Free Law Brief

Prepared by: [YOUR NAME]
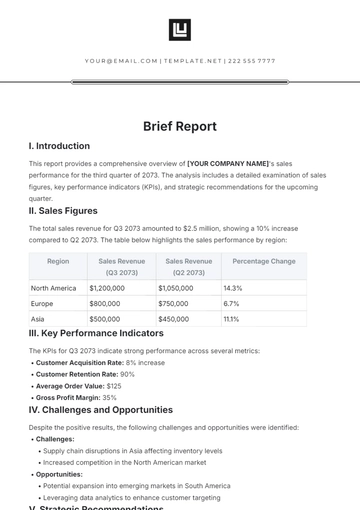
Company: [Your Company Name]
Introduction
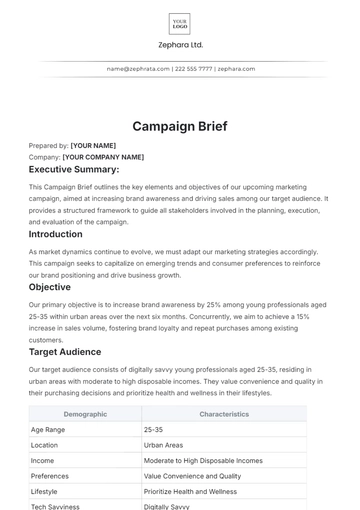
Intellectual property (IP) laws are a crucial component of legal frameworks worldwide, aimed at safeguarding the rights of creators, innovators, and inventors. These laws encompass a range of protections for intangible assets such as inventions, literary and artistic works, symbols, names, images, and designs. This brief provides an overview of the fundamental principles and key aspects of intellectual property laws, highlighting their significance in fostering innovation, creativity, and economic development.
Key Concepts and Principles
Types of Intellectual Property:
Patents: Grants exclusive rights to inventors of new and useful processes, machines, compositions of matter, or improvements thereof.
Copyrights: Protect original works of authorship fixed in any tangible medium of expression, including literary, artistic, musical, and dramatic works.
Trademarks: Protect distinctive signs, symbols, logos, or designs used to identify and distinguish goods or services in the marketplace.
Trade Secrets: Safeguard confidential information that provides a competitive advantage to a business and is not generally known to the public.
Duration and Scope of Protection:
Intellectual property rights vary in duration and scope depending on the type of protection.
Patents typically have a fixed term, whereas copyrights may last for the author's lifetime plus a certain number of years.
Trademarks can be renewed indefinitely as long as they are actively used in commerce.
Trade secrets are protected indefinitely as long as they remain confidential.
Enforcement Mechanisms:
Legal remedies for infringement of intellectual property rights include injunctive relief, damages, and in some cases, criminal prosecution.
Enforcement mechanisms vary across jurisdictions, with specialized intellectual property courts or tribunals in many countries.
International treaties such as the Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) provide a framework for harmonizing intellectual property laws globally.
Balancing Interests:
Intellectual property laws aim to strike a balance between protecting the rights of creators and innovators and promoting public access to knowledge and innovation.
Limitations and exceptions, such as fair use provisions in copyright law, allow for the use of copyrighted works for purposes such as education, criticism, and research.
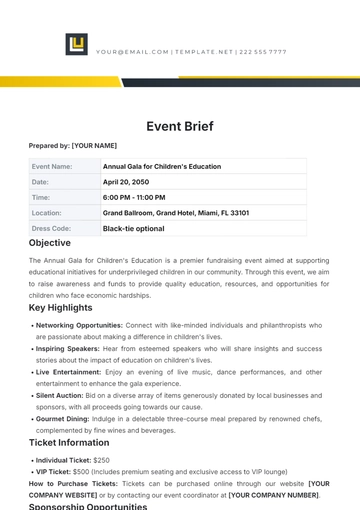
Significance and Impact
Intellectual property laws play a vital role in incentivizing innovation, creativity, and investment in research and development.
Strong intellectual property protections are associated with increased foreign direct investment, technology transfer, and economic growth.
Effective enforcement of intellectual property rights is essential for maintaining a level playing field in the marketplace and fostering fair competition.
Conclusion
Intellectual property laws serve as the cornerstone of innovation-driven economies, providing the legal framework necessary to protect and incentivize creativity, invention, and entrepreneurship. By safeguarding the rights of creators and innovators while promoting the dissemination of knowledge and ideas, these laws contribute to sustainable economic development and societal progress on a global scale.
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
Introducing the Law Brief Template by Template.net – your go-to solution for legal professionals. Crafted for clarity and efficiency, this editable and customizable template streamlines brief creation. Seamlessly edit in our Ai Editor Tool for precision and professionalism. Elevate your legal practice with a tool designed to simplify your workflow and enhance your presentations.