HVAC Validation Protocol
Department: | [Your Department] |
|---|---|
Date: | [Date] |
I. Objectives
The main objective of this HVAC validation protocol is to ensure the HVAC system's robustness, efficiency, and safety. It is designed to validate [Your Company Name]'s HVAC system per the defined regulatory requirements and industry standards. The secondary objectives include checking the system's adequacy, documenting evidence of its effective performance, and ensuring that [Your Name], the designated personnel, completes this process successfully and safely.
Furthermore, it aims to provide an understanding of the system and its interconnections, evaluate its performance, and report any discrepancies or deviations. Compliance with stringent regulations underpinning the HVAC system's usage, especially in critical environments, and proper data management are of the utmost importance.
II. Protocol Overview
The [Your Department]'s protocol overview seeks to present a succinct, comprehensive summary of our approach to the HVAC validation process. This involves a detailed examination of the system design, installation, operations, and maintenance within the facility.
Throughout this process, we will assess the system at various stages for compliance with predetermined guidelines. Using different methods and tools, we will determine the system's capacity to maintain optimum performance over time while identifying any potential areas of risk.
III. Procedure
In this section, we will outline the step-by-step process of validating our HVAC system. This process begins with a preliminary review, followed by an in-depth evaluation of various elements, testing, comparing results against benchmarks, and documenting our findings. Special emphasis must be placed on precautionary measures to ensure the validation exercise's safety.
The respective step of the procedure is as follows:
Step 1: Preliminary Review
| Step 5: Benchmark Comparison
|
Step 2: Preparing for Validation
| Step 6: Documentation and Reporting
|
Step 3: System Evaluation
| Step 7: Safety Precautions
|
Step 4: Performance Testing
| Step 8: Post-Validation Review
|
IV. Data Collection
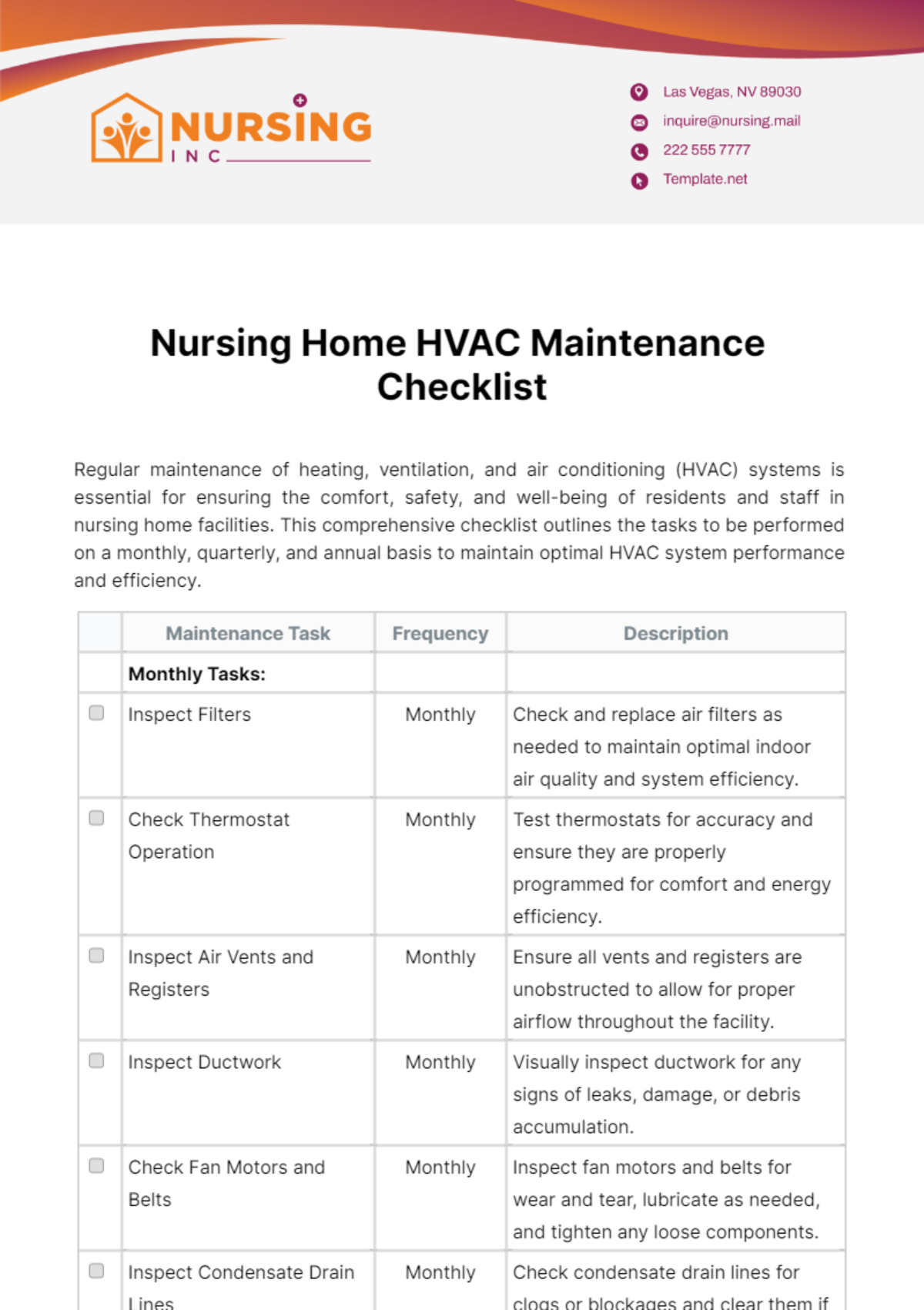
Gather all relevant documentation on the design specifications of the HVAC system, including schematics, blueprints, and technical manuals.
Collect records detailing the installation process of the HVAC system, including any modifications or updates made post-installation.
Obtain operational data logs capturing the system's performance metrics such as temperature, humidity levels, airflow rates, and energy consumption.
Compile maintenance reports documenting routine inspections, repairs, and servicing conducted on the HVAC system since its installation.
Record environmental conditions within the facility during the validation process, including ambient temperature, relative humidity, and air quality parameters.
V. Safety Considerations
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Ensure all personnel involved in the validation process are equipped with appropriate PPE such as gloves, safety glasses, and respiratory protection, if necessary.
Hazard Identification: Identify potential hazards associated with the HVAC system or its operation, such as electrical hazards, chemical exposure, or confined space risks, and implement control measures to mitigate these risks.
Emergency Procedures: Establish clear procedures for responding to emergencies, including fire, chemical spills, or equipment malfunctions, and ensure all personnel are trained in these procedures.
Lockout/Tagout Procedures: Implement lockout/tagout procedures to safely isolate energy sources before conducting maintenance or inspection activities on the HVAC system.
Compliance with Regulations: Ensure compliance with relevant regulatory requirements and industry standards governing HVAC system safety, such as OSHA standards, NFPA guidelines, and local building codes.
VI. Expected Results
Compliance Verification: Confirm that the HVAC system meets regulatory requirements and industry standards for design, installation, operation, and maintenance.
System Performance Assessment: Evaluate the system's ability to maintain desired environmental conditions within the facility, including temperature control, humidity regulation, and air quality management.
Identification of Deviations: Identify any deviations or discrepancies observed during the validation process and develop corrective actions to address these issues.
Documentation of Findings: Document all findings, observations, and test results obtained during the validation process in a comprehensive report for review and analysis.
Validation Approval: Upon successful completion of the validation process and resolution of any identified issues, obtain approval from relevant stakeholders to certify the HVAC system's validation.
VII. Conclusion
In conclusion, the HVAC validation protocol outlined above is essential for ensuring the robustness, efficiency, and safety of [Your Company Name]'s HVAC system. By adhering to established procedures and safety considerations, we can effectively collect data, assess system performance, and verify compliance with regulatory requirements and industry standards.
Through rigorous documentation and analysis of findings, we can identify areas for improvement and implement corrective actions to enhance the system's reliability and performance. Ultimately, the successful completion of the validation process will provide confidence in the HVAC system's ability to maintain optimal environmental conditions within the facility, thereby ensuring the comfort and safety of occupants while supporting operational needs.