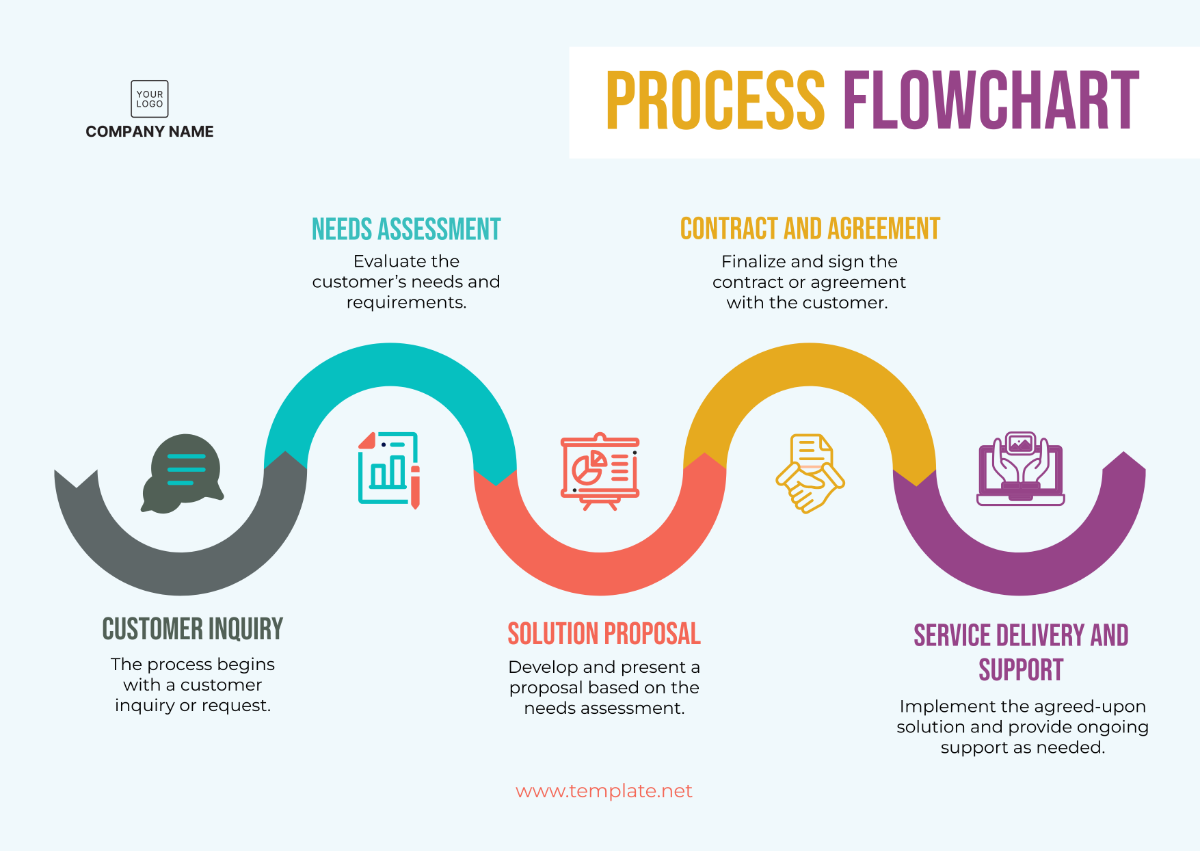
Operations Quality Control Protocol
I. Introduction
The Operations Quality Control Protocol establishes the framework and procedures for maintaining and ensuring the quality of products and processes within [Your Company Name]. By adhering to established quality control measures, [Your Company Name] aims to uphold customer satisfaction, meet regulatory requirements, and drive continuous improvement in product quality and reliability.
II. Purpose
The purpose of this protocol is to establish a robust framework for maintaining and enhancing the quality of products and services offered by [Your Company Name]. This protocol aims to:
Ensure Consistency: By defining standardized procedures and criteria for quality control, the protocol ensures consistency in product and service quality across all operations.
Meet Customer Expectations: By implementing rigorous quality control measures, [Your Company Name] strives to meet or exceed customer expectations for product performance, reliability, and safety.
Mitigate Risks: By identifying and addressing quality issues in a timely manner, the protocol helps mitigate risks associated with product defects, non-conformities, and customer dissatisfaction.
Enhance Competitiveness: By consistently delivering high-quality products and services, [Your Company Name] enhances its competitiveness in the marketplace, building trust and loyalty among customers.
Drive Continuous Improvement: By establishing a systematic approach to quality control, the protocol facilitates ongoing monitoring, evaluation, and improvement of quality processes, driving continuous improvement and innovation.
Ensure Compliance: By aligning quality control practices with relevant industry standards, regulatory requirements, and customer specifications, the protocol ensures compliance with legal and contractual obligations.
III. Scope
The Operations Quality Control Protocol encompasses all facets of quality control within [Your Company Name]'s operations, ensuring the consistent delivery of high-quality products and services. The scope of this protocol includes:
Product Range: Covering the entire spectrum of products manufactured or serviced by [Your Company Name], including [list specific product categories or types].
Manufacturing Processes: Encompassing all stages of the production process, from raw material acquisition to final product assembly, packaging, and distribution.
Facilities and Equipment: Including all facilities, machinery, tools, and equipment utilized in the manufacturing and quality control processes.
Personnel: Engaging all personnel involved in quality control activities, from quality control managers to production line operators, ensuring clear roles and responsibilities are defined.
Suppliers and Vendors: Extending to the quality assurance processes associated with incoming materials and components sourced from external suppliers and vendors.
Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring adherence to relevant industry standards, regulatory requirements, and customer specifications across all quality control activities.
IV. Definitions
Quality Control: The systematic process of ensuring that products meet specified quality standards and requirements through various inspection, testing, and validation procedures.
Non-Conformance: Any deviation from established quality standards, specifications, or requirements that may affect the quality or performance of a product or process.
Corrective Action: An action taken to address the root cause of a non-conformance or quality issue, aimed at preventing its recurrence and restoring compliance with quality standards.
Preventive Action: Proactive measures implemented to prevent the occurrence of non-conformances or quality issues by identifying and mitigating potential risks or root causes.
Quality Assurance: The process of planning and implementing quality control measures to ensure that products meet or exceed customer expectations and regulatory requirements.
Quality Management System (QMS): A set of policies, procedures, and processes designed to ensure consistent quality throughout all aspects of an organization's operations.
Defect: Any imperfection or flaw in a product or process that does not meet specified quality standards or customer requirements.
Acceptance Criteria: The defined standards or requirements that a product or process must meet to be considered acceptable or compliant.
Validation: The process of verifying that a product, process, or system meets specified requirements and fulfills its intended purpose.
Verification: Confirmation through evidence, examination, or investigation that specified requirements have been fulfilled.
V. Responsibilities
Quality Control Manager: Oversees the implementation of quality control procedures and ensures compliance with quality standards. Develops and maintains quality control documentation, conducts training for staff, and leads quality improvement initiatives.
Production Supervisor: Ensures that quality control measures are followed during the manufacturing process. Monitors production activities, identifies quality issues, and coordinates with the quality control team to address them promptly.
Quality Control Inspectors: Conduct inspections, tests, and audits to verify compliance with quality standards and specifications. Record and report quality control data, communicate findings to relevant stakeholders, and assist in implementing corrective actions.
Manufacturing Engineers: Collaborate with the quality control team to optimize manufacturing processes and improve product quality. Develop and implement quality control procedures, provide technical support for quality-related issues, and participate in root cause analysis investigations.
Supply Chain Managers: Ensure the quality of incoming materials and components by establishing and maintaining relationships with reliable suppliers. Collaborate with suppliers to address quality issues, implement quality improvement initiatives, and monitor supplier performance.
Customer Service Representatives: Act as a liaison between customers and the quality control team, addressing customer concerns and complaints related to product quality. Provide feedback to the quality control team to facilitate continuous improvement efforts and enhance customer satisfaction.
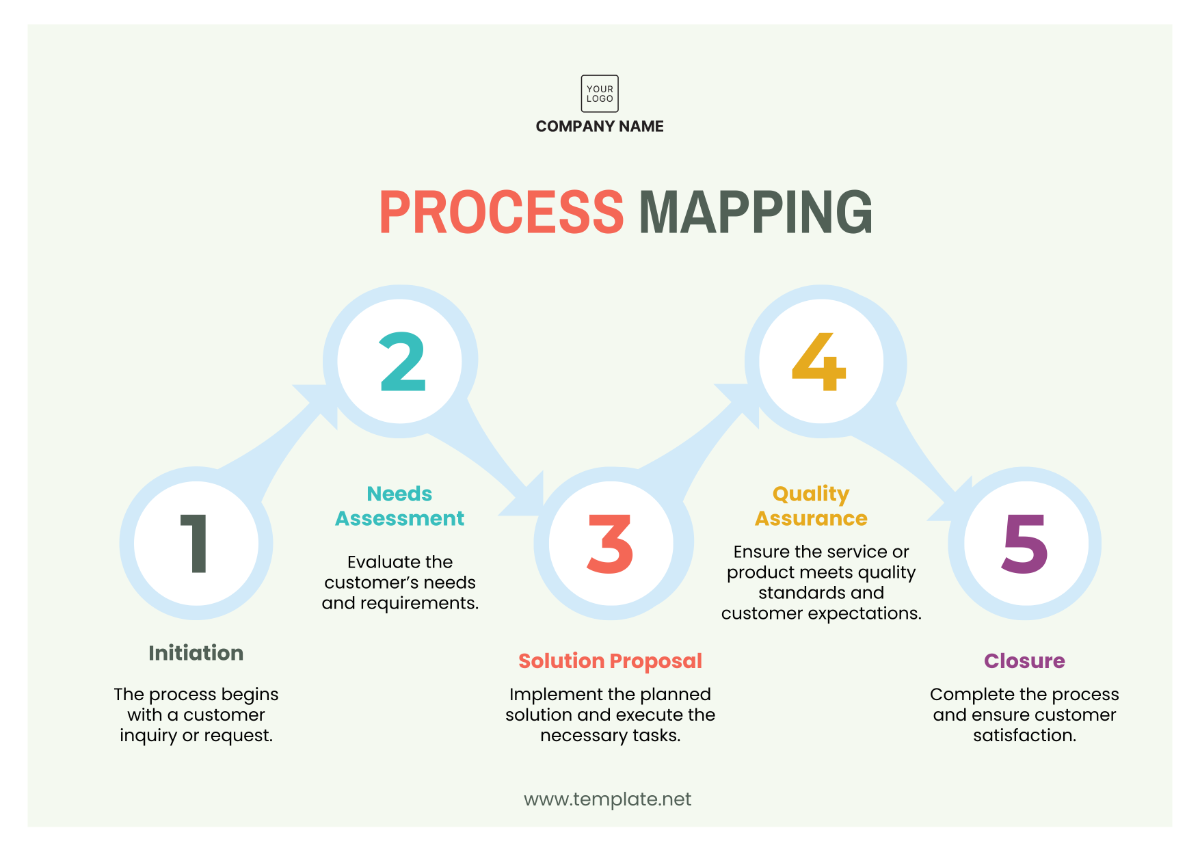
VI. Quality Control Procedures
A. Incoming Material Inspection
The incoming material inspection process of [Your Company Name] involves thorough assessment and verification of raw materials and components upon receipt. It aims to ensure that all incoming materials meet predefined quality standards and specifications before being utilized in the production process. Key aspects of the incoming material inspection include:
Visual Inspection: Conducting visual examinations to detect any visible defects, damages, or discrepancies in the appearance of the materials.
Dimensional Inspection: Measuring the dimensions and physical attributes of the materials to verify compliance with specified tolerances and requirements.
Material Testing: Performing various tests, such as hardness tests, chemical analysis, or material composition analysis, to assess the material properties and characteristics.
Sampling Procedures: Following established sampling plans to select representative samples from incoming material batches for inspection and testing.
Documentation and Record-Keeping: Documenting inspection results, including any deviations or non-conformities identified, and maintaining accurate records for traceability and quality assurance purposes.
B. In-Process Inspection
The in-process inspection stage of [Your Company Name] involves ongoing monitoring and evaluation of manufacturing processes and product quality throughout the production cycle. It aims to identify any deviations from quality standards or process parameters in real time to prevent defects and ensure product consistency. Key aspects of the in-process inspection include:
Process Monitoring: Continuously monitoring key process parameters, such as temperature, pressure, speed, and flow rates, to ensure they remain within specified ranges.
Product Sampling: Conducting periodic sampling of products at various stages of the production process to assess quality attributes and detect any issues early on.
Functional Testing: Performing functional tests or performance evaluations on products to verify proper operation and compliance with functional requirements.
Visual Inspection: Inspecting products visually for any defects, irregularities, or cosmetic imperfections that may affect quality or customer satisfaction.
Immediate Corrective Actions: Taking immediate corrective actions or making adjustments to the production process if any deviations or quality issues are identified during in-process inspections.
C. Final Product Inspection
The final product inspection of [Your Company Name] involves comprehensive assessment and testing of finished products to ensure they meet all specified quality standards and requirements. Key aspects of the final product inspection include:
Comprehensive Evaluation: Conducting thorough inspections and tests on finished products to verify their overall quality, functionality, and compliance with specifications.
Acceptance Criteria: Applying predefined acceptance criteria or quality standards to determine whether products meet the required quality levels and are suitable for release.
Sampling Plans: Following established sampling plans to select representative samples from product batches for inspection and testing.
Documentation and Reporting: Documenting inspection results, including any defects or non-conformities identified, and generating inspection reports for internal records and customer reference.
D. Non-Conformance Handling
Non-conformance handling of [Your Company Name] involves documenting, investigating, and taking appropriate corrective actions to rectify non-conformities and prevent their recurrence. Key aspects of non-conformance handling include:
Identification and Documentation: Promptly identifying and documenting any instances of non-conformance or quality deviations encountered during inspections or testing.
Root Cause Analysis: Conducting thorough investigations to determine the root cause(s) of non-conformities and identify contributing factors or underlying issues.
Corrective Actions: Developing and implementing corrective actions to address the root cause(s) of non-conformities and prevent their recurrence in the future.
Preventive Actions: Implementing proactive measures to prevent similar non-conformities from occurring in other products or processes by addressing underlying systemic issues or process weaknesses.
E. Corrective and Preventive Actions
[Your Company Name] outlined these corrective actions, which focus on rectifying existing non-conformities or quality deviations, and the preventive actions that aim to prevent their occurrence in the future. Key aspects of corrective and preventive actions include:
Root Cause Analysis: Conducting thorough investigations to identify the root cause(s) of quality issues or non-conformities and understand contributing factors.
Action Plan Development: Developing comprehensive action plans outlining specific steps, responsibilities, timelines, and resources required to implement corrective and preventive actions.
Implementation: Implementing corrective actions to address identified root causes and prevent recurrence of non-conformities, as well as preventive actions to mitigate risks and improve processes.
Monitoring and Verification: Monitoring the effectiveness of corrective and preventive actions through follow-up inspections, audits, or performance metrics to ensure sustained improvement.
Documentation and Reporting: Documenting all corrective and preventive actions taken, including the rationale, implementation details, and verification of effectiveness, and maintaining records for traceability and quality assurance purposes.
VII. Conclusion
The Quality Control Procedures outlined in this protocol serve as a foundation for ensuring the consistent delivery of high-quality products and services at [Your Company Name]. By adhering to established procedures for incoming material inspection, in-process monitoring, final product inspection, non-conformance handling, and corrective/preventive actions, we aim to uphold our commitment to quality excellence and customer satisfaction.
Through continuous monitoring, evaluation, and improvement of our quality control processes, we strive to identify areas for enhancement, address root causes of non-conformities, and implement proactive measures to prevent quality deviations. By fostering a culture of quality consciousness and accountability across all levels of the organization, we are dedicated to achieving operational excellence and maintaining the trust and confidence of our customers and stakeholders.
VIII. Appendices
Appendix A: Sample Quality Control Inspection Checklist
Appendix B: Root Cause Analysis Template
Appendix C: Corrective and Preventive Action Log
Appendix D: Non-Conformance Report Form
Appendix E: Training and Education Materials
Appendix F: Quality Control Documentation Guidelines