Free Pre-construction Meeting Brief

Prepared by: [YOUR NAME]
Company: [YOUR COMPANY NAME]
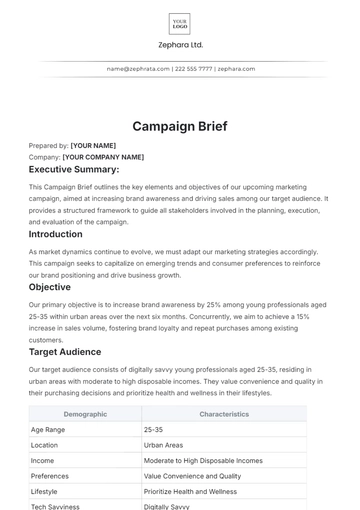
Executive Summary
The Pre-Construction Meeting Brief serves as a comprehensive document outlining key details and agenda items for an essential meeting before the commencement of a construction project. It aims to ensure alignment among all stakeholders regarding project requirements, timelines, responsibilities, and safety protocols.
Introduction
This document has been prepared to facilitate a thorough understanding of the project's scope, objectives, timelines, and expectations among all project team members. Each stakeholder must be well-informed and aligned before construction activities commence.
Project Scope and Objective
The objective of the [Project Name] is to revitalize the commercial district of Main Street downtown, enhancing its aesthetic appeal, infrastructure, and functionality. The scope of work encompasses:
Sidewalk Replacement: Removal and replacement of deteriorating sidewalks with durable, visually appealing materials to improve pedestrian safety and accessibility.
Street Lighting Upgrade: Installation of modern, energy-efficient LED street lights along Main Street to enhance visibility and security during nighttime hours.
Landscaping and Beautification: Implementation of landscaping enhancements, including new trees, flower beds, and decorative elements, to create an inviting atmosphere for residents and visitors.
Utility Infrastructure Improvement: Upgrading underground utilities such as water mains and sewer lines to improve reliability and accommodate future growth in the area.
Public Amenities Installation: Addition of benches, trash receptacles, and bike racks to provide amenities for pedestrians and cyclists, enhancing the overall experience on Main Street.
Facade Rehabilitation: Facade improvements for commercial buildings along Main Street to restore architectural character and attract new businesses to the area.
Timelines and Schedule
The project timeline for [Project Name], outlined below, delineates key milestones and deadlines crucial for its successful completion:
Activity | Start Date | End Date |
|---|---|---|
Commencement Date | March 15, 2050 | |
Completion of Site Preparation | March 16, 2050 | |
Foundation Construction | March 17, 2050 | April 5, 2050 |
Structural Framing | April 6, 2050 | April 20, 2050 |
Exterior Finishing | April 21, 2050 | May 10, 2050 |
Interior Fit-Out | May 11, 2050 | May 30, 2050 |
Final Inspection and Handover | June 1, 2050 | June 5, 2050 |
Critical Phases and Activities:
Permit Acquisition: Ensuring all necessary permits are obtained before commencement.
Foundation Pouring: Critical for structural integrity, requiring meticulous planning and execution.
Roof Installation: Protecting the interior from weather elements, is a pivotal phase to maintain project momentum.
Utilities Installation: Ensuring seamless integration of electrical, plumbing, and HVAC systems.
Interior Finishing: Including flooring, painting, and fixture installation, culming in project aesthetics.
Final Inspection: Verifying compliance with regulations and client specifications before handover.
Expectations and Quality Standards
The quality standards for [Project Name] are defined as follows:
Materials: All materials used in the construction process must meet industry standards and specifications. Any deviations from approved materials require prior approval from the project manager or designated authority.
Workmanship: Workmanship must be of the highest quality, ensuring precision, accuracy, and attention to detail in all construction activities. Craftsmanship should reflect a commitment to excellence and professionalism.
Compliance: Compliance with relevant building codes, regulations, and standards is mandatory. All construction work must meet or exceed legal requirements and adhere to local, state, and federal regulations.
Durability: Structures and components must be designed and constructed to withstand environmental conditions, wear and tear, and anticipated usage over the project's lifespan. Durability is paramount to ensuring the longevity and sustainability of the built environment.
Safety: Safety considerations are integral to quality standards. All construction activities must prioritize the safety of workers, occupants, and the public. Adherence to safety protocols, procedures, and best practices is non-negotiable.
Aesthetics: The visual appeal of the finished project is an essential aspect of quality. Attention should be paid to architectural aesthetics, finishes, and overall design coherence to achieve the desired aesthetic objectives.
Functionality: The functionality of the completed project is critical. Structures, systems, and components must perform their intended functions efficiently and reliably to meet user needs and expectations.
Documentation and Records: Accurate and comprehensive documentation of construction activities, inspections, and approvals is essential. Detailed records ensure accountability, and traceability, and facilitate future maintenance and renovations.
Safety Protocols and Procedures
Safety is paramount on [Project Name], and adherence to the following protocols and procedures is mandatory for all team members:
Site-Specific Hazards and Corresponding Safety Measures:
Electrical Hazards: Identify areas with exposed wires or electrical equipment. All electrical work must be performed by licensed electricians only.
Fall Hazards: Highlight areas with unprotected edges, elevated platforms, or roof edges. Implement fall protection measures such as guardrails, safety nets, or personal fall arrest systems (PFAS).
Heavy Machinery: Mark zones with heavy equipment movement. Establish clear pedestrian walkways and ensure all operators are trained and qualified to operate machinery.
Chemical Exposure: Identify areas where hazardous chemicals are stored or used. Provide Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) for all chemicals, and ensure proper ventilation and PPE are used during handling.
Confined Spaces: Identify confined spaces such as tanks, pits, or tunnels. Implement a confined space entry permit system and ensure adequate ventilation and rescue procedures are in place.
Emergency Procedures and Evacuation Routes:
Fire Emergencies: In the event of a fire, activate the nearest fire alarm pull station and evacuate the area immediately. Follow designated evacuation routes and assemble at the designated muster point.
Medical Emergencies: In case of injury or medical emergency, contact emergency services immediately. Administer first aid if trained to do so, and ensure the injured person receives medical attention promptly.
Natural Disasters: In the event of earthquakes, storms, or other natural disasters, seek shelter in designated safe areas or evacuate the site as directed by project supervisors.
Site-Specific Procedures: Familiarize yourself with site-specific emergency procedures outlined in the Emergency Response Plan (ERP) posted at various locations on the site.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Requirements:
Hard Hats: Hard hats must be worn at all times on-site, especially in areas where there is a risk of falling objects or overhead hazards.
Safety Glasses: Safety glasses or goggles are mandatory in areas where there is a risk of eye injury from flying debris or hazardous substances.
High-Visibility Apparel: Wear high-visibility vests or clothing in areas with moving vehicles or heavy machinery to ensure visibility to operators.
Respiratory Protection: Use respiratory protection such as dust masks or respirators in areas with airborne contaminants or hazardous fumes.
Hand Protection: Wear appropriate gloves when handling sharp objects, chemicals, or materials with rough edges to prevent cuts, abrasions, or chemical exposure.
Logistical Arrangements
Logistical arrangements for the execution of [Project Name] have been meticulously planned to ensure the smooth operation of construction activities. The following details outline the specific logistical arrangements:
Site Access Points and Restrictions:
Access Points: Entry to the construction site will be through [specific access points], which will be marked and monitored.
Restrictions: Certain areas of the site may be restricted to authorized personnel only. Access to these areas will be strictly controlled to ensure safety and security.
Procedures for Material Deliveries and Storage:
Material Deliveries: All material deliveries must be scheduled in advance and coordinated with the project manager. Deliveries will be directed to designated areas to minimize disruption to ongoing construction activities.
Storage Procedures: Materials will be stored in designated storage areas, ensuring easy access for construction teams while maintaining safety standards and minimizing obstruction on the site.
Temporary Facilities:
On-Site Offices: Temporary office facilities will be set up to accommodate project management staff, contractors, and other personnel requiring office space. These offices will be equipped with the necessary amenities to support administrative functions.
Restrooms and Break Areas: Temporary restroom facilities and break areas will be provided for the convenience and comfort of on-site workers, located in convenient and accessible locations within the project site.
Roles and Responsibilities
Each stakeholder involved in [Project Name] plays a crucial role in ensuring the successful execution of the project. Clear delineation of roles and responsibilities is essential to maintain accountability and facilitate effective communication throughout the project lifecycle.
Client:
Define project requirements, objectives, and desired outcomes.
Provide necessary approvals and permits.
Allocate financial resources as per the agreed budget.
Review and approve project deliverables and changes.
Communicate regularly with the project management team to stay informed about project progress.
General Contractor:
Oversee the overall construction process and ensure compliance with project specifications and quality standards.
Coordinate with subcontractors, suppliers, and vendors to procure materials and services.
Manage construction personnel, including scheduling and supervision of work activities.
Implement safety protocols and procedures on-site to ensure a safe working environment.
Communicate regularly with the client and project management team to provide progress updates and address any concerns.
Subcontractors:
Perform specific tasks or trades as outlined in the subcontract agreement.
Adhere to project schedules and quality standards set by the general contractor.
Coordinate with other subcontractors and the general contractor to ensure seamless integration of work.
Comply with safety regulations and procedures while carrying out construction activities.
Report progress and any issues encountered to the general contractor promptly.
Project Manager:
Serve as the primary point of contact between the client and the project team.
Develop and maintain the project schedule, ensuring timely completion of tasks and milestones.
Coordinate project resources, including personnel, equipment, and materials.
Monitor project progress and identify any deviations from the plan, implementing corrective actions as necessary.
Facilitate communication among stakeholders and ensure alignment on project objectives and expectations.
Design Team:
Develop project designs and construction documents by client requirements and building codes.
Provide technical expertise and guidance throughout the design and construction phases.
Address any design-related issues or changes that may arise during construction.
Coordinate with the general contractor and subcontractors to resolve design conflicts and ensure constructability.
Quality Control/Assurance Team:
Implement quality control procedures to ensure that construction activities meet specified standards and requirements.
Conduct inspections and testing to verify the quality of workmanship and materials.
Document and track any non-conformities or deficiencies, and work with the project team to address them promptly.
Provide training and guidance to construction personnel on quality standards and best practices.
Reporting Lines and Communication Channels:
The project manager serves as the central point of contact for all communication related to the project.
Regular progress meetings will be held, with attendance required from key stakeholders, including the client, general contractor, subcontractors, and relevant project team members.
Any issues or concerns should be reported to the project manager immediately for resolution.
Communication channels may include email, phone calls, virtual meetings, and on-site discussions, depending on the nature and urgency of the communication.
Risk Management
Risk management is a critical aspect of ensuring the successful execution of [Project Name]. The following strategies have been developed to address potential risks:
Identification of Potential Risks and Likelihood:
Our risk assessment process has identified several potential risks that may impact the project, including but not limited to:
Delays in material delivery due to supply chain disruptions.
Adverse weather conditions affecting construction activities.
Changes in regulatory requirements impacting project scope or timeline.
Unforeseen ground conditions lead to construction complications.
Each identified risk has been evaluated for its likelihood of occurrence, allowing us to prioritize our mitigation efforts effectively.
Mitigation Measures to Minimize Risks:
To address these potential risks, the following mitigation measures have been established:
Maintaining open communication with suppliers to anticipate and address any potential delays in material delivery.
Implementing flexible scheduling and contingency plans to accommodate adverse weather conditions.
Regularly monitoring regulatory updates and promptly adjusting project plans as necessary.
Conducting thorough site investigations and utilizing appropriate construction techniques to mitigate the impact of unforeseen ground conditions.
By proactively implementing these measures, we aim to minimize the likelihood and impact of potential risks on the project timeline and budget.
Assignment of Responsibility for Risk Management Tasks:
Responsibility for overseeing risk management tasks has been assigned as follows:
Project Manager: Overall responsibility for coordinating risk management efforts and ensuring that mitigation measures are implemented effectively.
Site Supervisor: Monitoring on-site conditions and promptly addressing any emerging risks or issues.
Procurement Team: Ensuring timely procurement of materials and equipment to minimize the risk of delays.
Regulatory Compliance Officer: Keeping abreast of changes in regulations and ensuring that the project remains in compliance throughout its duration.
Each team member is tasked with actively identifying, assessing, and addressing risks within their area of responsibility to contribute to the overall success of the project.
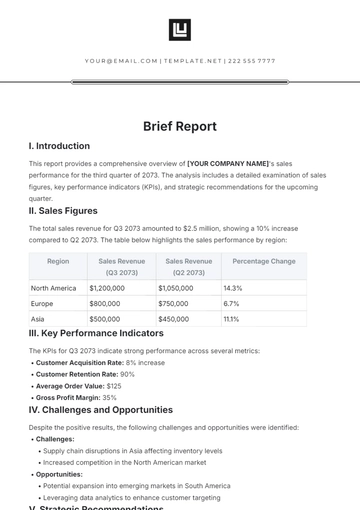
Budget and Cost Management
The budget for [Project Name] is as follows:
Total Budget: $5,000,000
Allocation for Major Expenses:
Materials: $1,500,000
Labor: $2,000,000
Equipment: $500,000
Procedures for monitoring and controlling costs:
Regular Cost Tracking: Utilize software tools or spreadsheets to track expenses against the budget consistently.
Expense Approval Process: Establish a clear process for approving expenditures to align with the budget.
Change Order Management: Evaluate changes to the scope of work for cost implications and obtain approval before implementation.
Cost Reporting: Generate regular reports highlighting budget deviations and areas for cost-saving measures.
Vendor and Subcontractor Management: Monitor costs associated with vendors and subcontractors to stay within budget.
Risk Management: Identify potential cost risks and implement strategies to mitigate them.
Continuous Improvement: Review and optimize cost management processes for efficiency gains and savings.
Resolving Outstanding Issues
Before the commencement of construction activities, it is imperative to address any outstanding issues or concerns promptly to mitigate risks of delays and disruptions to the project timeline. The following steps should be taken to effectively resolve outstanding issues:
Identification of Issues: Ensure that all stakeholders are aware of any outstanding issues or concerns that have been raised during the planning stages of the project. This may include discrepancies in project plans, unresolved contractual matters, or unclarified requirements.
Gather Relevant Information: Collect all necessary information related to the outstanding issues, including documentation, correspondence, and any relevant background context. This will aid in understanding the root cause of the issues and formulating appropriate solutions.
Convene Stakeholder Discussions: Facilitate discussions among relevant stakeholders, including project managers, contractors, subcontractors, and clients, to address the outstanding issues collaboratively. Encourage open communication and active participation to ensure all perspectives are considered.
Brainstorm Solutions: Engage stakeholders in brainstorming sessions to generate potential solutions to the identified issues. Encourage creative thinking and exploration of alternative approaches to find the most suitable resolution.
Evaluate Impact and Feasibility: Assess the potential impact of each proposed solution on project timelines, budgets, and quality standards. Evaluate the feasibility of implementing the solutions within the project constraints and consider any associated risks.
Decision-Making Process: Facilitate a decision-making process to select the most viable solution for each outstanding issue. Ensure that decisions are based on consensus among stakeholders and are aligned with the project objectives.
Implement Action Plans: Develop detailed action plans outlining the steps required to implement the chosen solutions. Assign responsibilities to relevant individuals or teams and establish clear timelines for completion.
Monitor Progress: Regularly monitor the progress of implementing the action plans to address outstanding issues. Keep stakeholders informed of any updates or changes and be prepared to adjust strategies as necessary.
Document Resolutions: Maintain comprehensive documentation of the resolutions to outstanding issues, including the decisions made, action plans, and outcomes achieved. This documentation serves as a reference for future project activities and helps ensure accountability.
Follow-Up and Communication: Conduct follow-up meetings or discussions to verify that the outstanding issues have been effectively resolved and to address any lingering concerns. Communicate the resolution outcomes to all relevant stakeholders to maintain transparency and alignment.
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
Introducing the Pre-construction Meeting Brief Template by Template.net: your key to efficient project planning. This customizable and editable template simplifies pre-construction meetings, ensuring clarity and precision. With our Ai Editor Tool, effortlessly tailor every detail to meet your requirements. Streamline your pre-construction processes with ease and confidence. Get started today and elevate your project planning with Template.net.