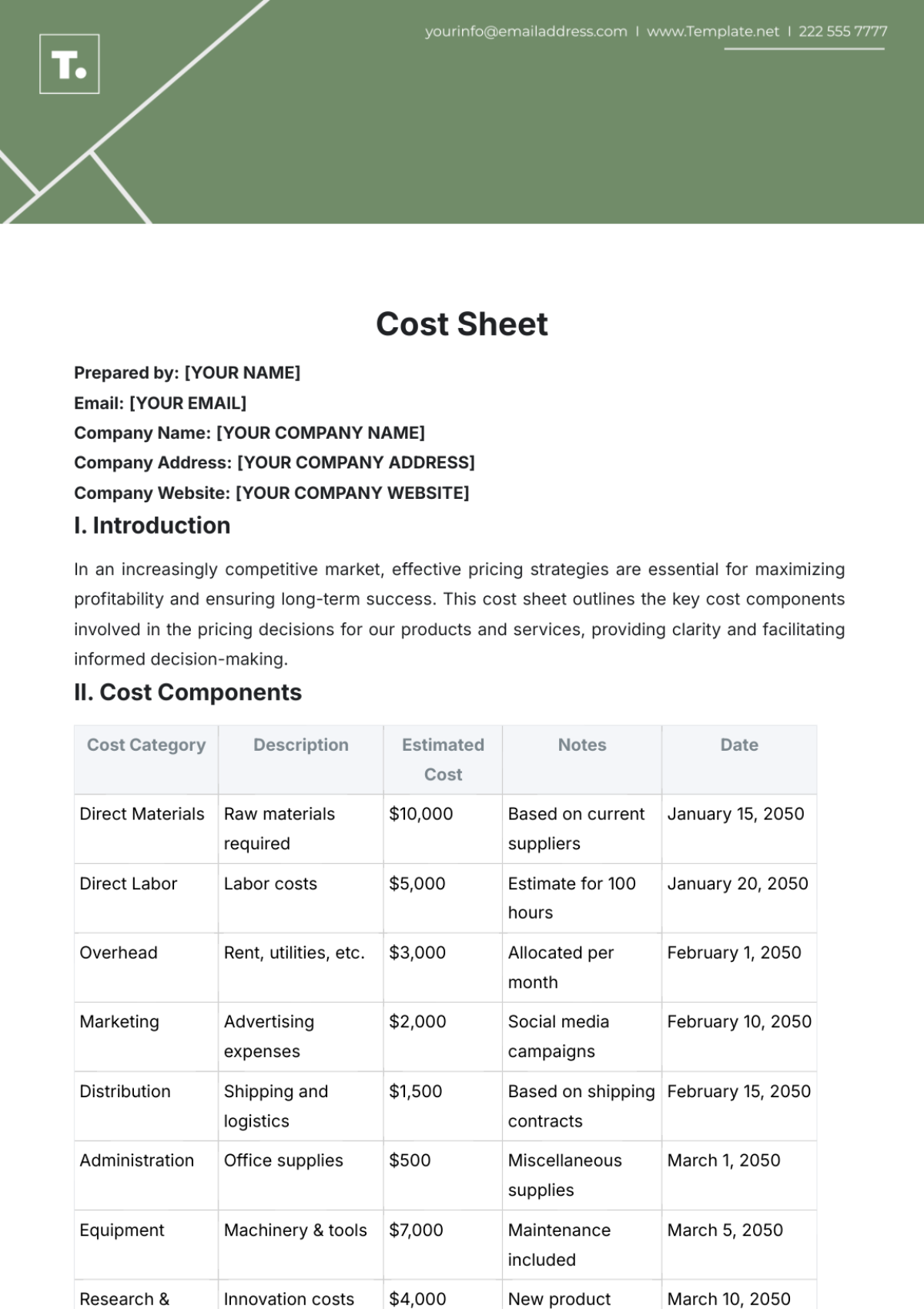
II. Budgeting and Forecasting
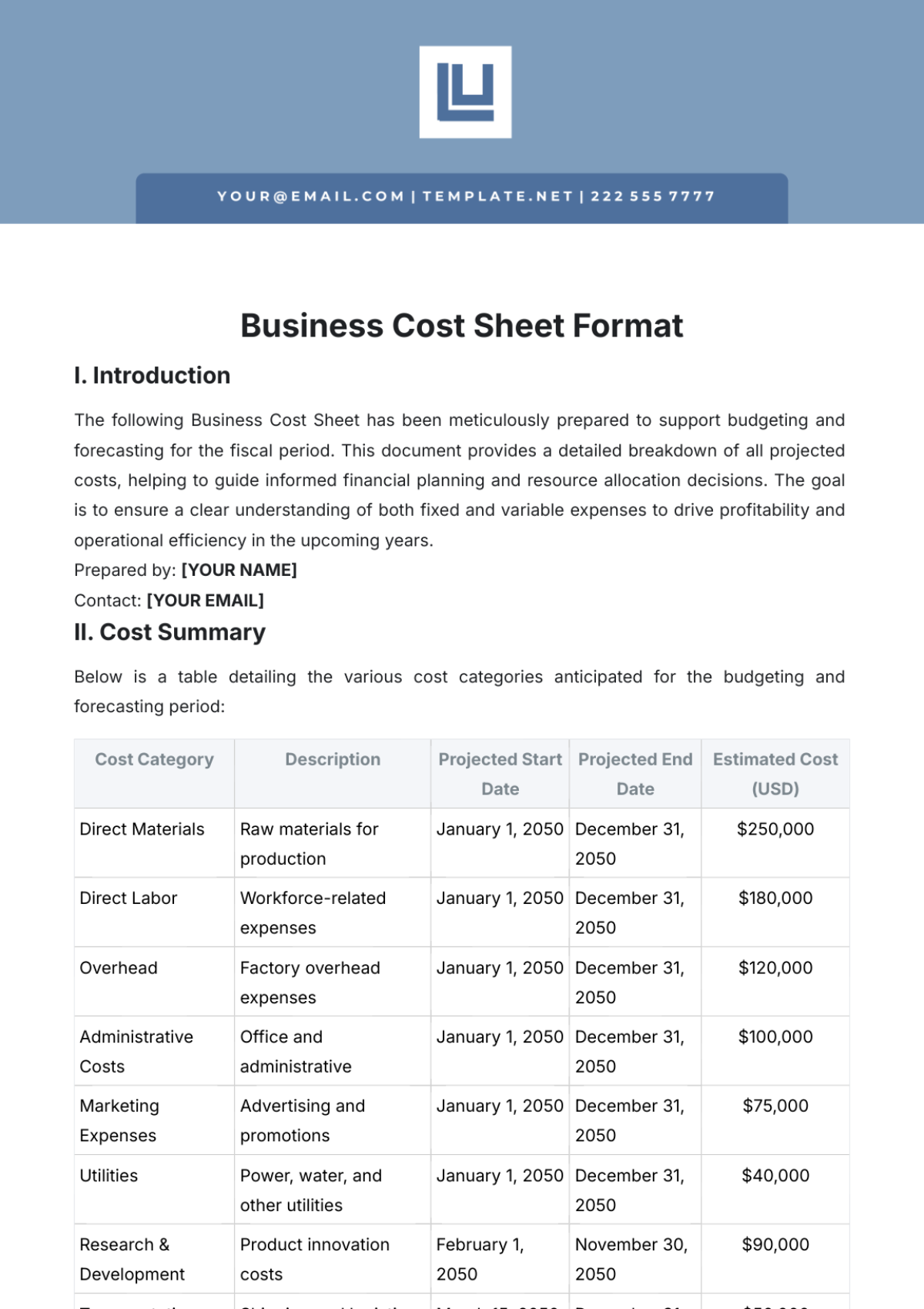
In this crucial section of financial management, [Your Company Name] emphasizes the development of detailed, strategic budgets for each department, the use of historical data for accurate forecasting of future costs, and the importance of regular budget reviews and adjustments to align with dynamic business objectives.
A. Development of Detailed Budgets
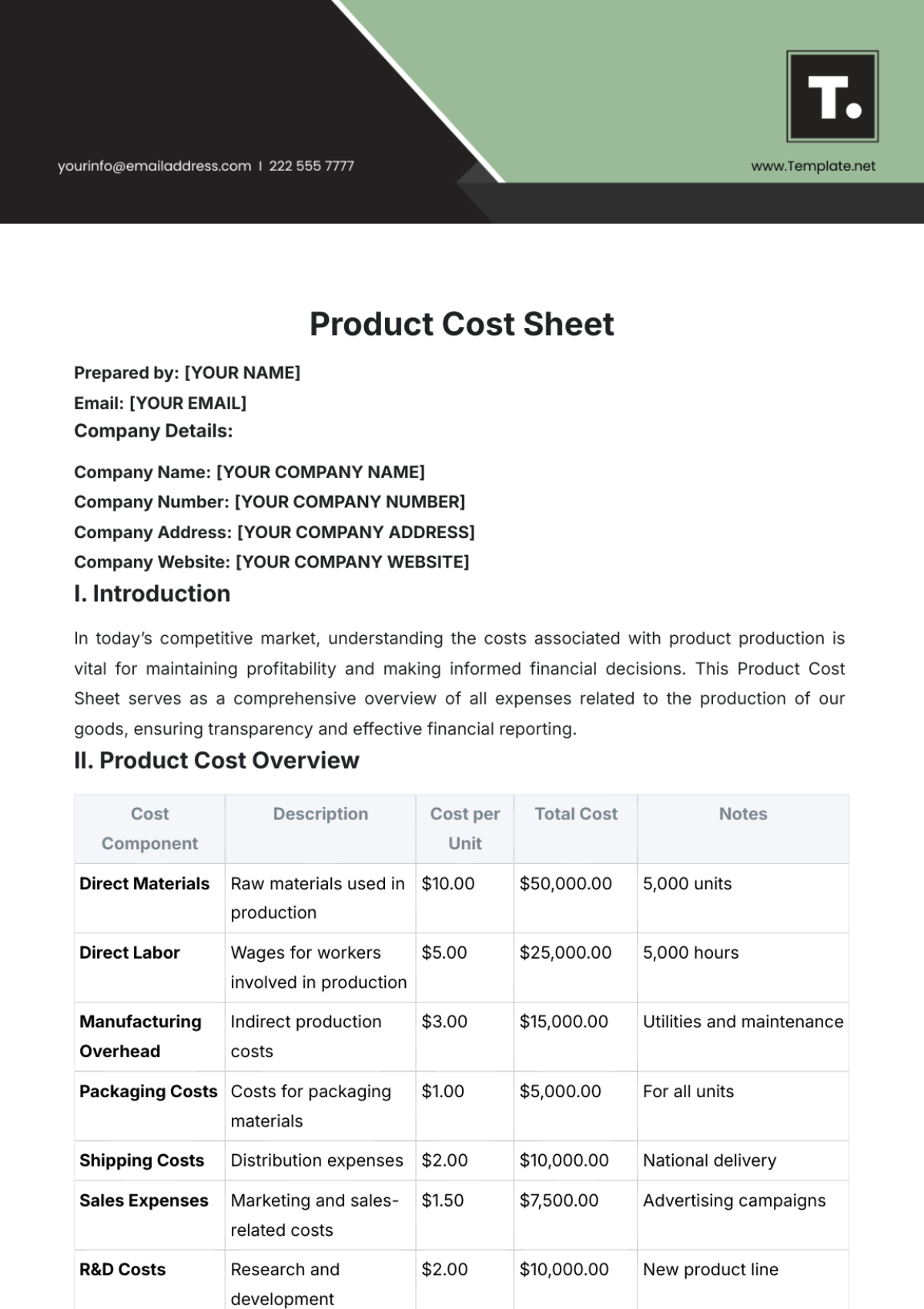
At [Your Company Name], each department meticulously develops its budget, incorporating a detailed analysis of historical spending patterns and projected future needs. For instance, our marketing department's budget includes allocations for digital advertising, event sponsorships, and market research, tailored to support upcoming product launches. Similarly, the R&D department's budget is structured around project timelines, technology upgrades, and staffing needs. These departmental budgets are not only numbers on a spreadsheet; they represent strategic plans, aligning financial resources with the company's broader strategic goals, such as market expansion or product innovation.
B. Forecasting Future Costs
Our financial team employs sophisticated forecasting methods to project future costs. Using past financial data, such as expenditure trends and revenue cycles, we build predictive models that take into account market dynamics, economic indicators, and industry trends. For instance, by analyzing the historical cost data of raw materials, we can forecast price fluctuations and plan our procurement accordingly. This forward-looking approach is instrumental in preparing for future financial scenarios, aiding in strategic planning, resource allocation, and contingency planning.
C. Regular Budget Review and Adjustment
Recognizing that the business environment is dynamic, we at [Your Company Name] have instituted a policy of regular budget reviews. This process involves comparing actual spending against budgeted figures and analyzing the reasons for any variances. Adjustments are then made to reflect changes such as shifts in market demand, new business opportunities, or unexpected expenses. For example, last quarter, we adjusted our IT budget upwards due to the unplanned need for advanced cybersecurity measures. These regular reviews and adjustments ensure that our budget remains a living document, closely aligned with our operational realities and company objectives.
III. Cost Reduction Strategies
This section outlines the cost reduction strategies implemented by [Your Company Name]. It details specific initiatives aimed at saving costs, opportunities for cost reduction in procurement and operations, and strategies for reducing overhead and operational inefficiencies.
A. Cost-Saving Initiatives
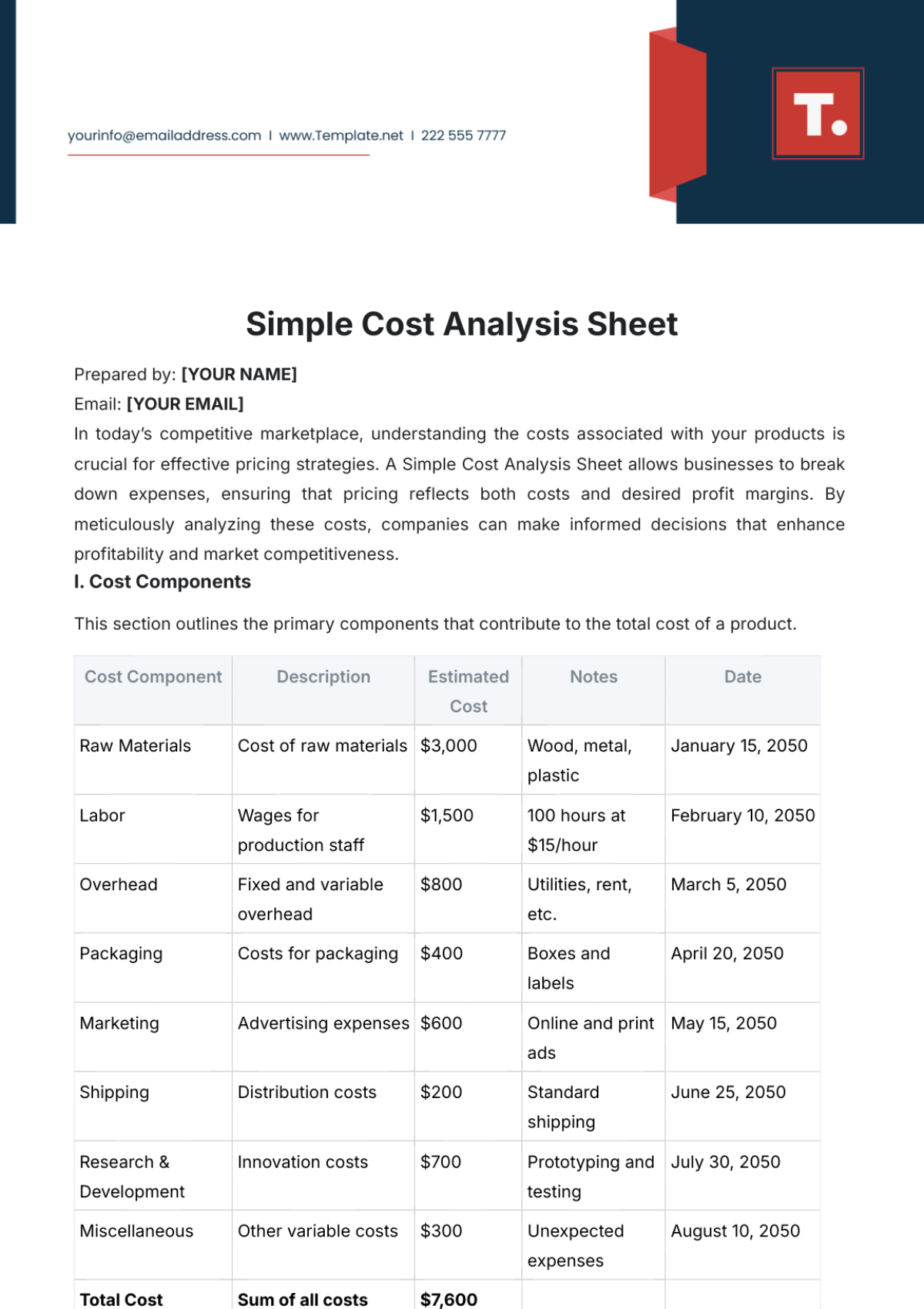
We implement strategic cost-saving measures such as process automation, renegotiation of contracts, and energy-efficient practices.
Initiative | Description |
Process Automation | Implementing automation in repetitive and manual processes to increase efficiency and reduce labor costs. |
Contract Renegotiation | Revisiting contracts with suppliers and service providers to negotiate more favorable terms. |
Energy-Efficient Practices | Implementing energy-saving measures in office and production areas to reduce utility costs. |
Telecommuting Options | Offering telecommuting options to reduce office space and related expenses. |
Digitalization of Records | Moving to a paperless environment to save on printing and storage costs. |
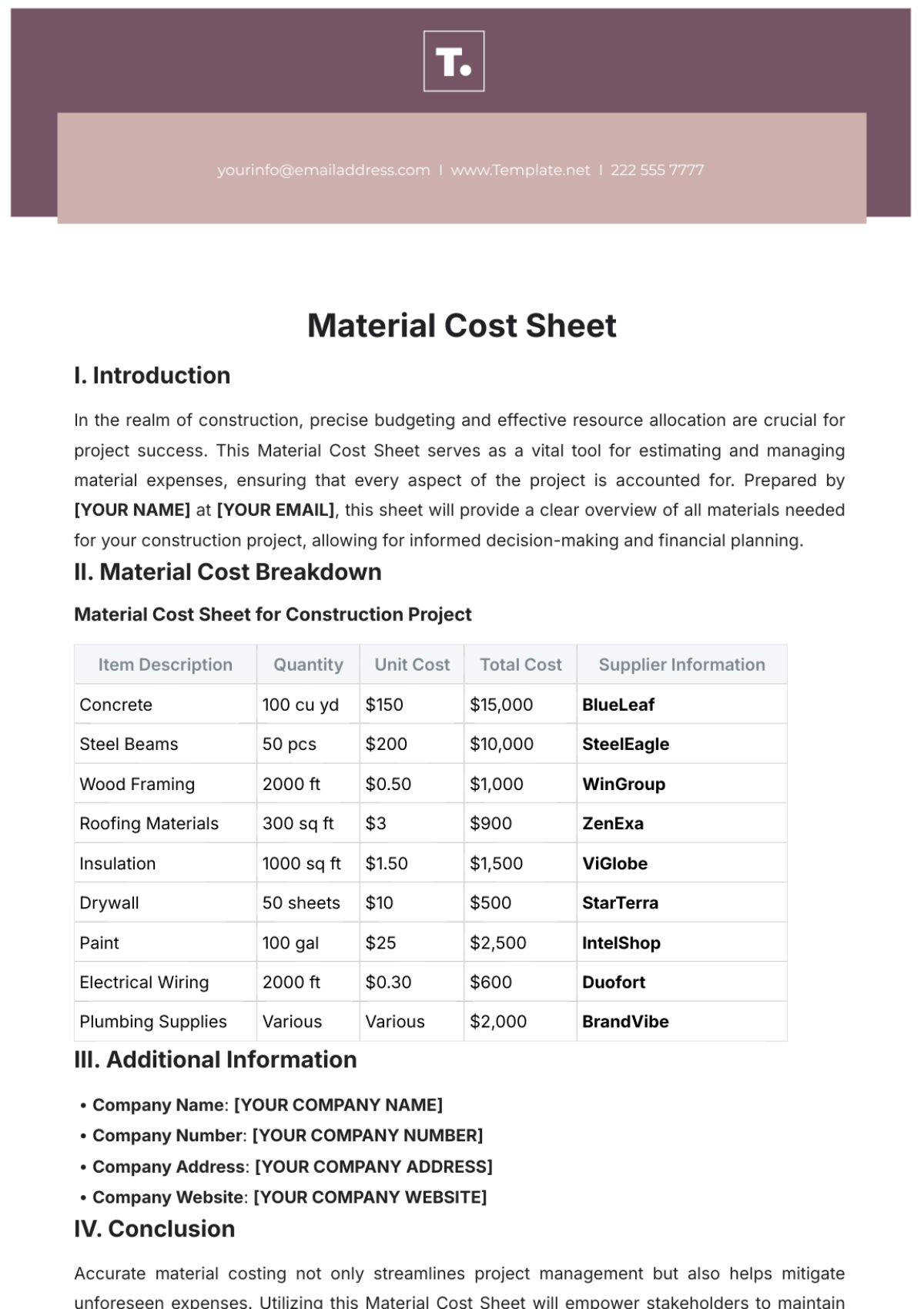
B. Cost Reduction in Procurement and Operations
[Your Company Name] explores opportunities for bulk purchasing, local sourcing, and streamlining operational processes to reduce costs.
Opportunity | Description |
Bulk Purchasing | Leveraging bulk purchasing to negotiate lower prices for raw materials and supplies. |
Local Sourcing | Sourcing materials and services locally to reduce transportation costs and support local businesses. |
Streamlining Processes | Optimizing operational processes to increase efficiency and reduce waste. |
Supplier Partnerships | Developing strategic partnerships with suppliers for mutually beneficial cost-saving arrangements. |
Inventory Management | Implementing just-in-time inventory to minimize storage costs and reduce waste. |
C. Reducing Overhead and Operational Inefficiencies
Regular reviews of overhead expenses are conducted to identify and eliminate inefficiencies, optimizing resource utilization.
Inefficiency | Solution |
Excessive Utility Usage | Installing energy-efficient systems and monitoring usage to reduce electricity and water costs. |
Unnecessary Space Utilization | Downsizing or restructuring office space to better fit current needs and reduce rent expenses. |
Redundant Staff Roles | Streamlining staff roles and responsibilities to increase efficiency and reduce payroll expenses. |
Outdated Technology | Upgrading to more efficient technology to improve productivity and reduce maintenance costs. |
Inefficient Supply Chain | Optimizing the supply chain to reduce transportation and logistics costs. |
IV. Monitoring and Reporting
This section details [Your Company Name]'s approach to monitoring and reporting on cost management. It includes systems for tracking expenses, regular reporting to evaluate performance, and the use of KPIs and metrics to measure the success of cost reduction strategies.
A. Cost Monitoring Systems
We establish robust systems for ongoing monitoring of costs against the budget, identifying variances promptly.
System | Sample Implementation | Benefit |
Automated Expense Tracking | Software tracking real-time expenses against budget allocations. | Enables immediate identification of budget overruns. |
Procurement Monitoring System | System to track purchase orders and supplier invoices. | Ensures procurement costs align with budget and identifies overspending areas. |
Utility Usage Monitors | Sensors and software to track energy and water usage. | Helps in identifying and reducing excessive utility costs. |
Payroll Management System | Automated system to monitor salaries, bonuses, and overtime payments. | Assists in controlling labor costs and preventing payroll errors. |
Inventory Management System | Software to track inventory levels and associated costs. | Reduces costs related to excess inventory and storage. |
B. Reporting Cost Management Performance
Regular reports are generated to provide insight into cost management performance, keeping key stakeholders informed.
Report Type | Sample Content | Purpose |
Monthly Cost Analysis Report | Department-wise breakdown of expenditures vs. budget. | Highlights areas with significant variances for management review. |
Quarterly Financial Summary | Summary of financial performance including revenues, expenses, and net income. | Provides a comprehensive overview of financial health and cost control efficiency. |
Annual Budget Review Report | Analysis of annual spending compared to the budget, with variance explanations. | Offers insights for future budget planning and adjustments. |
C. Tracking Cost Reductions
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and financial metrics are used to track and report the effectiveness of cost reduction strategies.
KPI/Metric | Sample Implementation | Purpose |
Expense-to-Revenue Ratio | Tracking the ratio of total expenses to total revenue. | Measures efficiency in managing costs relative to revenue generation. |
Cost Savings per Initiative | Amount saved from specific cost-cutting measures (e.g., energy-efficient upgrades). | Quantifies the financial impact of individual cost-saving initiatives. |
Budget Variance Percentage | Percentage difference between budgeted and actual expenses. | Indicates how well expenses are managed against the budget. |
V. Compliance and Risk Management
This section of [Your Company Name]'s financial protocol focuses on maintaining compliance with financial policies, managing risks associated with cost-cutting measures, and ensuring that cost reductions do not compromise product or service quality. It's vital for upholding standards while enhancing financial efficiency.
A. Compliance with Financial Policies
At [Your Company Name], our cost management practices are meticulously aligned with established financial policies and regulatory requirements. We conduct regular audits to ensure full compliance, focusing on areas like accounting standards, tax regulations, and financial reporting guidelines. For instance, our recent audit led to refining our expense reporting process, ensuring more accurate and transparent financial records. This strict adherence to compliance not only safeguards us from legal and financial repercussions but also reinforces investor and stakeholder confidence in our financial governance.
B. Risk Management in Cost-Cutting
In our pursuit of cost efficiency, we are acutely aware of the risks associated with aggressive cost-cutting. Our risk management approach involves a thorough analysis of potential impacts on operational integrity and customer satisfaction. For example, before deciding to streamline our customer service department, we conducted an impact analysis to ensure that customer experience would not be adversely affected. By balancing cost-saving objectives with risk considerations, we strive to make decisions that are financially prudent without compromising on essential business functions or service standards.
C. Maintaining Quality While Reducing Costs
[Your Company Name] is committed to maintaining, if not improving, the quality of our products and services even as we implement cost reductions. Our strategies include investing in efficient technology that enhances productivity, training employees for multifunctional roles, and optimizing supply chain management. A recent initiative saw us shifting to a just-in-time inventory system, significantly reducing inventory costs while maintaining our product quality and availability. This approach ensures that our cost-saving efforts contribute to long-term sustainability and profitability, without compromising our commitment to quality.
Through these measures, [Your Company Name] effectively manages financial performance while upholding the highest standards of compliance, risk management, and quality assurance.