Free Finance Strategic Payroll Management Document

Introduction
The Strategic Payroll Management Document serves as a comprehensive guide for managing and executing the payroll functions within our company. The primary goal of this document is to ensure a streamlined, compliant, and efficient payroll system that supports the organization's overall financial strategy. Payroll management is more than just calculating wages; it involves understanding the complexities of payroll legislation, using appropriate payroll systems, ensuring accurate payroll calculations, maintaining records, and responding effectively to employee queries. By adhering to the guidelines in this document, the company aims to achieve a balance between employee satisfaction, legal compliance, and operational efficiency.
Payroll Compliance and Legislation
Understanding Payroll Legislation
Payroll compliance is a critical aspect of payroll management, requiring a thorough understanding of various laws and regulations that impact payroll operations. This includes tax withholdings, employee classifications, minimum wage requirements, overtime rules, and other statutory deductions. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in significant penalties and damage to the company's reputation.
Legislation Type | Description | Impact on Payroll |
Tax Laws | Laws governing federal, state, and local tax withholdings | Determines tax withholding amounts |
Labor Laws | Regulations on minimum wage, overtime, etc. | Affects how wages are calculated |
Employee Classification | Rules defining exempt and non-exempt employees | Influences payroll calculations and benefits |
Updates and Continuing Education
Staying abreast of changes in payroll-related legislation is crucial. The company must establish a process for monitoring legislative updates and ensuring that the payroll system is updated accordingly. This might involve subscribing to legal updates, joining professional payroll associations, or attending webinars and training sessions.
Training Programs: Regular training sessions should be held for payroll staff to keep them informed about the latest payroll practices and legislative changes. This can be achieved through in-house training, online courses, or external workshops.
Update Process: A formal process for updating payroll systems and procedures in response to legislative changes should be in place. This includes a timeline for implementation and roles and responsibilities for managing updates.
Payroll Processing Systems
Selection of Payroll Systems
Choosing the right payroll system is crucial for efficient payroll management. The system should align with the company's size, complexity, and payroll needs. Factors to consider include cost, scalability, ease of use, integration capabilities with other HR and accounting systems, and the level of customer support offered.
Criteria | Description | Importance |
Cost | Initial setup cost and ongoing expenses | High |
Scalability | Ability to handle increased workload | Medium |
Integration | Compatibility with existing systems | High |
User-Friendly | Ease of use for payroll staff | Medium |
System Implementation and Maintenance
Once a payroll system is chosen, its implementation involves several key steps, such as data migration, user training, and system testing. A detailed implementation plan should be created, outlining the timeline, responsibilities, and resources needed.
Maintenance: Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the payroll system operates smoothly. This includes scheduled updates, backups, and audits to ensure data integrity and security.
Troubleshooting: Establish a protocol for identifying and resolving system issues promptly. This may involve in-house IT support or external vendor assistance.
Payroll Calculation and Disbursement
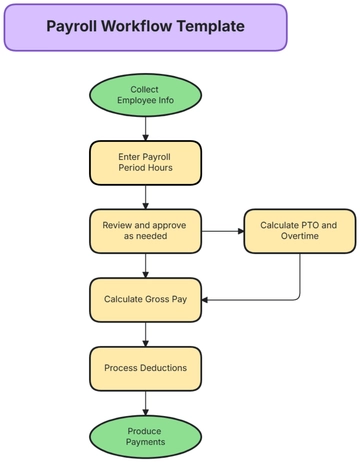
Payroll Calculation
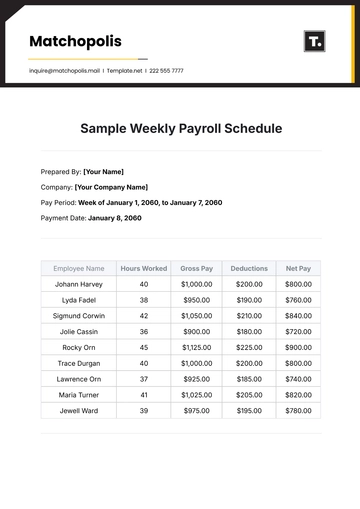
The payroll calculation process is a critical function that must be executed with precision and consistency. It involves computing gross pay, deducting taxes and other withholdings, and determining net pay. Each element of the payroll must be calculated in accordance with legal requirements and company policies.
Payroll Component | Description | Calculation Method |
Gross Pay | Total earnings before deductions | Based on salary agreements or hourly rates |
Taxes | Federal, state, and local taxes | According to tax tables and employee declarations |
Deductions | Benefits, retirement contributions, etc. | As per employee enrollments and policies |
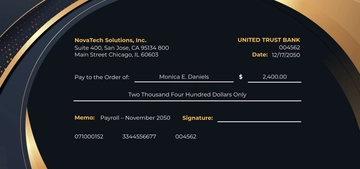
Disbursement Methods
The method of salary disbursement should be convenient for employees while ensuring security and compliance. Common methods include direct bank deposits, checks, or payroll cards. The choice of disbursement method can impact the speed and reliability of payment delivery.
Security Measures: Implementing robust security measures to protect sensitive payroll data during the disbursement process is essential. This includes encryption, secure transfer protocols, and regular security audits.
Employee Preferences: Consideration of employee preferences for payment methods can enhance satisfaction and convenience.
Record Keeping and Reporting
Payroll Records Management
Effective payroll records management is crucial for compliance, accuracy, and historical reference. The company must maintain accurate and up-to-date records of all payroll transactions. This includes employee personal details, pay rates, hours worked, deductions, and tax payments.
Record Type | Description | Retention Period |
Time Sheets | Records of hours worked by employees | 2 years |
Payroll Registers | Detailed records of each payroll process | 3 years |
Tax Forms | W-2s, 1099s, and other tax documents | 4 years |
Reporting Requirements
Regular payroll reporting is essential for financial management and compliance. Reports should be generated monthly, quarterly, and annually, detailing various payroll metrics and summaries.
Management Reports: Include summaries of payroll expenses, department-wise breakdowns, and variance analysis. These are critical for strategic decision-making.
Compliance Reports: Governmental compliance reports such as tax filings, social security contributions, and others must be prepared accurately and submitted within deadlines.
Employee Payroll Queries and Resolutions
Handling Employee Queries
A clear and efficient process for handling employee payroll queries is vital for employee satisfaction and trust. Employees may have questions about their pay slips, tax deductions, benefit deductions, or discrepancies in payments.
Query Process: Establish a formal process where employees can submit their queries, either through an online system or a physical form. Ensure a reasonable timeframe for response and resolution.
Information Access: Provide employees with access to their payroll information through a secure online portal where they can view their pay slips, tax information, and benefits deductions.
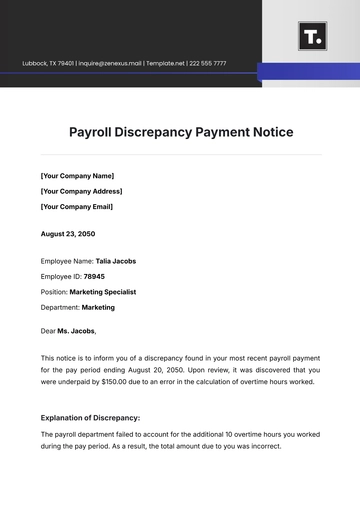
Dispute Resolution
In case of payroll disputes, a formal resolution process should be in place. This includes an initial review of the dispute, investigation, and a resolution process. An escalation matrix should be defined for disputes that cannot be resolved at the initial level.
Dispute Type | Initial Review | Escalation Point |
Pay Discrepancy | Payroll Department | HR Manager |
Tax Deduction Issue | Tax Specialist | Finance Director |
Benefit Deduction | Benefits Coordinator | HR Director |
Strategic Payroll Planning
Long-term Payroll Strategy
Developing a long-term payroll strategy is crucial for aligning the payroll function with the broader objectives of the company. This involves forecasting future payroll needs, considering technological advancements, and planning for workforce changes.
Alignment with Business Goals: The payroll strategy should support overall business objectives, such as cost management, employee satisfaction, and compliance.
Technological Advancements: Keeping abreast of technology trends in payroll processing, such as automation and cloud-based systems, to improve efficiency and accuracy.
Continuous Improvement
The pursuit of continuous improvement in payroll processes ensures the system remains effective, compliant, and responsive to the company’s changing needs.
Feedback Mechanisms: Regular feedback should be sought from employees and payroll staff to identify areas for improvement.
Performance Indicators: Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the efficiency and effectiveness of payroll processes.
KPI | Description | Target |
Processing Time | Time taken to complete the payroll process | Reduce by 10% annually |
Error Rate | Frequency of errors in payroll | Maintain below 0.5% |
Employee Queries | Number of payroll-related queries | Reduce by 15% annually |
Conclusion
In conclusion, effective payroll management is a cornerstone of sound financial practice within any organization. This document provides a comprehensive guide for managing the payroll process in a strategic manner, ensuring compliance, efficiency, and employee satisfaction. By adhering to the guidelines and practices outlined in the preceding sections, the company can achieve a robust and reliable payroll system that supports both operational and strategic objectives. Ongoing attention to legislative changes, technological advancements, and continuous process improvement will ensure that the payroll function remains a vital and well-managed aspect of the organization.
Appendices
Appendix A: Glossary of Terms
Gross Pay: Total earnings of an employee before any deductions are made.
Net Pay: The amount an employee receives after all deductions are made.
Withholding Tax: Taxes that are withheld from an employee’s salary and paid directly to the government.
FICA (Federal Insurance Contributions Act): U.S. federal payroll tax. It includes Social Security and Medicare taxes.
Exempt Employee: An employee who is exempt from overtime pay regulations.
Non-Exempt Employee: An employee who is entitled to overtime pay as per labor laws.
Payroll Ledger: A record showing all payroll transactions for each pay period.
Year-to-Date (YTD): The total of all deductions and earnings from the beginning of the year to the current payroll period.
401(k) Plan: A retirement savings plan sponsored by an employer allowing employees to save and invest a portion of their paycheck before taxes are taken out.
Appendix B: Contact Information for Payroll Department
Role | Name | Phone Number | |
Payroll Manager | [Your Name] | [Your Email] | [Your Contact Number] |
Payroll Specialist | [Name] | [Your Email] | [Your Contact Number] |
Tax Compliance Officer | [Your Name] | [Your Email] | [Your Contact Number] |
Employee Queries | [Name] | [Your Email] | [Your Contact Number |
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
Elevate your payroll strategy with Template.net's Finance Strategic Payroll Management Document Template. Editable and customizable, this document outlines strategic approaches to payroll management. It's key for financial leaders, offering insights into optimizing payroll processes, integrating best practices, and leveraging technology for effective, strategic payroll administration.