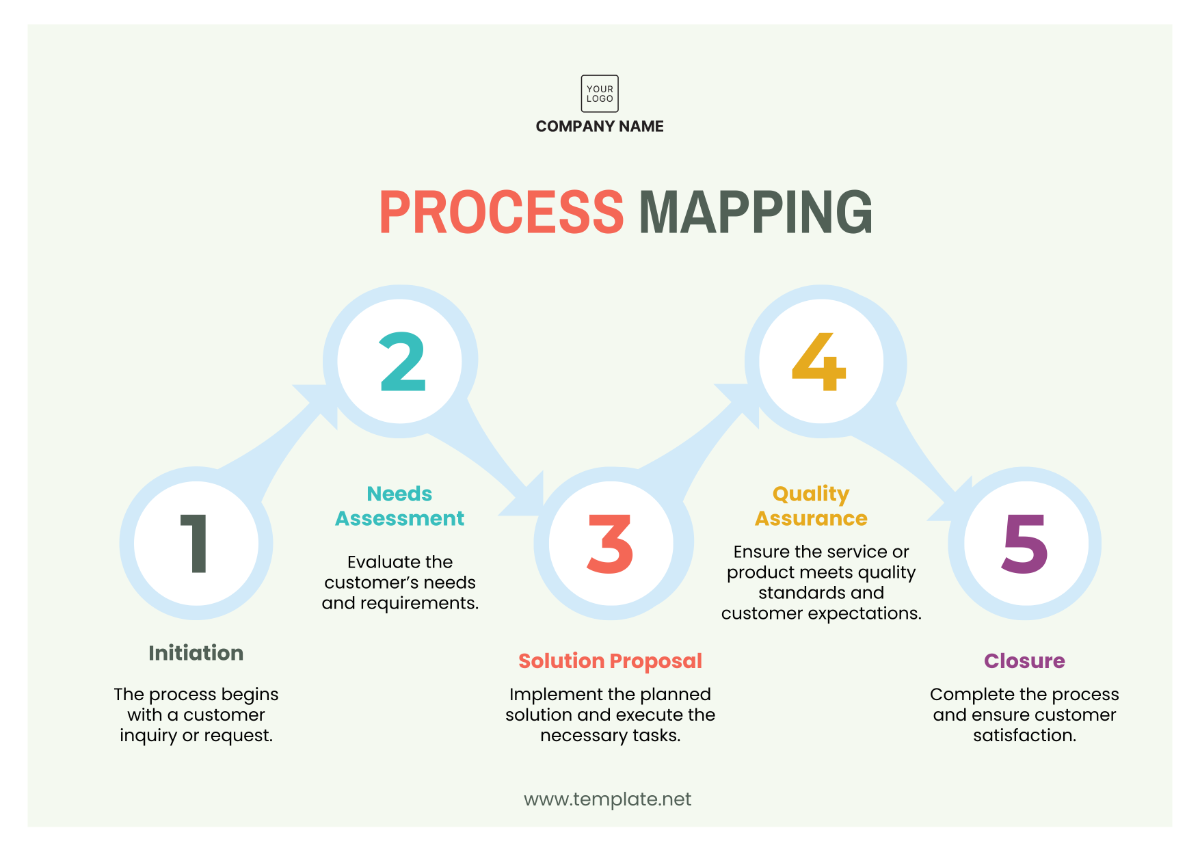
Operations Enterprise Risk Management Strategy Guide
Introduction
Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) refers to a comprehensive and integrated framework businesses implement to manage risks and seize potential opportunities. The objective is enhancing the organizational value. This guide will provide valuable insights into Operations ERM and outline strategic approaches suitable for [Your Company Name].
Implementing the ERM Framework
This phase will focus concretely on implementing the designed ERM framework in the organization. Our attention will revolve around:
Area | Focus Points |
|---|---|
Workflows | Streamlining risk-assessment workflows |
Policies | Documenting new risk management policies |
Monitoring | Setting up risk performance indicators |
Training | Training staff and stakeholders |
Communication | Implementing internal and external risk reporting |
Risk Governance
Effective risk governance is the foundation upon which a resilient and responsive enterprise risk management (ERM) framework is built. It ensures that risk management is not just a procedural formality but a strategic imperative that permeates the organizational culture. Our risk governance structure is designed to provide clear direction, accountability, and oversight over the entire ERM process.
ERM Steering Committee
The ERM Steering Committee is the apex body that provides strategic leadership for our ERM initiatives. Comprising senior executives from across various functions, the committee brings a wealth of experience and a holistic view of the organization's risk profile. The committee's responsibilities include:
Setting the risk appetite and tolerance levels that align with our strategic objectives and corporate values.
Approving and periodically reviewing the ERM framework to ensure it remains relevant and effective in the face of changing business dynamics and risk landscapes.
Ensuring that risk management practices are integrated into strategic planning and decision-making processes.
The ERM Steering Committee meets quarterly, or more frequently as needed, to review the organization's risk profile, the effectiveness of risk management strategies, and the status of significant risk mitigation actions.
Risk Management Office (RMO)
The Risk Management Office acts as the central hub for all ERM activities, coordinating efforts across the company to ensure a unified approach to managing risk. The RMO is staffed by risk management professionals who possess a deep understanding of the various risks facing the organization and the best practices in risk management. Key functions of the RMO include:
Facilitating risk identification and assessment processes across all business units.
Developing and maintaining the organization's risk management policies, procedures, and tools.
Providing training and support to business units to build risk management capabilities.
Monitoring the implementation of risk mitigation strategies and the effectiveness of the ERM framework.
The RMO plays a crucial role in embedding a risk-aware culture within the organization, ensuring that risk management considerations are an integral part of all business activities and processes.
Business Unit Risk Champions
Business Unit Risk Champions are appointed within each business unit to act as the focal point for ERM activities within their respective areas. These champions are selected based on their understanding of the business unit's operations, their leadership qualities, and their ability to influence change. Their responsibilities include:
Liaising with the RMO to ensure the alignment of business unit risk management activities with the overall ERM framework.
Leading the risk identification and assessment efforts within the business unit, ensuring that all significant risks are captured and evaluated.
Facilitating the development and implementation of risk mitigation plans within the business unit.
Promoting risk awareness and a proactive risk management culture within the business unit.
By decentralizing the responsibility for risk management, we ensure that risk considerations are embedded in the day-to-day operations and decision-making processes at the business unit level.
Risk Identification
Risk identification is the first step in the ERM process, where potential risks that could affect the organization's ability to achieve its objectives are identified. Our approach to risk identification is multifaceted, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of the risk landscape.
Risk Workshops and Brainstorming Sessions
We conduct regular risk workshops and brainstorming sessions that bring together stakeholders from various levels and functions within the organization. These sessions are designed to leverage the collective knowledge and experience of participants to identify potential risks. Facilitators use structured exercises and techniques to stimulate discussion and ensure that all perspectives are considered.
Risk Surveys and Questionnaires
Risk surveys and questionnaires are distributed across the organization to engage a broader audience in the risk identification process. These tools are designed to capture insights from employees who may have visibility into risks not apparent at higher levels of the organization. The surveys are analyzed to identify trends, emerging risks, and areas requiring further investigation.
Industry Analysis
Staying informed about industry trends, challenges, and emerging risks is critical for anticipating external risks that could impact our operations. Our approach includes:
Regularly reviewing industry reports, market research, and benchmarking studies.
Participating in industry forums, conferences, and professional associations to gain insights into best practices and emerging risk management challenges.
Engaging with industry analysts and experts to deepen our understanding of the risk landscape.
Historical Incident Review
Learning from past incidents and near-misses is a valuable source of risk intelligence. We conduct thorough analyses of historical incidents to identify root causes, contributing factors, and lessons learned. This retrospective view helps us identify recurring risks and vulnerabilities and informs the development of more effective risk mitigation strategies.
Risk Assessment
Following the identification of risks, we conduct a comprehensive assessment to understand their potential impact on our objectives and the likelihood of their occurrence. This assessment informs our prioritization of risks and guides our resource allocation for risk mitigation.
Risk Rating and Prioritization
Each identified risk is subjected to a rigorous assessment process, where it is rated based on its potential impact on the organization's strategic objectives, financial performance, reputation, and compliance obligations. The likelihood of the risk occurring is also evaluated, considering factors such as historical data, industry trends, and the effectiveness of existing controls. This rating process helps us prioritize risks, focusing our attention and resources on those that pose the greatest threat to our objectives.
Risk Heat Maps
Risk heat maps are visual tools that we use to represent the results of our risk assessment process. By plotting risks on a matrix based on their impact and likelihood, we provide a clear and intuitive overview of the organization's risk profile. Heat maps help in communicating risk information to stakeholders, facilitating discussions around risk tolerance and mitigation priorities.
Scenario Analysis
Scenario analysis involves developing detailed scenarios for significant risks to understand their potential impact under various conditions. This process helps us:
Explore the range of possible outcomes for the most critical risks, enhancing our understanding of their potential implications.
Test the resilience of our strategies and plans against extreme but plausible scenarios.
Identify gaps in our preparedness and response capabilities, guiding the development of more robust risk mitigation and response plans.
Through scenario analysis, we gain insights into the dynamics of significant risks, enabling more informed decision-making and enhancing our overall risk resilience.
By systematically governing, identifying, and assessing risks, [Your Company Name] ensures that our ERM strategy is comprehensive, proactive, and integrated into the fabric of our operations, supporting our mission to achieve operational excellence and sustainable growth in an uncertain and rapidly changing environment.
Risk Mitigation
Our risk mitigation strategies are tailored to address the specific nature and severity of each identified risk, with options including:
Risk Avoidance: Changing business practices to remove the risk entirely.
Risk Reduction: Implementing controls or changes to processes to reduce the likelihood or impact of the risk.
Risk Transfer: Shifting the risk to a third party, such as through insurance or outsourcing.
Risk Acceptance: Deciding to accept the risk, often because the cost of mitigation exceeds the potential impact.
Each mitigation strategy is accompanied by an action plan, outlining the steps, resources, responsibilities, and timelines for implementation.
Risk Monitoring and Reporting
Continuous monitoring of the risk environment and the effectiveness of our risk management strategies is essential for the dynamic adjustment of our ERM practices. Our monitoring and reporting mechanism includes:
Key Risk Indicators (KRIs): Metrics designed to provide early warning signs of increasing risk exposure.
Regular Risk Reviews: Scheduled reviews of the risk management process and the status of risk mitigation efforts.
ERM Dashboard: A comprehensive reporting tool that provides a real-time overview of the risk status, KRIs, and the progress of mitigation plans to senior management and relevant stakeholders.
ERM Integration with Strategy and Operations
Integrating ERM into our strategic planning and operational processes ensures that risk management is a part of daily decision-making. This integration involves:
Strategic Planning: Incorporating risk assessments into strategic planning sessions to ensure that potential risks are considered in strategic decisions.
Project Management: Embedding risk management practices into project management methodologies to identify and mitigate risks throughout the project lifecycle.
Performance Management: Linking risk management outcomes to performance metrics and incentives to encourage risk-aware decision-making across the organization.
Training and Awareness
Building a risk-aware culture is vital for the success of our ERM strategy. We are committed to providing ongoing training and awareness programs for all employees, covering:
ERM Principles and Practices: Educating employees on the importance of ERM and their role in the risk management process.
Specific Risk Training: Targeted training sessions on managing key risks relevant to different business units or functions.
Learning from Incidents: Sharing lessons learned from risk events and near-misses to improve risk awareness and prevention.
Continuous Improvement
Our ERM strategy is subject to continuous improvement, driven by feedback from the ERM processes, audits, and reviews. We are committed to:
Regular ERM Program Reviews: Assessing the effectiveness of the ERM framework and making necessary adjustments.
Stakeholder Feedback: Soliciting feedback from internal and external stakeholders to improve risk management practices.
Benchmarking and Best Practices: Comparing our ERM practices with industry standards and adopting best practices for continuous improvement.
Conclusion
The Operations Enterprise Risk Management Strategy Guide for [Your Company Name] represents our holistic approach to managing risks in a complex and dynamic business environment. By embedding ERM into our culture and operations, we enhance our resilience, protect our assets, and secure our competitive advantage. Through continuous monitoring, review, and improvement of our ERM practices, we are committed to achieving operational excellence and sustainable growth.