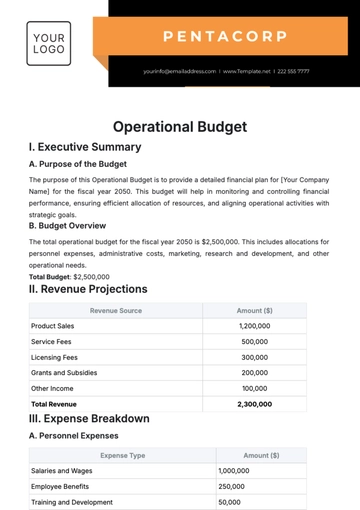
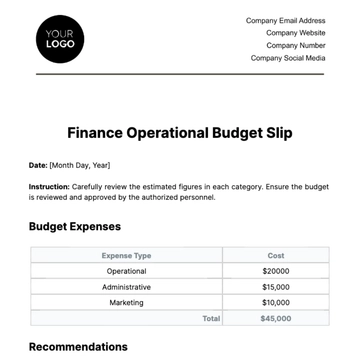
Free Accounting Budget Compliance Document

This Accounting Budget Compliance Document is designed to ensure the financial integrity and transparency of [Your Company Name]. Adherence to budgetary policies and procedures is paramount to maintain the organization's fiscal responsibility.
Purpose
The purpose of this document is to establish a comprehensive framework for budget management within [Your Company Name], facilitating adherence to financial regulations and fostering transparent financial practices to support organizational goals effectively.
Scope
This document applies to all departments and projects within [Your Company Name], guiding the entire budgeting lifecycle from initial planning to ongoing monitoring and eventual audit. It ensures consistency and accountability across the organization.
Responsibilities
A. Finance Department
In addition to overseeing the budgeting process and conducting regular internal audits, the finance department plays a crucial role in providing guidance and support to ensure compliance with financial regulations and best practices.
B. Department Heads
Department heads are not only accountable for developing accurate and realistic budgets but also for actively participating in budget reviews and providing necessary explanations for variances to ensure financial transparency.
C. Budget Managers
Budget managers are tasked with closely monitoring expenditures against approved budgets, promptly identifying and addressing any significant variances to maintain financial discipline and alignment with organizational goals.
D. Compliance Officers
Compliance officers play a vital role in conducting periodic reviews to ensure that budgeting practices align with established policies and guidelines, thereby mitigating risks and enhancing overall financial integrity.
Budgeting Process
A. Budget Request:
Departments submit detailed budget requests outlining their financial needs, with a focus on transparency and accuracy to facilitate informed decision-making by the finance department and budget approval committee.
B. Review and Approval:
The finance department reviews the requests for accuracy and compliance, seeking necessary clarifications.
Budgets are then submitted to the [Budget Approval Committee] for evaluation and approval.
C. Communication:
Transparent communication of approved budgets to relevant stakeholders fosters alignment and understanding of financial priorities, facilitating effective resource allocation and decision-making across the organization.
Budget Approval
Step | Activity | Responsible Party |
|---|---|---|
Budget | Approval Committee Evaluation: - Evaluation based on financial feasibility, strategic alignment, and organizational impact. | Budget Approval Committee |
Monitoring and Reporting
A. Ongoing Monitoring:
Regular reviews of actual expenditures against approved budgets by budget managers ensure proactive identification of variances, enabling timely corrective actions to maintain financial discipline.
B. Frequency of Reports:
Monthly financial reports, distributed to department heads and stakeholders, provide timely insights into budget performance, facilitating informed decision-making and strategic adjustments as needed.
C. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs):
Established KPIs serve as benchmarks to measure budget performance and identify areas for improvement, guiding continuous optimization of budgetary practices and resource allocation.
Controls and Audits
A. Internal Controls:
[Your Company Name] maintains robust internal controls to safeguard against financial irregularities.
Authorization processes are in place to ensure that expenditures align with approved budgets.
B. Internal Audits:
The internal audit team conducts regular audits to verify compliance with budgetary policies and procedures. Their responsibilities encompass:
Risk Assessment: Conducting comprehensive risk assessments to identify potential weaknesses in budgeting processes and internal controls, thereby enabling proactive risk management strategies.
Audit Planning: Developing detailed audit plans based on risk assessments, outlining the scope, objectives, and methodologies to be employed during audits.
Audit Execution: Performing detailed examinations of budgetary practices and expenditures to verify compliance with established policies and procedures. This includes assessing the accuracy of financial data, reviewing authorization processes, and evaluating adherence to budgetary constraints.
Reporting: Communicating audit findings and recommendations to management, highlighting areas of non-compliance, internal control deficiencies, and opportunities for improvement. Internal auditors provide actionable insights to facilitate decision-making and enhance operational efficiency.
Follow-up: Monitoring the implementation of audit recommendations and verifying the effectiveness of corrective actions taken by management to address identified issues. This ensures continuous improvement and strengthens the organization's internal control environment.
C. External Audits:
External auditors are engaged periodically to provide an unbiased assessment of [Your Company Name]'s financial practices. Their roles and responsibilities include:
Financial Statement Audit: Conducting a thorough examination of [Your Company Name]'s financial statements to provide assurance regarding their accuracy, completeness, and compliance with applicable accounting standards and regulations.
Compliance Audit: Verifying compliance with external regulations, contractual obligations, and industry standards to ensure adherence to legal and regulatory requirements.
Audit Planning and Execution: Developing audit plans based on risk assessments and conducting fieldwork to gather evidence and assess the effectiveness of internal controls. External auditors employ a systematic approach to gather sufficient and appropriate audit evidence to support their opinions.
Reporting: Issuing an audit report detailing findings, conclusions, and recommendations to management, shareholders, and regulatory authorities. External auditors provide an independent opinion on the fairness of [Your Company Name]'s financial statements and the effectiveness of its internal controls.
Exceptions and Variances
Any deviations from the approved budget must be documented and explained. The Budget Review Committee reviews and approves any exceptions, ensuring transparency and accountability.
To enhance the effectiveness of budget monitoring, [Your Company Name] establishes specific thresholds for significant variances and protocols for addressing them. These thresholds serve as early warning indicators, allowing timely intervention to mitigate risks and maintain financial discipline.
A. Thresholds for Significant Variances
Percentage Deviation: Any deviation exceeding [5%] of the budgeted amount is considered significant and requires immediate attention.
Absolute Variance: Variances exceeding [$10,000] are deemed significant and warrant investigation to identify root causes and corrective actions.
B. Protocols for Addressing Significant Variances
Root Cause Analysis: Upon identifying a significant variance, the budget manager conducts a thorough root cause analysis to understand the underlying factors contributing to the deviation.
Corrective Action Plan: Based on the root cause analysis, a corrective action plan is developed to address the variance effectively. This plan may include adjustments to spending, reallocation of resources, or process improvements.
Escalation Process: If the variance persists despite corrective actions, it is escalated to higher management levels for further review and intervention.
Revised Forecasting: In cases where variances are anticipated to impact future periods, the budget manager revises forecasting models to reflect updated projections and inform strategic decision-making.
Approval:
[Your Name]
[Your Position]
[Date]
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
Achieve financial compliance effortlessly with the Accounting Budget Compliance Document Template from Template.net. This editable and customizable document ensures adherence to budgetary regulations. Tailor it to your specific needs with ease using our Ai Editor Tool. Stay in control of your budgetary processes, ensuring seamless compliance. Elevate your financial management with this comprehensive and user-friendly template.
You may also like
- Budget Sheet
- Personal Budget
- Non Profit Budget
- Monthly Budget
- Project Budget
- HR Budget
- Company Budget
- Home Budget
- Weekly Budget
- College Budget
- Business Budget
- Construction Budget
- Small Business Budget
- Hotel Budget
- Annual Budget
- Home Renovation Budget
- Household Budget
- Student Budget
- Grocery Budget
- Marketing Budget
- Corporate Budget
- Startup Budget
- Manufacturing Budget
- Church Budget
- University Budget
- Annual Budget Plan
- Event Budget
- Operating Budget
- Travel Budget
- Food Budget
- IT and Software Budget
- School Budget
- Real Estate Budget
- Sales Budget
- Conference Budget
- Budget Finance
- Freelancer Budget
- Budget Advertising