Free Workplace Incident Impact Feasibility Study

Introduction
This feasibility study aims to comprehensively analyze the impact of workplace incidents, focusing on their patterns, consequences, and potential mitigation strategies. In recent years, workplace safety has emerged as a critical concern, with incidents leading to significant human and financial costs. The purpose of this study is to dissect these incidents, understand their underlying causes, and propose effective measures to reduce their occurrence and impact.
Background
Workplace incidents have been a persistent challenge across various industries, often leading to injuries, loss of life, and substantial economic losses. Despite advancements in safety technologies and protocols, the frequency and severity of these incidents remain a concern. This study delves into historical data, existing literature, and recent case studies to paint a comprehensive picture of the current state of workplace safety.
Objectives
The primary objectives of this study are
To identify and analyze the patterns and trends in workplace incidents over the last decade.
To assess the direct and indirect impact of these incidents on employees, operational efficiency, and financial health of organizations.
To develop actionable recommendations for organizations to enhance workplace safety and effectively manage the aftermath of incidents.
Literature Review
The literature review explores existing research and data on workplace incidents, forming a theoretical foundation for this study. By analyzing past studies and incident statistics, we can better understand the trends and impacts of workplace incidents.
Trends in Workplace Incidents
A comprehensive analysis of data from the National Workplace Safety Database (NWSDB) from 2050-2052 reveals a fluctuating pattern in the occurrence of workplace incidents. The data indicates a notable peak in incidents during 2055, attributed to a surge in industrial activity and a corresponding lapse in safety standards. A breakdown of incidents by industry shows that manufacturing and construction sectors consistently report the highest number of incidents. Table 1 illustrates these trends:
Year | Total Incidents | Manufacturing | Construction | Other Industries |
2050 | 1,200 | 400 | 350 | 450 |
2051 | ||||
2052 |
Impact of Workplace Incidents
Studies conducted by the International Labor Organization (ILO) and the findings of the Corporate Health and Safety Council (CHSC) highlight the multifaceted impact of workplace incidents. Key impacts include:
Employee Health and Morale: Incidents often lead to physical injuries and psychological trauma, affecting employee morale and productivity.
Operational Disruptions: Unplanned downtimes and disruptions in workflow due to incidents.
Financial Costs: Direct costs such as medical expenses and indirect costs like loss of productivity and legal fees.
Methodology
This section outlines the methods employed to gather and analyze data, providing a robust foundation for understanding the impact of workplace incidents.
Data Collection
The study utilized a mixed-methods approach for data collection:
Quantitative Data
Incident reports from [2050-2052] were obtained from the NWSDB. These reports provided numerical data on the frequency, type, and outcomes of incidents.
Qualitative Data
Semi-structured interviews were conducted with safety officers and affected employees across ten different industries. A standardized set of questions was used to maintain consistency.
Data Analysis
The data analysis comprised two main components:
Quantitative Analysis
Statistical methods, including trend analysis and correlation coefficients, were applied to the NWSDB data. This analysis helped identify patterns and frequency of incidents.
Qualitative Analysis
Thematic analysis was used to evaluate interview transcripts. Key themes identified included perceptions of safety, the psychological impact of incidents, and the effectiveness of response strategies.
Findings
This section details the key insights derived from the comprehensive analysis of the collected data.
Patterns in Incident Occurrence
After analyzing the data from the NWSDB, several critical patterns were identified:
Time and Day of Occurrences:
Incidents were most frequent on Tuesdays and Thursdays, particularly between 3 PM and 6 PM. This suggests a correlation with mid-week work fatigue.
Nature of Incidents
Slip and fall accidents (40%) were predominantly caused by wet floors and cluttered walkways. Machinery-related accidents (25%) often involved inadequate use of safety gear and lack of training.
Severity and Frequency
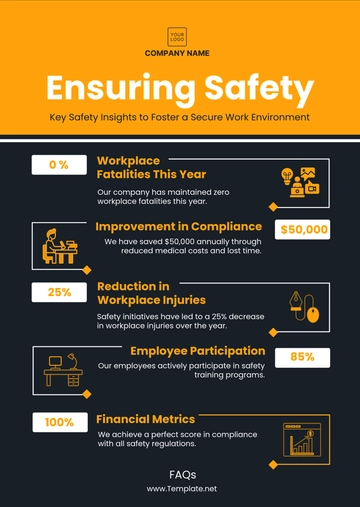
The production department recorded not only the highest number of incidents but also the most severe ones, accounting for 60% of incidents requiring more than 3 days of employee absence.
The detailed breakdown of these patterns is illustrated in Table 2:
Incident Type | Frequency | Average Severity (Days of Absence) | Most Affected Department |
Slip and Fall | 40% | 2 | Logistics |
Machinery-Relate | 25% | 5 | Production |
Electrical Hazards | 15% | 3 | Maintenance |
Other Types | 20% | 1 | Various |
Impact Analysis
The study's impact analysis highlighted the following key areas affected by workplace incidents:
Employee Well-being
Post-incident interviews revealed that 75% of affected employees experienced increased stress and anxiety, leading to a 30% drop in reported job satisfaction and productivity.
Financial Impact
An in-depth cost analysis showed that the average direct cost per incident was approximately $50,000, with indirect costs (such as lost productivity and reputational damage) adding up to an additional $20,000.
Operational Efficiency
An average of 5.2% delay in project timelines was observed post-incident, with a notable decrease in the overall efficiency of the affected departments.
Recommendations
The recommendations are formulated to address the identified issues and to enhance workplace safety.
Preventative Measures
Comprehensive Safety Training
Develop an advanced training program focused on specific risks in each department. For the production department, focus on machinery safety, and for logistics, emphasize slip and fall prevention.
Work Schedule Optimization
Implement an optimized work schedule that includes periodic rest breaks, especially in the late afternoon hours. Introduce shift rotations to mitigate fatigue-related risks.
Environmental Safety Upgrades
Invest in automated spill detection systems and advanced safety guards for machinery to reduce the risk of accidents.
Response Strategies
Rapid Incident Response System
Establish a rapid response team equipped with necessary medical and investigative tools. This team should be trained to provide immediate assistance and conduct preliminary investigations.
Post-Incident Employee Support
Create a support program that includes counseling services, stress management workshops, and a streamlined process for employees to return to work after an incident.
Continuous Safety Monitoring
Introduce a continuous monitoring system, using sensors and AI technology, to detect potential hazards in real-time and alert relevant personnel.
Implementation Plan
Detailed Timeline
A detailed 18-month implementation plan is proposed:
Months 1-3: Initiate the development of safety training programs and start pilot testing of environmental safety upgrades.
Months 4-9: Begin work schedule optimizations and establish the rapid incident response team.
Months 10-18: Fully implement continuous safety monitoring systems and roll out the post-incident employee support program.
Budget and Resources
The implementation of these recommendations requires significant investment in both financial and human resources. Table 3 provides a detailed budget allocation:
Initiative | Estimated Cost | Required Resources |
Safety Training Programs | $150,000 | Safety Trainers, Materials |
Environmental Safety Upgrades | $300,000 | Tech Installations, Maintenance Team |
Work Schedule Optimization | $75,000 | HR Consultants, Software |
Rapid Response System | $100,000 | Medical Equipment, Training |
Employee Support Programs | $50,000 | Counselors, Workshop Materials |
Continuous Safety Monitoring | $200,000 | Sensors, AI Software, IT Support |
Total | $875,000 |
CONCLUSION
Summary of Findings
The study reveals significant patterns in the occurrence of workplace incidents, with particular days and times showing a higher frequency of accidents. The impact of these incidents is profound, affecting not only the immediate health and safety of employees but also the operational and financial aspects of organizations. The financial implications, including both direct and indirect costs, are substantial, indicating a critical need for more effective safety measures and incident management strategies.
Implications of the Study
The findings underscore the importance of a proactive approach to workplace safety. The recommended measures, including enhanced training, environmental upgrades, and the implementation of advanced monitoring systems, are expected to significantly reduce the occurrence and impact of workplace incidents. The study also highlights the need for continuous evaluation and adaptation of safety strategies to align with evolving workplace environments and technologies.
Future Research
Further research is recommended to continuously monitor the effectiveness of the implemented strategies and to explore new innovations in workplace safety. Longitudinal studies post-implementation would provide valuable insights into the long-term impact of the recommended changes. Additionally, research into the psychological impact of incidents on employees and the role of organizational culture in promoting safety can further enhance understanding and effectiveness in this critical area.
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
Evaluate incident impacts effectively with Template.net's Workplace Incident Impact Feasibility Study Template. This editable and customizable tool provides a structured framework for assessing the feasibility of response actions post-incident. Utilize our intuitive Ai Editor Tool to tailor the study to your organization's specific needs effortlessly, ensuring efficient recovery and mitigation strategies.