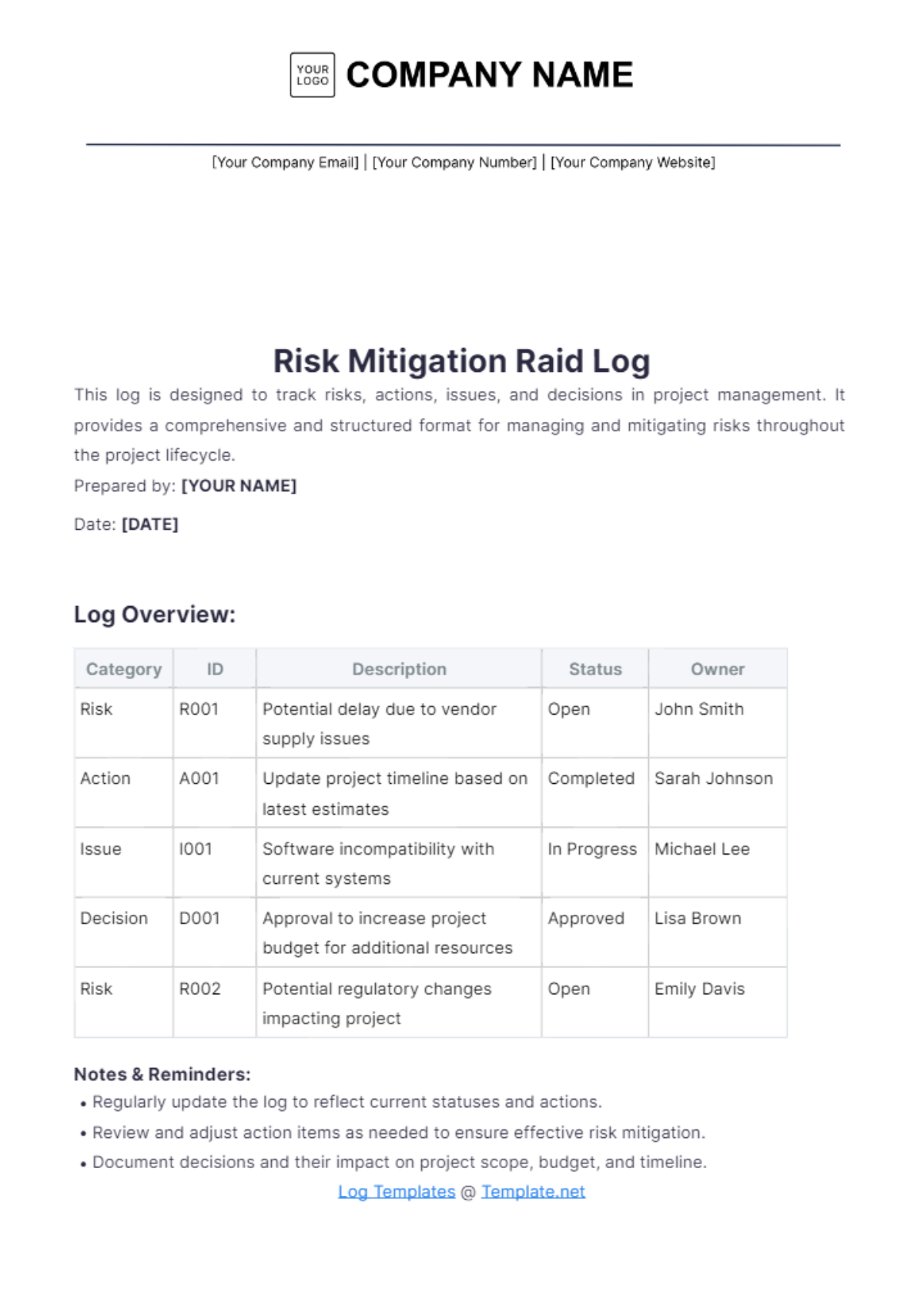
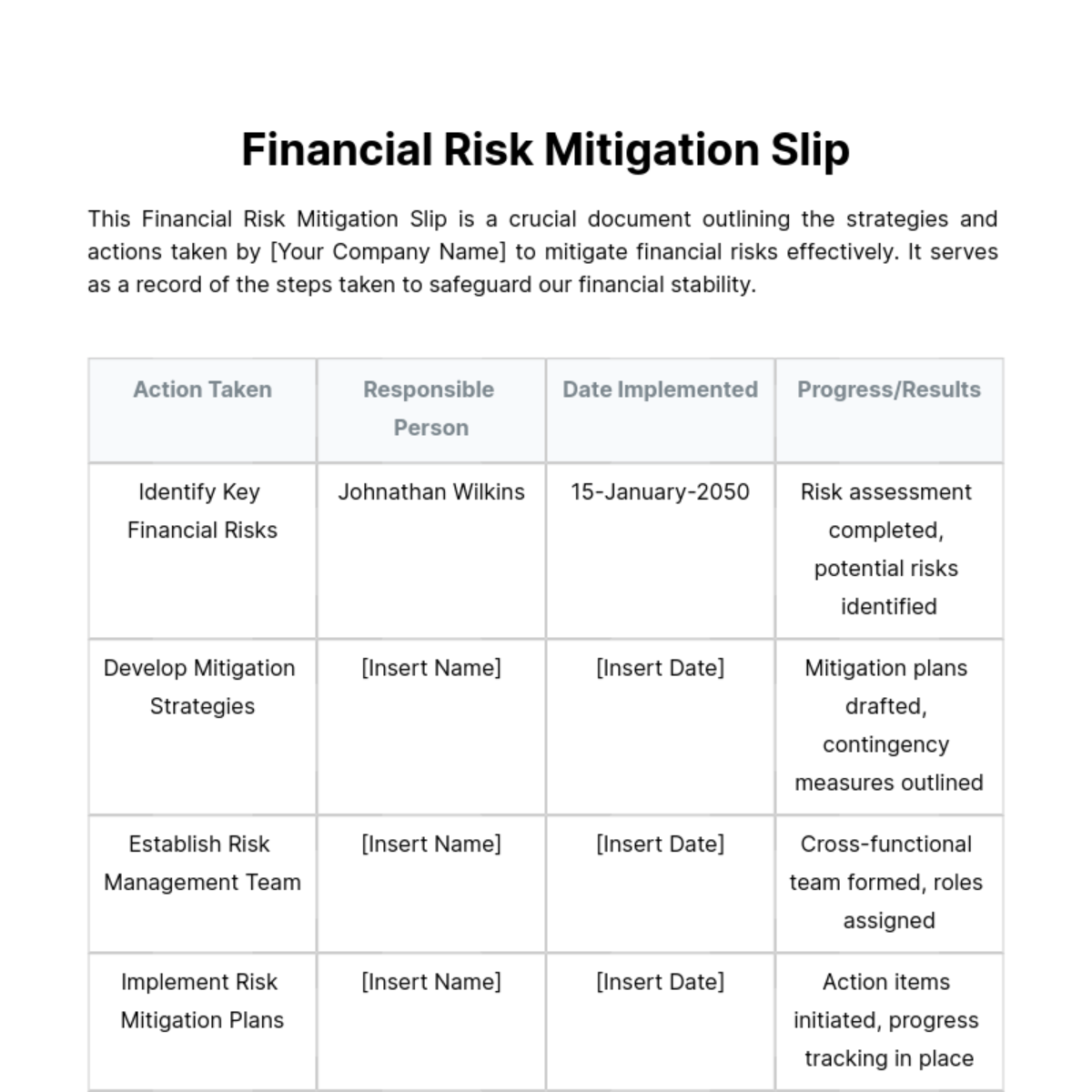
Hazard Mitigation Strategy
I. Executive Summary
Our strategy focuses on identifying and mitigating hazards to ensure the safety of our employees and the public. This plan outlines a comprehensive approach to assess risks, establish goals, implement strategies, and regularly evaluate progress. By prioritizing hazard mitigation, we aim to safeguard lives, property, and the environment while complying with all relevant regulations and legal requirements.
II. Introduction
This Hazard Mitigation Strategy underscores our commitment to disaster resilience, ensuring that we meet or exceed all health and safety requirements. Our approach is founded on rigorous hazard assessments, vulnerability analyses, and comprehensive risk evaluations. By adhering to these principles, we aim to not only mitigate risks but also strengthen our overall preparedness. This document outlines our proactive steps to minimize vulnerabilities and enhance the safety and well-being of all stakeholders involved.
III. Hazard Assessment
In this section, we conduct a comprehensive Hazard Assessment to identify potential threats and risks that could impact our operations, employees, and the community. Our diligent approach to hazard assessment is in full compliance with the health and safety standards. The following is a list of five key hazards that have been identified as particularly relevant to our organization:
Natural Disasters: These include earthquakes, hurricanes, floods, and wildfires. We assess the likelihood and potential impacts of these events on our facilities and personnel.
Chemical Hazards: We identify and evaluate potential chemical hazards present in our workplace, ensuring adherence to regulations like OSHA's Hazard Communication Standard.
Biological Hazards: This includes the assessment of biological agents that may pose health risks, such as pathogens or infectious diseases, particularly relevant in healthcare settings.
Physical Hazards: We assess physical hazards like machinery, equipment, and infrastructure vulnerabilities to prevent accidents and injuries.
Human Factors: This includes the evaluation of human-related hazards, such as ergonomic issues, training gaps, and fatigue management, which can affect workplace safety.
Through this comprehensive hazard assessment, we aim to create a safer working environment, protect the well-being of our employees, and meet the rigorous safety standards outlined by the law.
IV. Vulnerability Assessment
In this section, we conduct a thorough Vulnerability Assessment to evaluate our organization's susceptibility to the hazards identified earlier. This assessment aligns with health and safety standards and helps us identify areas that require mitigation measures. Here are five key aspects we consider during our vulnerability assessment:
Infrastructure Vulnerabilities: We examine the physical integrity of our buildings, machinery, and systems to assess their resilience against various hazards.
Operational Vulnerabilities: This involves evaluating the impact of disruptions on our day-to-day operations and identifying critical processes that may be vulnerable.
Human Resource Vulnerabilities: We assess the readiness and capacity of our workforce to respond to hazards, including their training and knowledge of safety procedures.
Community Vulnerabilities: Considering the potential effects on neighboring communities, we collaborate with local authorities to ensure our mitigation efforts align with community needs.
Supply Chain Vulnerabilities: We identify vulnerabilities in our supply chain, aiming to ensure the continuity of essential goods and services in the face of hazards.
V. Risk Assessment
In this section, we perform a comprehensive Risk Assessment to quantify the potential impact and likelihood of the hazards and vulnerabilities identified earlier.
Below is a table presenting five key risks, considering their impact and likelihood:
Hazard | Impact | Likelihood | Risk Level |
Natural Disasters | High | Moderate to High | Significant |
Chemical Hazards | Moderate to High | Low to Moderate | Moderate |
Biological Hazards | Moderate | Low to Moderate | Moderate |
Physical Hazards | Moderate | Low to Moderate | Moderate |
Human Factors | Moderate | Low | Low to Moderate |
VI. Goals and Objectives
In this section, we establish clear goals and objectives that guide our Hazard Mitigation Strategy. These goals and objectives serve as a roadmap for our mitigation efforts.
Goals | Objectives |
Our primary goal is to prioritize the safety and well-being of our employees. We aim to create a workplace that is resilient to hazards, reducing the risk of injuries and illnesses.
We are committed to safeguarding our facilities, equipment, and assets. Our goal is to minimize the impact of hazards on our operations, ensuring business continuity.
As a responsible corporate citizen, our goal is to contribute to the resilience of the communities we operate in. We will collaborate with local authorities and stakeholders to support community-wide hazard mitigation efforts. |
Develop and implement regular safety training programs to ensure that all employees are well-prepared to respond to hazards effectively.
Invest in infrastructure improvements and disaster-resistant building designs to reduce vulnerability to natural disasters and other hazards.
Establish community outreach programs to educate and collaborate with local residents and businesses on hazard mitigation, aligning with US law requirements. |
These goals and objectives provide a clear framework for our hazard mitigation efforts, guiding our actions to minimize risks and enhance safety, while also ensuring compliance with the health and safety standards.
VII. Mitigation Strategies
In this section, we outline our Hazard Mitigation Strategies to address the identified hazards and vulnerabilities effectively. These strategies are presented in the table below, providing a clear and organized overview of our mitigation measures.
Hazard | Mitigation Strategies |
Natural Disasters | Develop and implement an emergency response plan. |
Retrofit buildings to withstand seismic activity. | |
Establish off-site data backup and recovery systems. | |
Chemical Hazards | Conduct regular chemical risk assessments. |
Provide comprehensive training for chemical handling. | |
Maintain an up-to-date chemical inventory. | |
Biological Hazards | Implement strict hygiene and infection control measures. |
Develop a pandemic response plan. | |
Provide employee health monitoring and vaccination programs. | |
Physical Hazards | Regularly inspect and maintain machinery and equipment. |
Provide personal protective equipment (PPE) and enforce its use. | |
Conduct safety audits and address identified hazards promptly. | |
Establish clear safety signage and guidelines. | |
Human Factors | Develop and enforce fatigue management policies. |
Provide ongoing training and skills development. | |
Establish reporting mechanisms for near-miss incidents. |
VIII. Implementation Plan
In this section, we provide a comprehensive Implementation Plan that ensures the effective execution of our Hazard Mitigation Strategies while complying with US health and safety standards:
Strategic Goal Setting: Define clear, measurable objectives for hazard mitigation, tailored to address specific risks identified in the risk assessment phase. These goals should align with regulatory requirements and organizational safety policies.
Resource Allocation and Management: Allocate necessary resources, including financial, human, and technological, to support the implementation of mitigation strategies. This also involves assigning roles and responsibilities to team members, ensuring clear accountability.
Training and Capacity Building: Implement comprehensive training programs to equip staff with the necessary skills and knowledge for hazard mitigation. Regular drills and exercises should be conducted to reinforce learning and preparedness.
Technology Integration: Utilize advanced technologies for monitoring hazards, improving communication, and enhancing the overall efficiency of mitigation efforts. This could include the deployment of early warning systems, risk management software, and emergency response tools.
Regulatory Compliance: Ensure strict adherence to all relevant US health and safety regulations. Regularly update the plan to incorporate changes in legal requirements and industry best practices.
Continuous Monitoring and Evaluation: Establish a robust mechanism for the ongoing monitoring of the implementation process. Regular evaluations should be conducted to assess the effectiveness of the mitigation strategies and make necessary adjustments.
Emergency Response Coordination: Develop and maintain effective coordination with local emergency response teams and other relevant agencies. This ensures a unified and prompt response in the event of a hazard materializing.
Public Awareness and Education: Conduct public awareness campaigns and educational programs to inform and educate the community about hazard risks and mitigation measures. Community involvement is crucial for enhancing overall safety and resilience.
This Implementation Plan is a dynamic document, requiring periodic reviews and updates to reflect evolving risks and the continuous improvement of mitigation strategies. Its comprehensive nature guarantees that all aspects of hazard mitigation are meticulously addressed, aligning with the highest standards of health and safety.
IX. Monitoring and Evaluation
In this section, we detail our Monitoring and Evaluation framework, ensuring that our Hazard Mitigation Strategies remain effective. We employ a structured approach to assess progress and make informed decisions. The following list comprises five key elements of our Monitoring and Evaluation process:
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Define measurable KPIs for each mitigation strategy, allowing us to track progress and outcomes accurately.
Regular Audits and Inspections: Conduct routine audits and inspections to ensure that implemented measures align with our objectives and meet regulatory requirements.
Incident Reporting and Analysis: Establish a system for reporting and analyzing incidents or near-misses, enabling us to identify areas for improvement.
Stakeholder Feedback: Seek input and feedback from employees, partners, and the community to gauge the effectiveness and relevance of our hazard mitigation efforts.
Periodic Review and Adjustment: Regularly review our strategies, KPIs, and the overall Hazard Mitigation Strategy to make necessary adjustments based on evolving risks and changing circumstances.
Through diligent monitoring and evaluation, we aim to continuously enhance our hazard mitigation efforts, ensuring a safe environment for our employees and the community.
X. Public Outreach and Communication
Our Public Outreach and Communication strategy, emphasizing the importance of engaging with the public, clients, and partners. Effective communication is essential for building awareness and trust. The following list highlights five key components of our approach:
Community Engagement: Foster partnerships and open channels of communication with local communities to ensure they are informed about our hazard mitigation efforts.
Client Collaboration: Maintain regular communication with clients, sharing updates on safety measures and seeking feedback on their specific needs.
Transparency and Reporting: Provide transparent and timely reporting on hazard mitigation progress to all stakeholders, demonstrating our commitment to safety.
Training and Awareness Programs: Develop educational programs for employees, clients, and the public to raise awareness about potential hazards and safety protocols.
Crisis Communication Plan: Establish a crisis communication plan to effectively communicate in the event of an emergency or disaster, ensuring clear and accurate information dissemination.
Through these communication strategies, we aim to build strong relationships with stakeholders, enhance awareness of our hazard mitigation efforts.