Finance Accounts Management Protocol
Introduction
The purpose of this Finance Accounts Management Protocol is to establish a standardized and effective framework for managing our organization's financial accounts. This protocol is designed to guide our finance team in maintaining accurate and consistent financial records, ensuring ethical financial practices, and supporting informed decision-making processes.
Scope of the Protocol
This protocol covers a comprehensive range of areas within our financial management system, including, but not limited to:
Account Setup and Management
Financial Reporting
Budgeting and Forecasting
Expenditure and Revenue Management
Audit and Compliance
Risk Management
The protocol applies to all financial accounts managed by our organization, including operational accounts, investment accounts, reserve funds, and any other financial instruments or platforms we utilize.
Importance of Effective Finance Accounts Management
Effective management of finance accounts is crucial for maintaining the financial health and integrity of our organization. It ensures that:
Financial decisions are based on accurate and up-to-date information.
There is compliance with financial regulations and standards, reducing the risk of legal repercussions.
Organizational resources are utilized efficiently, supporting our strategic objectives and goals.
Financial risks are managed proactively, safeguarding our assets and investments.
Stakeholders have confidence in our financial management capabilities.
Roles and Responsibilities
This section delineates the key roles involved in the management of our financial accounts and outlines the specific responsibilities associated with each position. Understanding these roles and responsibilities is essential for ensuring effective and efficient financial management within our organization.
Roles | Responsibilities |
Chief Financial Officer (CFO) | Oversees all financial operations. Develops financial strategy. Ensures compliance with financial regulations |
Financial Accountant | Manages and maintains financial records. Prepares financial statements. Conducts account reconciliations |
Budget Analyst | Develops and monitors organizational budgets. Analyzes budget variances. Provides budget forecasts |
Revenue Manager | Oversees income generation processes. Manages billing and receivables. Analyzes revenue trends |
Expenditure Officer | Administers accounts payable. Ensures efficient handling of expenses. Reviews and approves expenditures |
Compliance Officer | Monitors adherence to financial laws and standards. Coordinates audits. Advises on regulatory compliance |
Risk Manager | Identifies and assesses financial risks. Develops risk mitigation strategies. Monitors risk management plans |
Financial Analyst | Conducts financial analysis and reporting. Provides insights on financial health. Supports decision-making |
IT Systems Manager | Manages financial software and systems. Ensures data security and integrity. Supports technology upgrades |
Account Setup and Management
This section outlines the procedures and guidelines critical for setting up, managing, and modifying various types of financial accounts within our organization. Adhering to these procedures ensures consistency, compliance, and efficiency in our financial operations.
A. Setting Up New Accounts
Determine the necessity for a new account based on operational requirements.
Obtain authorization from the CFO or designated authority.
Complete necessary forms and documentation.
Classify the account type (e.g., operational, investment) based on its intended use.
Coordinate with the chosen financial institution to set up the account.
Register the account in our internal financial systems and databases.
Assign account management responsibilities to appropriate personnel.
B. Managing Different Types of Accounts
Account Type | Management Guidelines |
Operational | Ensuring adequate liquidity for day-to-day operations |
Investment | Alignment with our organization’s investment strategy |
Reserve Funds | Limited access and stringent withdrawal protocols |
C. Account Modifications and Closures
Conduct a thorough review and provide justification for any modifications.
Seek approval from the CFO or relevant authority for the proposed changes.
Update all relevant documents and records to reflect the changes.
Inform all relevant departments and stakeholders of the account modification.
Make any necessary financial adjustments, such as transferring funds.
Update internal financial systems and databases to reflect new account status.
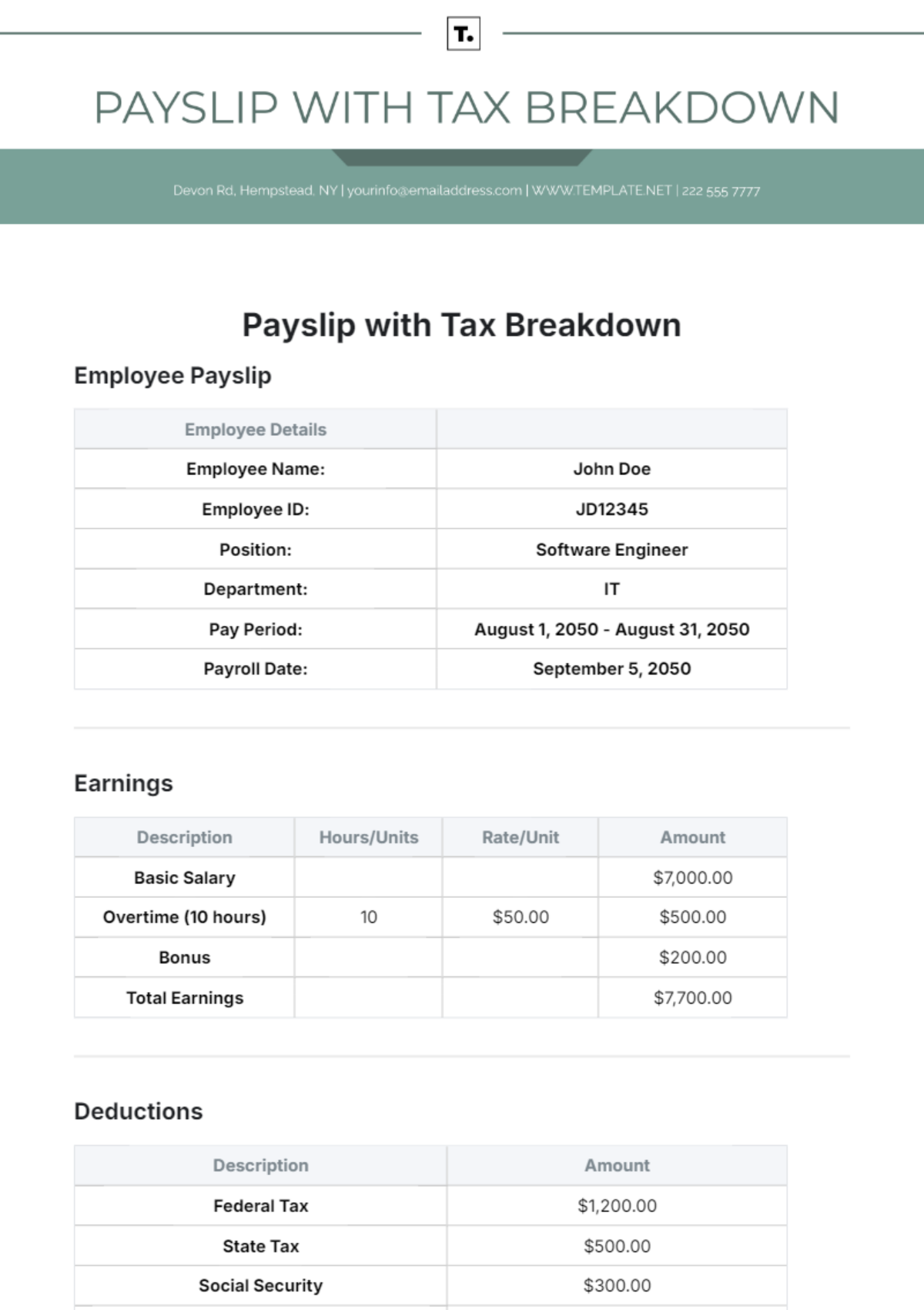
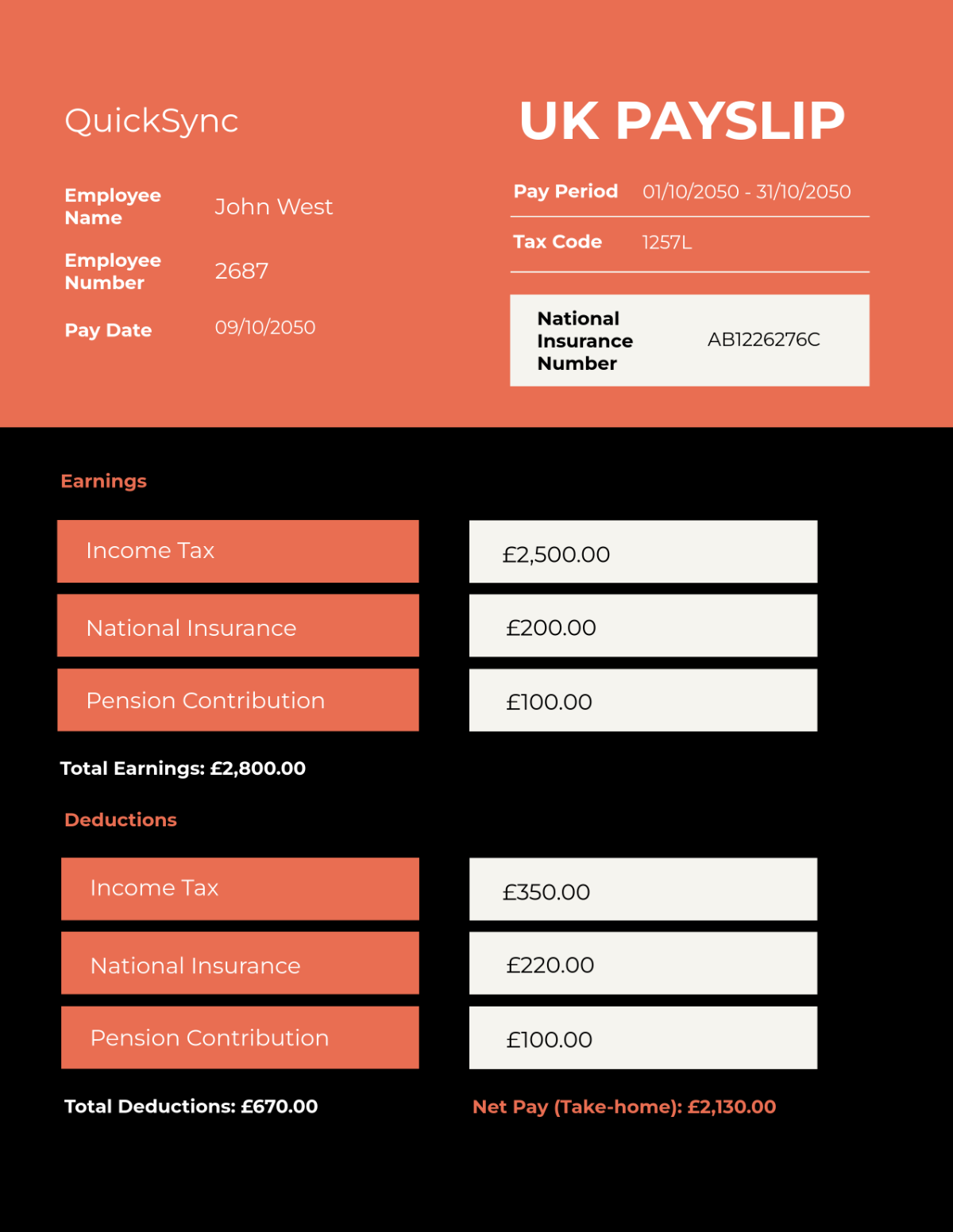
Financial Reporting
This section establishes clear guidelines to ensure accuracy, transparency, and consistency in our financial reporting processes. These guidelines are crucial for maintaining the integrity of our financial data and for providing stakeholders with reliable and timely information.
A. Guidelines for Financial Reporting
Report Type | Frequency | Format | Description |
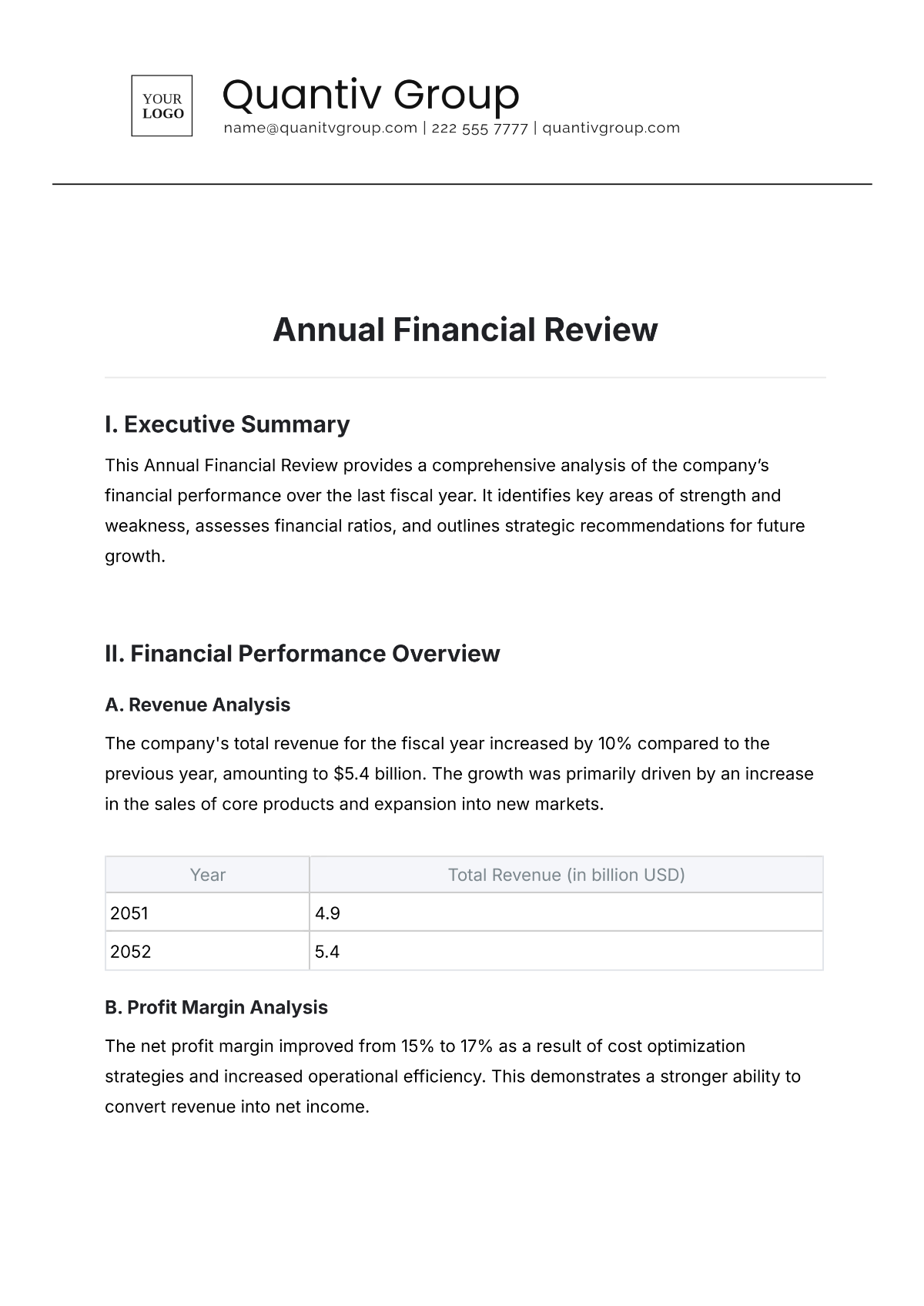
Income Statement | Quarterly and Annually | Digital (PDF) and Hard Copy | Provides a summary of revenues and expenses |
Balance Sheet | Quarterly and Annually | Digital (PDF) and Hard Copy | Shows the financial position at a given time |
Cash Flow Statement | Quarterly and Annually | Digital (PDF) and Hard Copy | Details cash inflows and outflows |
Budget Report | Annually | Digital (Excel, PDF) and Hard Copy | Compares budgeted figures with actuals |
Audit Report | Annually | Digital (PDF) and Hard Copy | Contains findings from internal/external audits |
B. Standards for Accurate and Ethical Reporting
Ensure all financial reports accurately reflect the organization's financial status without misrepresentation.
Apply consistent accounting principles and standards in all reports.
Adhere to the reporting schedule to provide timely information to stakeholders.
Present financial data in a clear and understandable manner, avoiding technical jargon where possible.
Ensure all reports comply with relevant accounting standards and regulatory requirements.
Maintain the confidentiality of sensitive financial information, disclosing it only to authorized personnel.
Budgeting and Forecasting
This section is designed to provide a structured approach for planning and predicting our financial performance. Effective budgeting and accurate forecasting are crucial for the financial stability and strategic planning of our organization.
A. Creating, Reviewing, and Updating Budgets
Gather historical financial data and current market trends as a basis for the budget.
Involve all departments to submit budget requests and forecasts for their operations.
Compile and draft the initial budget incorporating departmental inputs and strategic goals.
Conduct a thorough review of the draft budget by finance managers and the CFO, followed by necessary approvals.
Distribute the approved budget to all departments and stakeholders.
Regularly monitor actual spending against the budget, identifying variances.
Update the budget periodically to reflect changes in business conditions, strategic direction, or market trends.
Perform an end-of-year budget review to assess performance and inform the next year's budget.
B. Guidelines for Financial Forecasting
Utilize historical financial data to identify trends.
Consider external factors such as market conditions, forecasts, and trends.
Develop different financial scenarios to anticipate potential future challenges.
Engage various departments to provide input and perspectives.
Update forecasts regularly to reflect new financial data.
Strive for precision in forecasts, but also maintain flexibility.
Include risk analysis in forecasting to understand potential impacts.
Clearly communicate financial forecasts to relevant stakeholders.
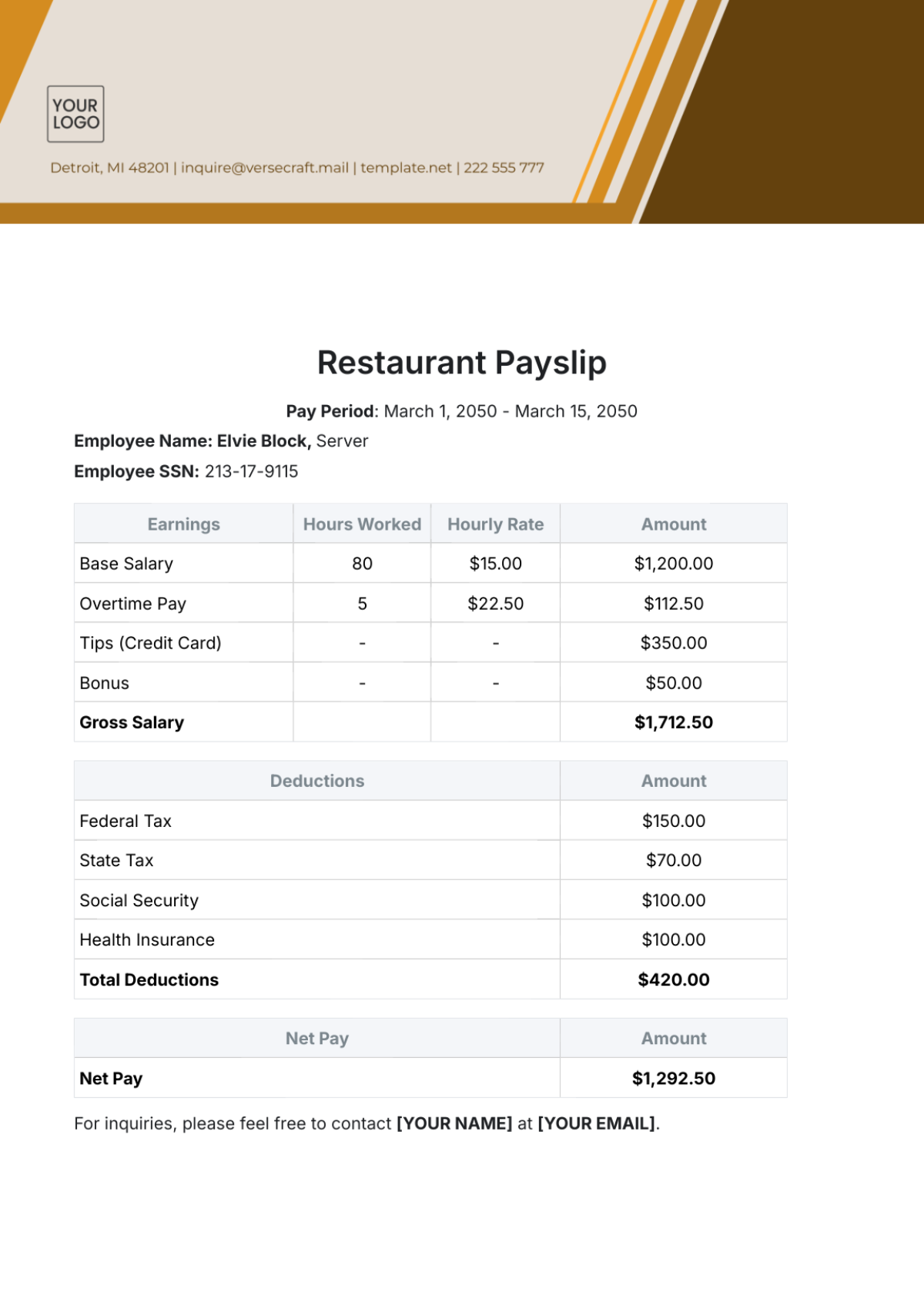
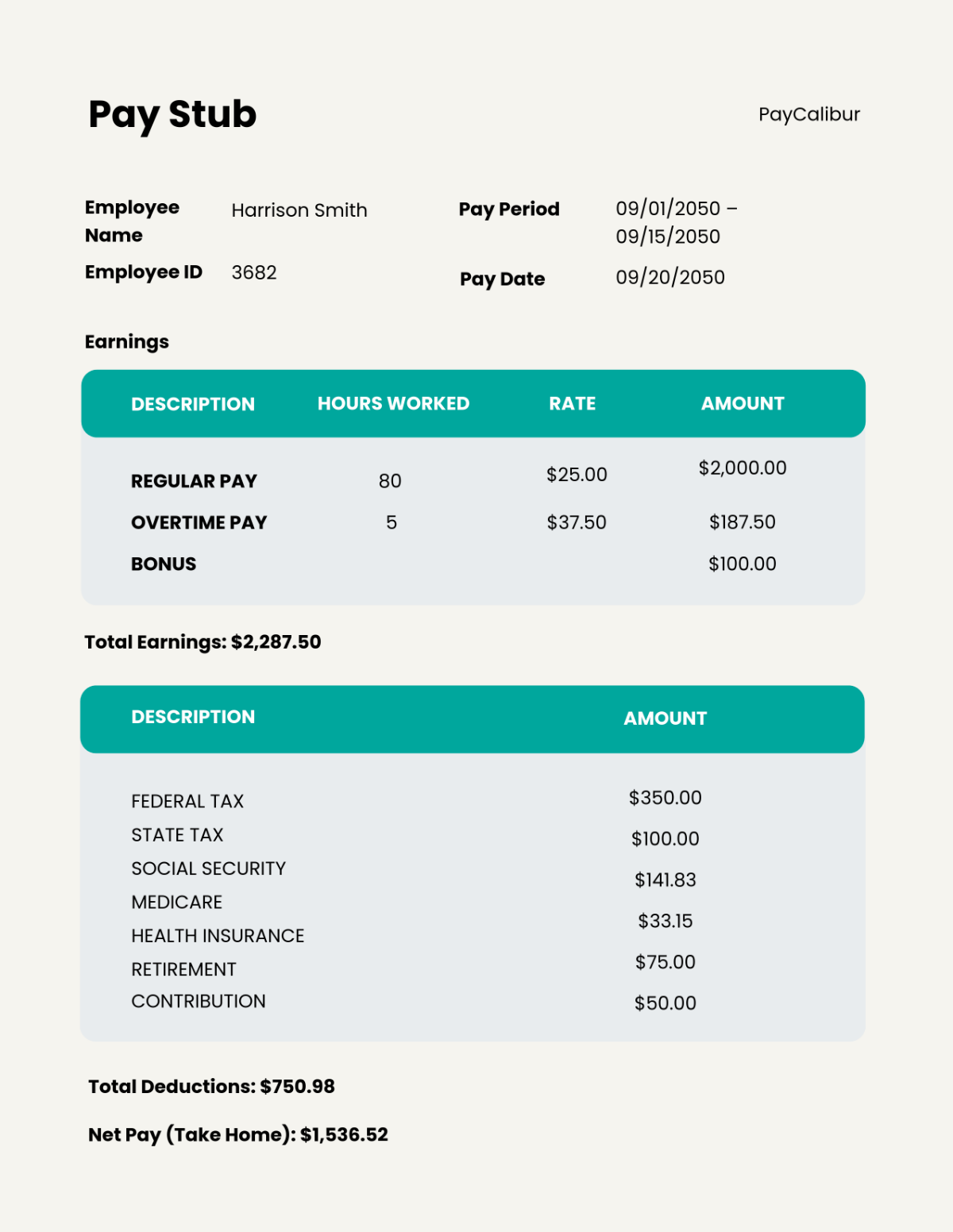
Expenditure Management
This section is crucial for maintaining control over organizational spending and ensuring financial integrity. It outlines systematic procedures for the approval, recording, verification, and reconciliation of all expenditures.
A. Approving and Recording Expenditures
All significant expenditures must receive pre-approval from the designated authority, usually a department head or financial manager.
Establish clear expense limits for various categories and levels of management to streamline the approval process.
Require complete documentation for each expenditure, including invoices, receipts, and justification for the expense.
Implement the use of purchase orders for larger transactions to ensure proper tracking and authorization.
Promptly record all approved expenditures in our financial accounting system to maintain up-to-date financial records.
Conduct regular reviews of expenditure reports to monitor spending patterns and compliance with budgets.
B. Expense Verification and Reconciliation
Regularly verify recorded expenditures against supporting documentation to ensure accuracy.
Reconcile recorded expenditures with bank statements on a monthly basis to detect any discrepancies.
Encourage departments to review their expenditure reports regularly to identify any anomalies or areas of overspending.
Maintain clear audit trails for all expenditures, allowing for easy tracing and verification.
Implement a procedure for promptly addressing any discrepancies or irregularities found during verification and reconciliation.
Provide regular training to staff involved in expenditure management to ensure understanding and compliance with protocols.
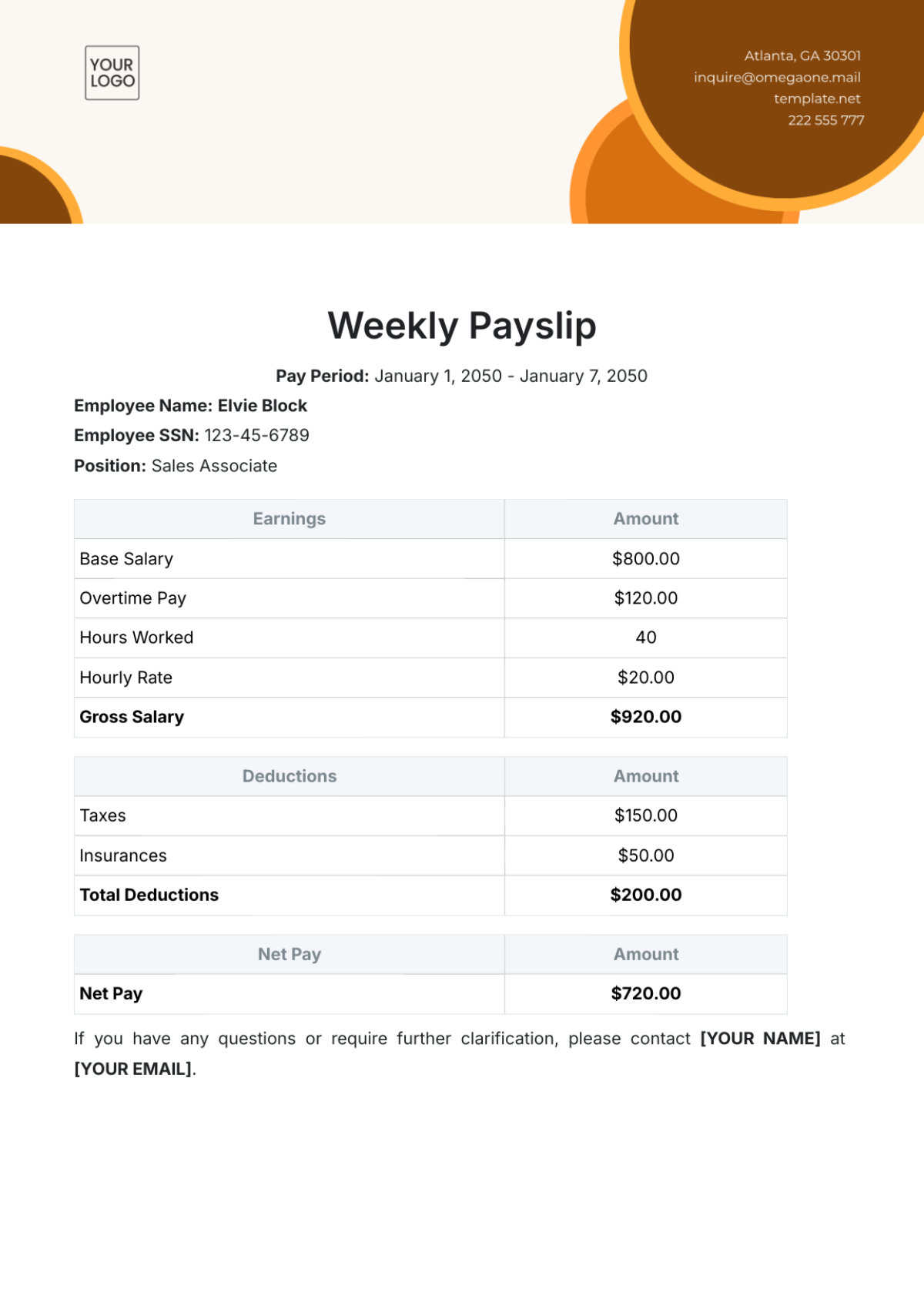
Revenue and Income Management
This section is dedicated to optimizing and maintaining the integrity of our revenue streams. Efficient and accurate handling of revenue and income is fundamental to our financial stability and growth.
A. Recording and Managing Revenue and Income
Ensure all revenue and income are recorded promptly and accurately in our financial system.
Categorize and track revenue by its source (e.g., sales, services, investments) for clear insight.
Perform regular reconciliations of recorded revenues with bank deposits to ensure accuracy and completeness.
Issue receipts or invoices for all transactions as proof of income and for record-keeping.
Analyze revenue trends regularly to identify patterns, anomalies, or areas for improvement.
Include detailed revenue information in periodic financial reports for transparency and analysis.
B. Overdue Payments and Receivables
Strictly adhere to due dates and follow up promptly on overdue payments.
Implement automated reminder systems for upcoming and overdue payments to facilitate timely collection.
Conduct regular reviews of accounts receivable to monitor outstanding balances and aging.
In cases of long-standing receivables, engage in negotiation or settlement processes, if necessary, to recover owed amounts.
Create provisions for bad debts based on historical data and current receivables status.
C. Credit Policy
All customers requesting credit must complete a credit application. The approval of credit is contingent on a satisfactory assessment of their financial history and credit references.
There is a standard payment term of Net 30 days for all credit sales. Customers are encouraged to settle their accounts within this timeframe to maintain good credit standing.
Credit limits are determined based on the customer's creditworthiness and transaction history. These limits are subject to periodic reviews and adjustments based on ongoing credit evaluations.
Late payments are subject to penalties. A monthly interest charge of 1.5% is applied to all overdue balances, emphasizing the importance of timely payments.
Invoices are issued promptly upon delivery of goods or services. A regular billing cycle is maintained to ensure consistent and timely billing communication.
Customers have the right to dispute billing charges. All disputes must be submitted in writing within 30 days of the invoice date, and will be addressed promptly to ensure fair and accurate billing.
D. Handling Delinquent Accounts
Accounts are flagged as delinquent if the payment exceeds the due date by a set period, typically 30 days.
A reminder notice is sent to the debtor, highlighting the overdue payment and requesting immediate settlement.
If payment is not received within a grace period (10 days after the reminder), apply late payment penalties, typically 2% of the overdue amount.
Interest is charged on the overdue amount at a rate of 1.5% per month until full payment is made.
Conduct regular follow-up through emails, phone calls, or letters at set intervals, such as every 15 days.
Send a formal warning notice to the debtor, stating potential legal actions if the payment is not settled.
If payment is still not received, hand over the account to a debt collection agency for further action.
As a last resort, initiate legal action for debt recovery.
Suspend the account to prevent further transactions and limit financial risk.
Report the delinquency to credit bureaus, potentially impacting the debtor's credit rating.
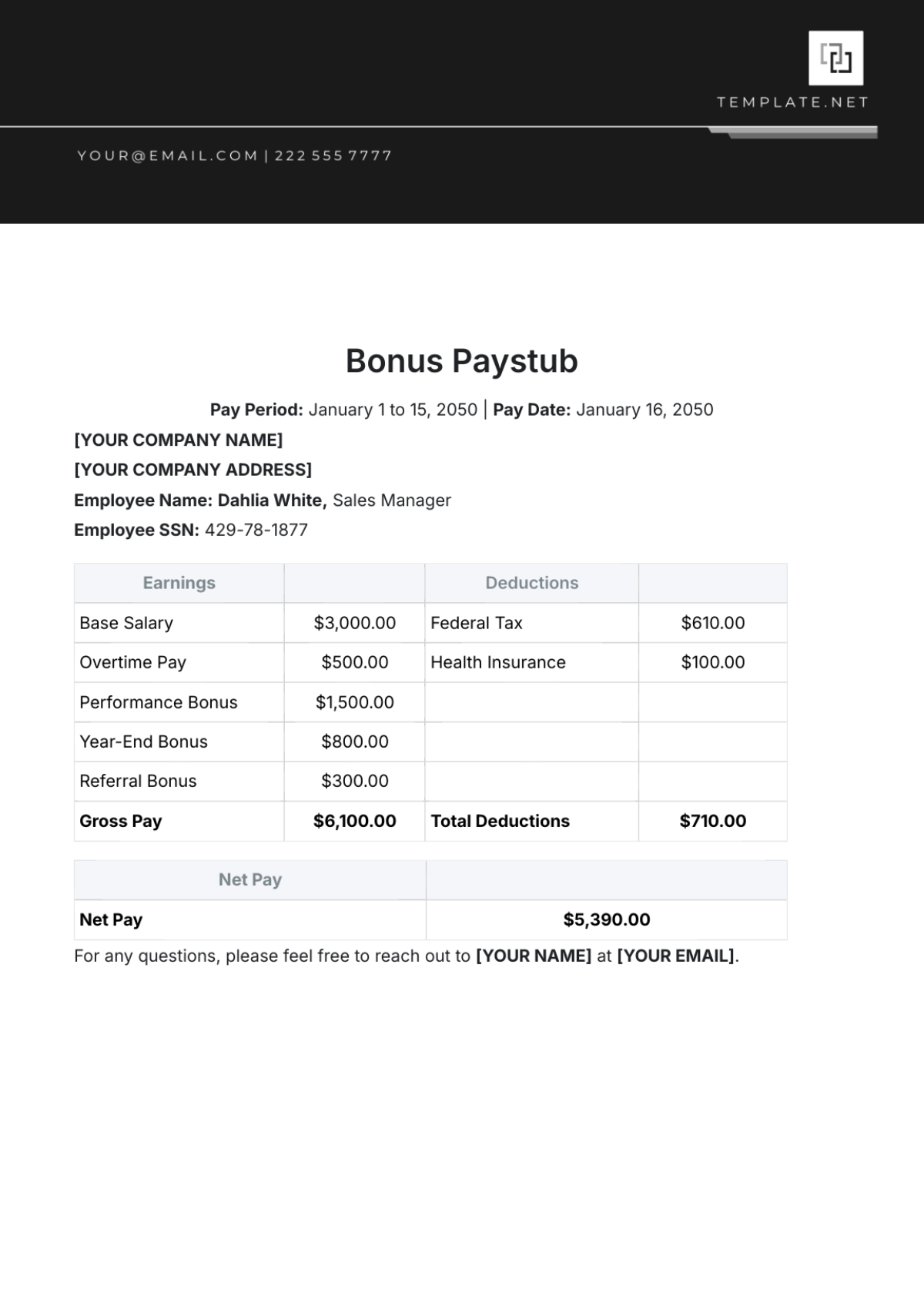
Audit Compliance
This section is pivotal in ensuring that our financial practices adhere to established standards and regulations, maintaining our reputation and operational legality. Rigorous auditing and compliance measures are integral to upholding transparency, accuracy, and integrity in our financial operations.
A. Internal and External Audits
Schedule internal audits quarterly and external audits annually.
Develop detailed audit plans that outline the scope, objectives, and timelines.
Engage qualified and independent auditors for external audits.
Furnish all necessary financial records, reports, and documentation to auditors.
Act on the recommendations and findings from audit reports.
Conduct a senior management review of audit reports.
Share audit results with relevant stakeholders.
B. Compliance Guidelines
Regulations | Compliance Guidelines |
Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) | Implement stringent internal controls; conduct regular SOX audits; ensure top management certifies the accuracy of financial information. |
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) | Adhere to GAAP standards in all financial reporting; ensure consistency in financial recording and reporting processes. |
Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act | Engage in proactive risk management; ensure transparency in financial transactions; comply with consumer protection regulations. |
Internal Revenue Service (IRS) Regulations | Timely and accurate filing of all tax-related documents; adherence to tax laws for deductions and credits; maintain detailed records for tax purposes. |
Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (FCPA) | Avoid corrupt practices in international business; maintain robust anti-corruption policies; conduct regular FCPA compliance training. |
Technology and Software Use
In this section, we emphasize the importance of leveraging technology to enhance the efficiency and accuracy of our financial operations. The guidelines and protocols outlined here ensure the effective and secure use of financial management software and tools.
A. Using Financial Management Software and Tools
Choose software that best fits our financial management needs and integrates seamlessly with other systems.
Ensure that all financial software is regularly updated and maintained for optimal performance.
Implement strict access controls to financial software, allowing only authorized personnel to use the systems.
Regularly back up financial data to prevent loss in case of system failures or other incidents.
Provide comprehensive training to all users of financial software to ensure correct and efficient usage.
Ensure proper integration of financial software with other business systems for cohesive data management.
B. Data Security and Confidentiality
Use strong authentication methods, like two-factor authentication, to enhance security.
Conduct regular security audits of financial systems to identify and rectify vulnerabilities.
Encrypt sensitive financial data both in transit and at rest.
Require staff with access to sensitive financial data to sign confidentiality agreements.
Develop and implement an incident response plan for potential security breaches.
Ensure compliance with relevant data protection laws and regulations.
Training and Development
This section is dedicated to fostering continuous learning and skill enhancement in finance accounts management. Through structured training programs, we aim to keep our team updated with best practices, new regulations, and technological advancements.
Training Module | Description | Frequency | Duration |
Basic Financial Accounting | Covers fundamentals of accounting principles | Annual | 2 Days |
Advanced Financial Management | In-depth training on financial analysis and management | Biennial | 3 Days |
Software and Technology Training | Hands-on training on financial software and tools | As Needed | 1 Day |
Regulatory Compliance | Updates on current financial laws and regulations | Annual | 2 Days |
Risk Management Strategies | Training on identifying and managing financial risks | Biennial | 2 Days |
Ethical Financial Practices | Ethics and integrity in financial management | Annual | 1 Day |
Data Security and Confidentiality | Ensuring the security of financial information | Annual | 1 Day |
Amendment and Revision Procedures
In this section, we outline the process for updating and modifying this protocol to ensure it remains relevant and effective.
Schedule regular reviews of the protocol, at least annually, to assess its effectiveness and relevance.
Encourage team members to propose amendments based on observed challenges or changes in financial management practices.
Establish a committee to review proposed amendments, which will then be forwarded to senior management for approval.
Document all changes, including the rationale and expected impact, for transparency and future reference.
Communicate any amendments to all relevant personnel to ensure awareness and compliance.
Provide training, if necessary, on the new procedures or changes introduced in the protocol.
Monitor the implementation of amendments and gather feedback for future improvements.