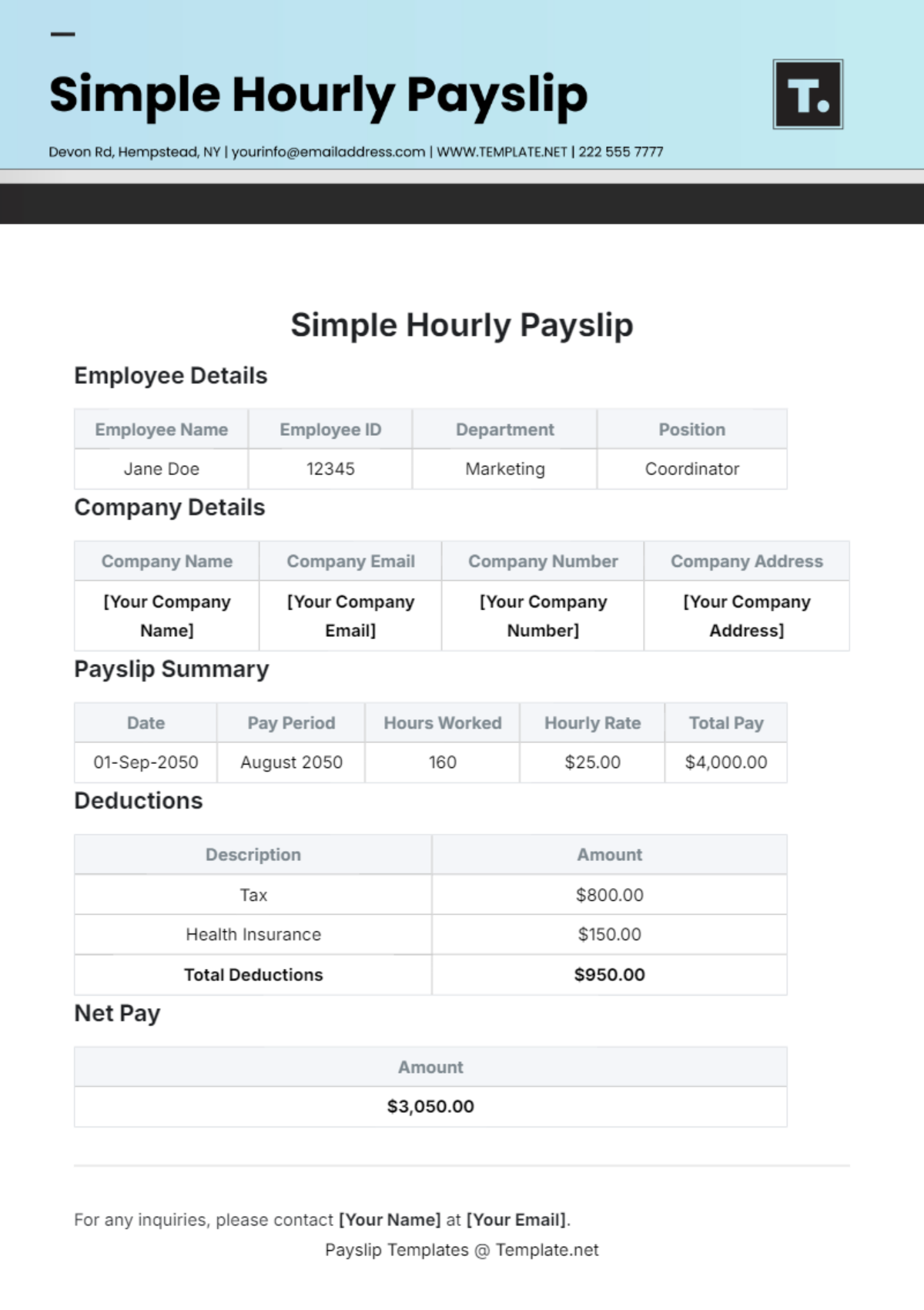
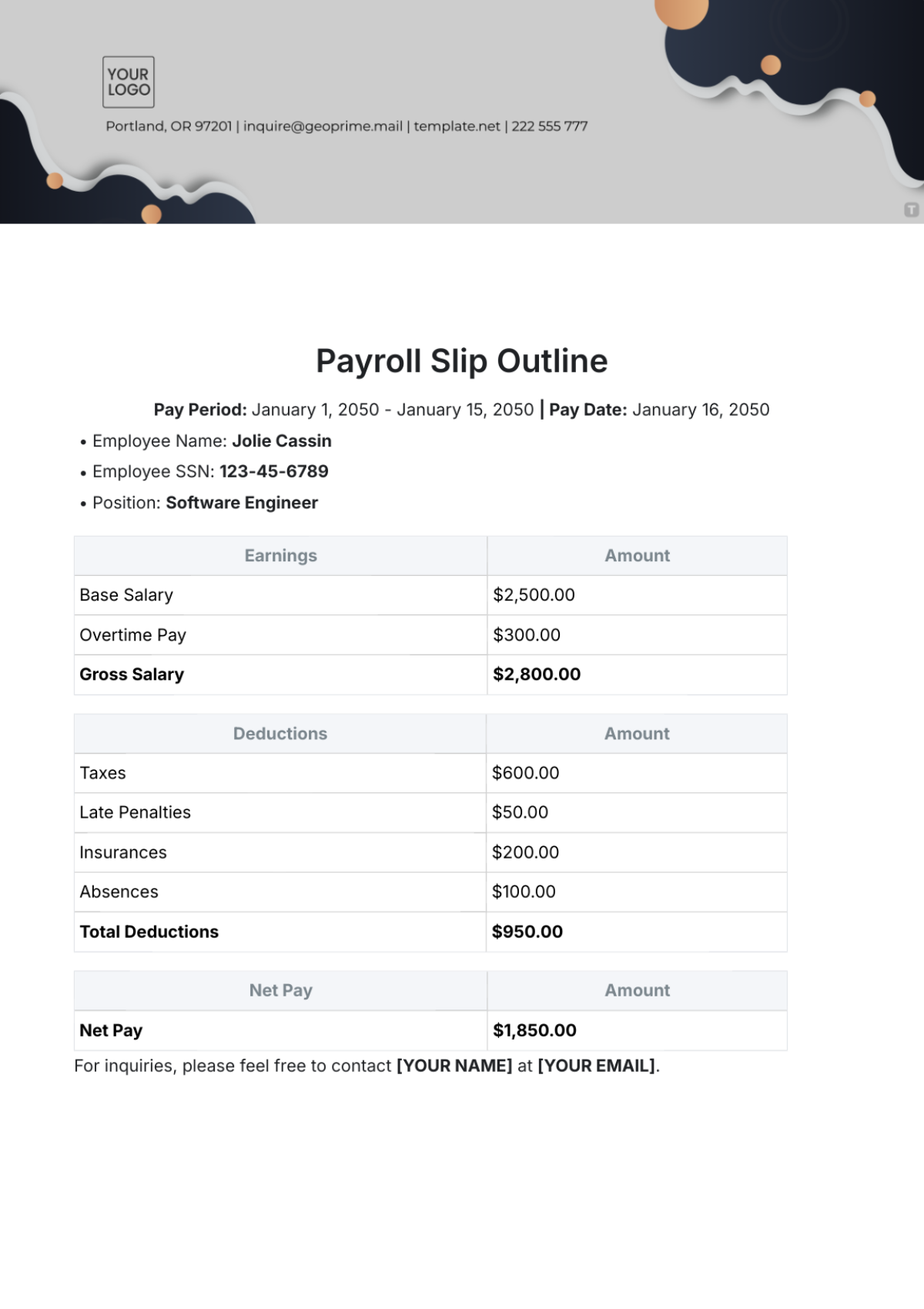
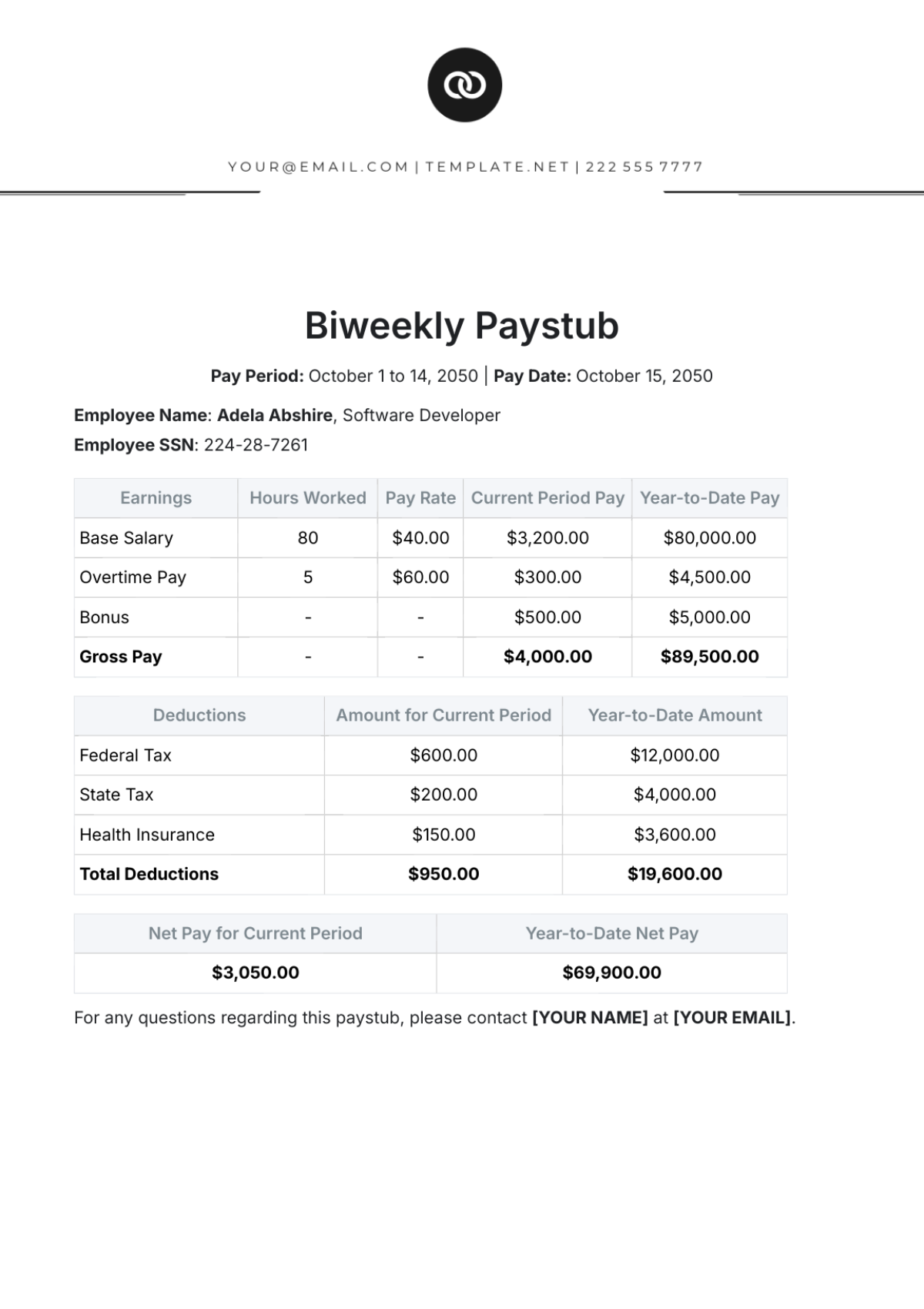
Payroll Accounting Crisis Management Protocol
Introduction
A. Overview
The Payroll Accounting Crisis Management Protocol is designed to guide [Your Company Name] in effectively responding to and managing crises related to payroll accounting. This protocol outlines the necessary procedures and strategies to mitigate the impact of such crises on employees, stakeholders, and the overall operation of the company.
B. Scope
This protocol covers crises that may arise from errors, fraud, system failures, or any other event affecting the accuracy and reliability of payroll accounting. It applies to all employees involved in payroll processes and extends to external parties, including clients and regulatory bodies.
Emergency Contact Information
A. [Your Company Name] Emergency Contacts
Name | Position | Contact Number | |
|---|---|---|---|
[Your Name] | Payroll Manager | [Your Number] | [Your Email] |
B. External Contacts
Contact Type | Name | Contact Number | |
|---|---|---|---|
IT Support | [IT Support Name] | (555) 234-5678] | [itsupport@yourcompany.com] |
Notification and Communication
A. Internal Communication Plan
In the event of a payroll accounting crisis, prompt communication with internal stakeholders is crucial. The following steps outline the internal communication plan:
Immediate Notification: The Payroll Manager or Backup Payroll Manager will immediately notify the CEO and HR Manager.
Emergency Meeting: A crisis management team meeting will be convened within [24 hours] to assess the situation and devise an action plan.
Internal Announcement: Following the initial assessment, a company-wide internal announcement will be made within [48 hours] through email, company intranet, and, if necessary, a virtual town hall.
B. External Communication Plan
When communicating with external parties, transparency and accuracy are paramount:
Regulatory Bodies: The Legal Advisor will be responsible for informing relevant regulatory bodies within [72 hours] of identifying the crisis.
Client Communication: The PR & Communication contact will coordinate the messaging for client communication, ensuring a consistent and reassuring message is delivered within [72 hours].
Crisis Assessment and Analysis
A. Initial Crisis Assessment
Efficient crisis assessment is key to formulating an effective response:
Incident Reporting: Employees will report payroll discrepancies to the Payroll Manager or Backup Payroll Manager immediately through a designated incident reporting system.
Assessment Team: A cross-functional team, including representatives from payroll, finance, and IT, will conduct an initial assessment within [24 hours] to identify the nature and scope of the crisis.
B. Root Cause Analysis
Understanding the root causes is crucial for preventing future crises:
Root Cause Team: A specialized team, led by the IT Support, will conduct a thorough root cause analysis within [5 business days] of identifying the crisis.
Recommendations: The team will provide actionable recommendations to address identified root causes and prevent similar incidents in the future.
Temporary Payroll Procedures
A. Temporary Payroll Processing
In the face of a crisis, it is imperative to ensure the continuity of payroll processing:
Backup Systems: Activate backup payroll systems within [12 hours] to resume essential payroll functions.
Interim Payroll Team: A designated interim payroll team, led by the Backup Payroll Manager, will handle payroll processing until the crisis is resolved.
B. Communication with Employees
Transparent communication with employees is essential during a crisis:
Employee Notification: Communicate temporary payroll procedures to employees via email within [48 hours], detailing any changes in payment schedules or methods.
FAQs and Support: Provide a comprehensive FAQ document and establish a support hotline to address employee concerns and inquiries related to payroll.
Legal and Compliance Considerations
A. Legal Implications
Addressing legal implications is crucial to safeguard the company's interests:
Legal Review: Engage the Legal Advisor to conduct a thorough review of legal implications within [72 hours] of crisis identification.
Legal Actions: Initiate legal actions or remediation measures as recommended by the Legal Advisor to mitigate potential legal consequences.
B. Compliance Checklist
Maintaining compliance is essential even in crisis situations:
Compliance Audit: Conduct a compliance audit within [10 business days] to ensure adherence to relevant regulations and standards.
Remediation Plan: Develop a remediation plan to address any compliance gaps identified during the audit, with a clear timeline for implementation.
Recovery Plan
A. Recovery Timeline
A structured recovery plan is essential for returning to normal payroll operations:
Phase 1: | Stabilization ([5 days]): Focus on stabilizing immediate issues, including system restoration and addressing critical payroll discrepancies. |
B. Continuous Improvement
Learning from the crisis is essential for ongoing improvement:
Post-Crisis Analysis ([20 days]): Conduct a detailed analysis of the crisis response, identifying strengths and areas for improvement.
Implementation of Improvements ([30 days]): Implement improvements based on the analysis, including system enhancements, additional training, and process revisions.
Documentation and Reporting
A. Incident Report
Accurate documentation is vital for future reference and analysis:
Incident Report Form: Employees will complete an incident report form within [24 hours] of identifying a payroll issue, providing detailed information on the discrepancy.
Submission and Review: Incident reports will be submitted to the Payroll Manager for review and inclusion in the crisis documentation.
B. Post-Crisis Report
Sharing insights with stakeholders is crucial for transparency:
Post-Crisis Report Contents: The post-crisis report will include a summary of the incident, actions taken, lessons learned, and recommendations for improvement.
Distribution ([45 days]): The report will be distributed to the executive team, relevant department heads, and external stakeholders such as clients and regulatory bodies.
Training and Awareness
A. Employee Training
Ongoing training ensures that employees are well-prepared to handle payroll crises:
Regular Training Sessions: Conduct quarterly training sessions for all employees involved in payroll processes, covering error identification, incident reporting, and crisis response procedures.
Simulated Drills: Implement simulated crisis drills annually to test employee readiness and improve response times.
B. Awareness Programs
Raising awareness is essential for a proactive approach to crisis prevention:
Internal Communications: Regularly share tips, updates, and best practices related to payroll accuracy and fraud prevention through internal communication channels.
Campaigns ([2 times a year]): Launch biannual awareness campaigns, leveraging email, intranet, and company meetings to reinforce the importance of accurate payroll practices.
Review and Revision
A. Periodic Review
Regular reviews are critical for keeping the protocol up-to-date:
Quarterly Reviews: Conduct quarterly reviews of the Payroll Accounting Crisis Management Protocol to identify any gaps or changes needed.
Feedback Collection: Gather feedback from the crisis management team, employees, and external stakeholders during each review.
B. Revision Procedure
A structured approach ensures that the protocol remains effective:
Trigger for Revision (After major payroll system updates): Whenever there are significant updates to the payroll system or regulations, initiate a revision of the protocol.
Revision Team and Timeline: Form a revision team including representatives from payroll, legal, and IT to review and update the protocol within [15 business days] of triggering a revision.
Conclusion
In closing, the Payroll Accounting Crisis Management Protocol is a foundational framework designed to safeguard [Your Company Name]'s payroll processes during times of crisis. The commitment to maintaining the protocol's effectiveness is evident through:
Regular Reviews ([Quarterly]): Quarterly reviews ensure that the protocol is current, effective, and aligned with emerging threats and industry standards.
Continuous Improvement ([Ongoing]): The protocol includes a robust continuous improvement cycle, with post-crisis analyses leading to actionable improvements within [30 days] of identifying opportunities.
Transparency and Communication ([Throughout]): Open communication is maintained with internal and external stakeholders throughout the crisis, with regular updates, reports, and post-crisis reviews.
Employee Training and Awareness ([Ongoing]): Regular training sessions, simulated drills, and awareness campaigns contribute to a vigilant and well-prepared workforce.
Adaptive Revision Process ([As needed]): The structured revision process ensures that the protocol adapts to changes in the payroll system, regulations, or identified weaknesses.
This protocol serves as a dynamic and evolving guide, reflecting [Your Company Name]'s commitment to resilience, transparency, and the continuous enhancement of its payroll accounting crisis response capabilities. By adhering to this protocol, we fortify our ability to navigate and overcome challenges, ensuring the integrity of our payroll processes and maintaining the trust of our employees and stakeholders.