Operations Health and Safety Protocol Document
I. Introduction
A. Purpose
The purpose of this document is to establish a comprehensive framework for managing health and safety within [Your Company Name]. It aims to mitigate risks, prevent incidents, and promote a culture of safety across all operations by providing clear guidelines and procedures for employees to follow.
B. Scope
This protocol applies to all employees, contractors, and visitors operating within [Your Company Name] premises or engaged in activities related to [Your Company Name] operations. It encompasses all areas of the workplace, including office spaces, manufacturing facilities, warehouses, and outdoor work sites. Additionally, it applies to any activities conducted off-site or remotely on behalf of [Your Company Name].
C. Responsibilities
It is the responsibility of all individuals associated with [Your Company Name] to prioritize health and safety in their daily activities. Management holds the primary responsibility for establishing and maintaining a safe work environment, providing necessary resources, training, and oversight to ensure compliance with health and safety protocols. Supervisors are responsible for enforcing health and safety regulations within their respective areas of authority, conducting regular inspections, and addressing any safety concerns promptly. Employees are responsible for adhering to established protocols, reporting hazards and incidents, and actively participating in safety training and awareness programs. By working together, all stakeholders contribute to the creation of a safe and healthy workplace culture.
II. General Health and Safety Guidelines
A. Risk Assessment
Before commencing any task, employees must conduct a thorough risk assessment to identify potential hazards and assess the level of risk associated with each hazard. The risk assessment process involves several steps, including:
Identifying hazards: Employees should identify any potential sources of harm or danger in the workplace, including physical, chemical, biological, and ergonomic hazards.
Evaluating risks: Once hazards have been identified, employees must assess the likelihood and severity of potential harm posed by each hazard.
Implementing control measures: Based on the risk assessment findings, employees should implement control measures to eliminate or mitigate identified hazards.
Reviewing and monitoring: Risk assessments should be reviewed regularly to ensure they remain current and relevant.
A risk assessment matrix may be used to categorize risks based on their likelihood and severity, allowing for the prioritization of control measures and allocation of resources to high-risk areas.
Likelihood | Consequence | Risk Level | Action Required |
|---|---|---|---|
Low | Negligible | Low | Monitor |
Medium | Minor | Medium | Implement Controls |
High | Major | High | Urgent Action Required |
B. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
The use of PPE is essential in areas where hazards cannot be adequately controlled by other means. [Your Company Name] will provide necessary PPE to employees based on the hazards present in their work environment. Examples of commonly used PPE include:
Safety glasses: Protect the eyes from impact, flying debris, or chemical splashes.
Hard hats: Provide head protection in areas where there is a risk of falling objects or overhead hazards.
Gloves: Protect the hands from cuts, abrasions, chemicals, or extreme temperatures.
Hearing protection: Reduce exposure to high levels of noise that could cause hearing damage.
Respiratory protection: Prevent inhalation of harmful dust, fumes, or airborne contaminants.
Employees are required to wear appropriate PPE as instructed and ensure it is properly maintained and replaced as needed. Training on the selection, use, and care of PPE will be provided to all employees to ensure they understand its importance and how to use it effectively.
C. Emergency Procedures
Emergency procedures are in place to ensure a prompt and effective response to any emergency situation that may arise in the workplace. These procedures cover a range of potential emergencies, including but not limited to:
Fire emergencies: Procedures for evacuating the building, using fire extinguishers, and reporting fires.
Medical emergencies: Protocols for providing first aid, summoning medical assistance, and evacuating injured individuals.
Chemical spills: Guidelines for containing spills, evacuating affected areas, and notifying appropriate personnel.
Natural disasters: Plans for sheltering in place, evacuating to safe locations, and communicating with emergency responders.
All employees must familiarize themselves with emergency procedures specific to their work area, including evacuation routes, assembly points, and emergency contact information.
D. Reporting Incidents
Reporting incidents, including accidents, near misses, and hazards, is essential for maintaining a safe work environment and preventing future incidents. All employees are required to report any incidents they witness or are involved in promptly. The incident reporting process involves the following steps:
Immediate response: Employees should take immediate action to address any immediate hazards or injuries and ensure the safety of themselves and others.
Notification: Employees should report the incident to their supervisor or designated safety officer as soon as possible. If the incident involves serious injury, property damage, or environmental impact, employees should contact emergency services immediately.
Incident documentation: A formal incident report should be completed documenting details of the incident, including the date, time, location, individuals involved, and a description of what happened.
Investigation: The incident will be investigated to determine the root causes and contributing factors. This may involve interviewing witnesses, conducting site inspections, and reviewing relevant documentation.
Corrective actions: Based on the investigation findings, corrective actions will be implemented to prevent recurrence of similar incidents in the future.
III. Workplace Safety
A. Hazardous Substances Management
Effective management of hazardous substances is crucial to ensuring workplace safety. The management of hazardous substances involves the following key steps:
Identification: All hazardous substances used or produced in the workplace are identified and labeled appropriately. Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) or Safety Data Sheets (SDS) are maintained for each hazardous substance, providing detailed information on its properties, hazards, and safe handling procedures.
Risk assessment: The risks associated with each hazardous substance are assessed to determine appropriate control measures.
Control measures: This may include engineering controls such as ventilation systems or containment measures, administrative controls such as restricted access or training programs, and the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, goggles, or respirators.
Training and awareness: Employees who work with or near hazardous substances receive comprehensive training on safe handling practices, emergency procedures, and the proper use of PPE.
Monitoring and review: Incident investigations are conducted following any spills, leaks, or exposures to hazardous substances, and corrective actions are implemented to prevent recurrence.
B. Electrical Safety
Electrical safety is a priority at [Your Company Name] to prevent electric shock, fires, and other hazards associated with the use of electricity. Key elements of our electrical safety program include:
Inspection and testing: Electrical equipment and systems are inspected and tested regularly to identify any defects or deficiencies. This includes visual inspections, thermographic surveys, and electrical testing by qualified personnel.
Lockout/tagout (LOTO): Lockout/tagout procedures are implemented to control hazardous energy sources during maintenance or servicing of electrical equipment.
Grounding and bonding: Proper grounding and bonding techniques are used to minimize the risk of electric shock and ensure the safe operation of electrical systems.
Overcurrent protection: Overcurrent protection devices such as circuit breakers and fuses are installed to protect against short circuits, overloads, and other electrical faults. These devices are regularly tested and maintained to ensure they function correctly.
Training and awareness: Employees who work with or near electrical equipment receive training on electrical safety practices, including hazard recognition, safe work practices, and emergency procedures.
C. Fire Safety
Fire safety is a critical aspect of workplace safety at [Your Company Name]. Strict fire safety protocols are in place to prevent fires, protect occupants in the event of a fire, and minimize property damage. Key components of our fire safety program include:
Fire prevention: Fire prevention measures are implemented to minimize the risk of fires starting in the workplace.
Fire detection and alarm systems: Automatic fire detection and alarm systems are installed throughout the facility to provide early warning of a fire. These systems include smoke detectors, heat detectors, and manual pull stations, which are tested regularly to ensure they are operational.
Emergency evacuation procedures: Emergency evacuation procedures are established to ensure the safe and orderly evacuation of occupants in the event of a fire.
Firefighting equipment: Portable fire extinguishers, hose reels, and other firefighting equipment are strategically located throughout the facility to enable prompt response to a fire.
Emergency response planning: Comprehensive emergency response plans are developed to guide employees and emergency responders in the event of a fire. These plans outline roles and responsibilities, communication procedures, and protocols for coordinating with emergency services.
D. Machinery Safety
Machinery safety is a priority at [Your Company Name] to protect employees from hazards such as entanglement, crushing, and impact. Key elements of our machinery safety program include:
Machine guarding: All machinery is equipped with appropriate guards and protective devices to prevent contact with moving parts and other hazards.
Lockout/tagout (LOTO): Lockout/tagout procedures are implemented to control hazardous energy sources during maintenance or servicing of machinery.
Operator training: Operators of machinery receive comprehensive training on safe operating procedures, including startup, shutdown, and emergency stop procedures.
Maintenance and inspection: Machinery is inspected and maintained regularly to identify any defects or deficiencies that could compromise safety.
Risk assessment: Risk assessments are conducted for each piece of machinery to identify potential hazards and assess the level of risk associated with each hazard.
IV. Environmental Safety
A. Waste Management
Effective waste management practices are essential to minimize environmental impact and ensure regulatory compliance. [Your Company Name] follows strict protocols for the collection, segregation, storage, transportation, and disposal of waste generated during its operations. Key components of our waste management program include:
Waste identification: All waste generated in the workplace is classified and labeled according to its properties, hazards, and disposal requirements.
Waste minimization: Efforts are made to reduce waste generation through source reduction, recycling, and reuse initiatives.
Storage and containment: Hazardous wastes are stored in designated storage areas equipped with appropriate containment measures to prevent spills, leaks, or other releases.
Transportation and disposal: Hazardous wastes are transported and disposed of by licensed waste management contractors in accordance with applicable regulations.
B. Pollution Prevention
Pollution prevention measures are implemented to minimize the release of pollutants into the environment and protect air, water, and soil quality. Key elements of our pollution prevention program include:
Emissions controls: This includes the use of pollution control technologies such as scrubbers, filters, and catalytic converters to remove or reduce pollutants before they are released into the atmosphere.
Spill prevention and response: Spill prevention measures are implemented to minimize the risk of accidental releases of hazardous substances.
Stormwater management: Stormwater runoff from [Your Company Name] facilities is managed to prevent pollution of surface water bodies such as rivers, lakes, and streams.
Waste minimization: Efforts are made to reduce the generation of waste and pollutants through source reduction, recycling, and reuse initiatives.
C. Energy Conservation
Energy conservation measures are implemented to reduce energy consumption, lower operating costs, and minimize environmental impact.Key components of our energy conservation program include:
Energy audits: Regular energy audits are conducted to identify opportunities for improving energy efficiency and reducing energy consumption.
Equipment upgrades: Energy-efficient equipment and technologies are installed or retrofitted to replace older, less efficient equipment. This includes upgrading lighting systems, HVAC systems, and production machinery to use less energy and operate more efficiently.
Operational improvements: Operational changes are implemented to optimize energy use and reduce waste. This includes implementing energy management systems, establishing energy-saving procedures, and training employees on energy conservation best practices.
Employee engagement: Employees are encouraged to participate in energy conservation efforts and contribute ideas for reducing energy consumption.
V. Health and Hygiene
A. Cleanliness and Sanitation
Maintaining cleanliness and sanitation in the workplace is essential for preventing the spread of germs and ensuring a safe and healthy environment for all employees. Key components of our cleanliness and sanitation program include:
Regular cleaning: All work areas, including offices, restrooms, break rooms, and common areas, are cleaned regularly using appropriate cleaning agents and disinfectants.
Waste disposal: Waste bins are provided throughout the facility for the proper disposal of trash, recyclables, and hazardous materials.
Personal hygiene: Employees are encouraged to practice good personal hygiene habits, including regular handwashing with soap and water, covering coughs and sneezes with a tissue or elbow, and avoiding touching their face with unwashed hands.
Illness prevention: Employees who are feeling unwell or experiencing symptoms of illness are encouraged to stay home to prevent the spread of illness to others.
B. Illness Prevention
Preventing the spread of illness is a top priority at [Your Company Name] to protect the health and well-being of employees and maintain a safe and productive work environment. In addition to promoting good personal hygiene practices, [Your Company Name] implements various measures to prevent the spread of illness, including:
Vaccination programs: [Your Company Name] offers vaccination programs to employees to protect against common infectious diseases such as influenza and COVID-19.
Health screenings: Health screenings may be conducted periodically to identify individuals who may be at risk of spreading illness to others. This may include temperature checks, symptom assessments, or testing for infectious diseases.
Sick leave policies: [Your Company Name] has policies in place to support employees who need to take time off due to illness. Sick leave benefits may include paid time off, flexible scheduling, or access to telecommuting options to accommodate employees who need to stay home.
Remote work options: In situations where remote work is feasible, [Your Company Name] may offer employees the option to work from home if they are feeling unwell or have been exposed to illness.
C. Ergonomics
Ergonomics plays a critical role in promoting employee health and well-being by optimizing the design of workstations and equipment to reduce the risk of musculoskeletal disorders and other ergonomic-related injuries. Key elements of our ergonomics program include:
Workstation assessments: Ergonomic assessments are conducted for employees who spend prolonged periods working at a desk or workstation.
Ergonomic controls: Based on the findings of ergonomic assessments, appropriate controls are implemented to minimize ergonomic risk factors and improve employee comfort and productivity.
Training and education: Employees receive training on ergonomic principles and best practices to help them identify and address ergonomic risk factors in their work environment.
Injury prevention: [Your Company Name] encourages employees to report any discomfort or pain they experience while working so that prompt action can be taken to address ergonomic issues.
VI. Training and Education
A. Initial Induction Training
All new employees at [Your Company Name] receive comprehensive health and safety induction training as part of their onboarding process. This training covers essential topics related to workplace health and safety, including:
Company policies and procedures: New employees learn about [Your Company Name]'s health and safety policies, procedures, and expectations for compliance.
Hazard recognition: Employees are trained to identify common workplace hazards and understand the risks associated with their work environment.
Emergency procedures: New employees receive instruction on emergency procedures, including evacuation routes, assembly points, and emergency contact information.
Personal protective equipment (PPE): Employees learn about the proper selection, use, and maintenance of PPE required for their job tasks.
B. Ongoing Training
In addition to initial induction training, [Your Company Name] provides ongoing health and safety training to employees to ensure they remain informed about relevant policies, procedures, and best practices. Ongoing training may cover a variety of topics, including:
Hazard-specific training: Employees receive training on specific hazards present in their work environment, such as chemical safety, electrical safety, or machinery safety.
Refresher training: Periodic refresher training is provided to reinforce key health and safety concepts and ensure employees maintain competency in their job tasks.
Regulatory updates: Employees are informed about changes to health and safety regulations and standards that may affect their work activities.
Incident investigation and reporting: Training is provided on incident investigation and reporting procedures to ensure employees know how to respond to incidents and hazards appropriately.
C. Emergency Drills
Emergency drills are conducted periodically to test the effectiveness of emergency procedures and ensure employees are prepared to respond appropriately in emergency situations. These drills may include:
Fire drills: Employees practice evacuating the building in response to a simulated fire alarm to familiarize themselves with evacuation routes and procedures.
Medical emergency drills: Employees practice responding to medical emergencies such as cardiac arrest or severe injuries by providing first aid and summoning medical assistance.
Chemical spill drills: Employees practice responding to chemical spills by containing the spill, evacuating affected areas, and notifying appropriate personnel.
Severe weather drills: Employees practice sheltering in place or evacuating to safe locations in response to severe weather events such as tornadoes or hurricanes.
VII. Safety Inspections and Audits
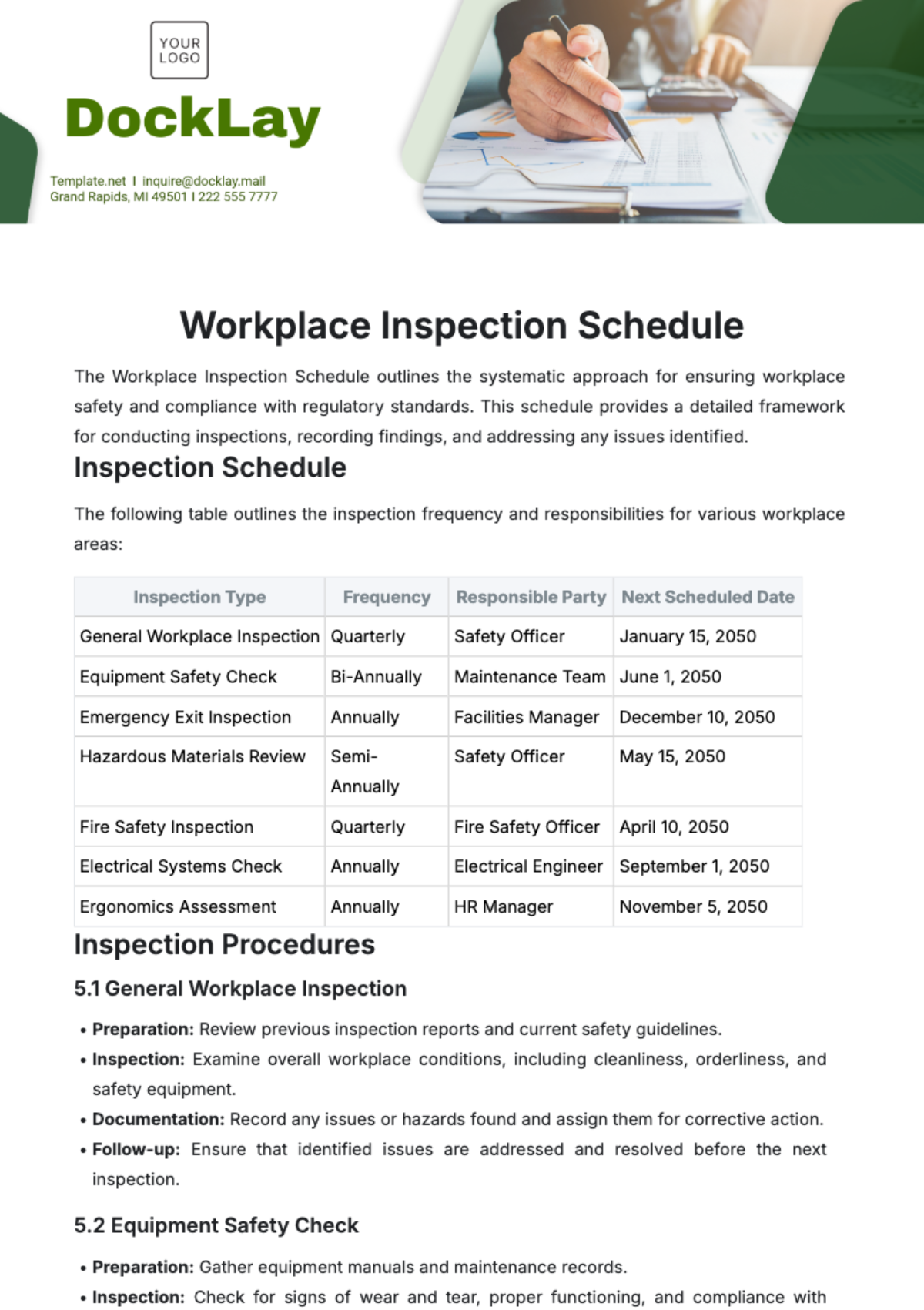
A. Regular Inspections
These inspections are carried out by trained personnel, including safety officers, supervisors, and designated safety representatives, using standardized checklists and procedures. Key aspects of our safety inspection program include:
Frequency: Safety inspections are conducted on a regular basis, with the frequency determined based on the level of risk associated with the work environment and the specific hazards present.
Scope: Inspectors assess various aspects of workplace safety, including the condition of equipment and machinery, the effectiveness of safety controls, housekeeping practices, and employee compliance with safety procedures.
Documentation: Inspection findings are documented using standardized inspection forms or software systems. Inspectors record details of any hazards or deficiencies observed, along with recommendations for corrective actions.
Follow-up actions: Following each safety inspection, corrective actions are identified and assigned to responsible individuals or departments.
B. Audits and Reviews
These audits are typically conducted by internal or external auditors with expertise in health and safety management and may cover various aspects of the health and safety program, including:
Compliance with regulations: Auditors assess [Your Company Name]'s compliance with applicable health and safety regulations, standards, and industry best practices.
Effectiveness of controls: Auditors evaluate the effectiveness of safety controls and procedures implemented by [Your Company Name] to mitigate workplace hazards. This includes assessing the adequacy of risk assessments, the implementation of control measures, and the monitoring of safety performance indicators.
Management commitment and leadership: Auditors assess the commitment of [Your Company Name]'s management to health and safety and the effectiveness of leadership in promoting a culture of safety throughout the organization.
Employee involvement and engagement: Auditors evaluate the level of employee involvement and engagement in health and safety activities at [Your Company Name].
VIII. Incident Management
A. Incident Reporting
Incident reporting is a critical component of [Your Company Name]'s health and safety management system, enabling the prompt identification, investigation, and resolution of workplace incidents. Key aspects of our incident reporting process include:
Immediate reporting: Employees are required to report incidents as soon as possible after they occur to ensure prompt response and investigation.
Incident classification: Incidents are classified based on their severity and potential impact on health and safety. This may include categorizing incidents as minor, moderate, or serious, or using other classification systems to prioritize response and investigation efforts.
Investigation and analysis: Following the reporting of an incident, an investigation is conducted to determine the root causes and contributing factors. This may involve interviewing witnesses, examining the scene of the incident, reviewing relevant documentation, and analyzing data to identify underlying causes.
Corrective actions: Based on the findings of the investigation, corrective actions are implemented to address the root causes of the incident and prevent recurrence.
Documentation and recordkeeping: Details of all incidents, including incident reports, investigation findings, and corrective actions, are documented and retained in accordance with regulatory requirements and internal procedures.
B. Emergency Response
In addition to incident reporting and investigation, [Your Company Name] has procedures in place for responding to emergencies and providing assistance to employees in need. Key aspects of our emergency response procedures include:
Emergency preparedness: [Your Company Name] conducts emergency preparedness activities to ensure employees are familiar with emergency procedures and know how to respond effectively in emergency situations.
Emergency communication: [Your Company Name] has systems in place for communicating with employees during emergencies and providing timely updates and instructions.
Emergency evacuation: [Your Company Name] has procedures in place for evacuating employees from the workplace in the event of an emergency.
Emergency medical care: [Your Company Name] has procedures in place for providing emergency medical care to employees who are injured or become ill during an emergency.
IX. Safety Training Records
A. Documentation
Accurate and comprehensive safety training records are maintained at [Your Company Name] to ensure that employees receive the necessary training to perform their jobs safely and effectively. Key aspects of our safety training records management include:
Training tracking system: [Your Company Name] utilizes a centralized training tracking system to record and manage employee training records.
Employee profiles: Each employee has a training profile within the training tracking system, which contains information about their training history, certifications, and competencies.
Training records documentation: Documentation of training records includes details such as the date of training, training topic, training provider, duration of training, and trainer credentials.
Record retention: Training records are retained for a specified period in accordance with regulatory requirements and internal policies. Records may be retained electronically or in hard copy format, depending on the preference of [Your Company Name] and any applicable legal requirements.
B. Compliance
Maintaining compliance with training requirements is essential to ensure that employees have the knowledge and skills necessary to perform their job tasks safely. Key aspects of our training compliance management include:
Training needs analysis: [Your Company Name] conducts periodic assessments to identify training needs and ensure that employees receive the training necessary to perform their job tasks safely and effectively.
Training scheduling: [Your Company Name] schedules training sessions based on employee job roles, job responsibilities, and training requirements.
Training effectiveness evaluation: [Your Company Name] evaluates the effectiveness of training programs through assessments, evaluations, and feedback from participants.
Corrective actions: [Your Company Name] takes corrective actions to address any deficiencies or non-compliance identified during training reviews or audits.
X. Safety Performance Metrics
A. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Monitoring safety performance through key performance indicators (KPIs) is essential for evaluating the effectiveness of [Your Company Name]'s health and safety management system and identifying areas for improvement. Key safety performance indicators include:
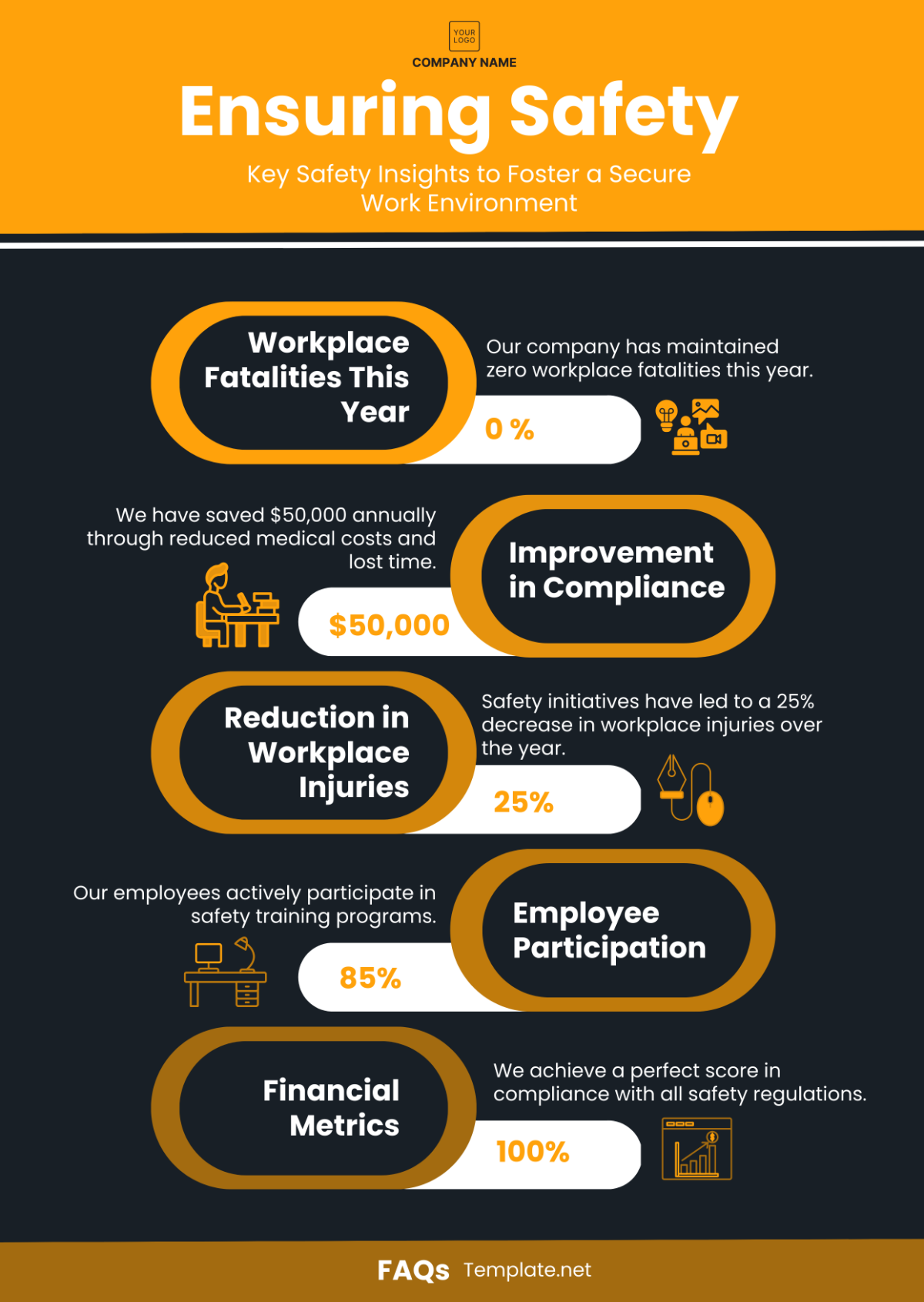
Incident rate: The incident rate measures the number of workplace incidents, including accidents, injuries, illnesses, and near misses, per [insert unit of measurement] hours worked.
Lost time injury frequency rate (LTIFR): The LTIFR measures the number of lost time injuries per [insert unit of measurement] hours worked. Lost time injuries are injuries that result in time lost from work beyond the day of the injury.
Near miss reporting rate: The near miss reporting rate measures the number of near misses reported by employees per [insert unit of measurement] hours worked. Near misses are incidents that could have resulted in injury or damage but did not.
Safety training completion rate: The safety training completion rate measures the percentage of employees who have completed required safety training within a specified time period.
Safety inspection findings closure rate: The safety inspection findings closure rate measures the percentage of identified hazards or deficiencies that have been addressed and resolved following safety inspections. A higher closure rate indicates more effective hazard control and a safer work environment.
B. Data Collection and Analysis
Data on safety performance metrics are collected regularly from various sources, including incident reports, training records, safety inspections, and audits. Data are analyzed to identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement in [Your Company Name]'s health and safety performance. Key aspects of safety performance data collection and analysis include:
Data collection methods: Data on safety performance metrics are collected using standardized data collection methods and tools, ensuring consistency and reliability of data.
Data analysis techniques: Data are analyzed using statistical techniques and tools to identify trends, patterns, and correlations in safety performance metrics.
Performance reporting: Safety performance data are reported regularly to management and other stakeholders through safety performance reports and dashboards.
Continuous improvement: [Your Company Name] uses safety performance data to drive continuous improvement in its health and safety management system.