Free Health & Safety Awareness Guide

Introduction
Welcome to the Health & Safety Awareness Guide, a comprehensive resource designed to ensure the well-being and safety of all our employees in the workplace. This guide serves as a cornerstone for understanding the various aspects of health and safety, emphasizing our commitment to creating a secure and healthy work environment.
Health and safety in the workplace are not just regulatory requirements; they are integral to maintaining a productive and positive work culture. This guide covers essential topics, from recognizing and managing workplace hazards to implementing emergency procedures and promoting overall wellness. Our aim is to equip every member of our organization with the knowledge and tools necessary to contribute to a safer workplace.
Whether you are a new employee or have been part of our team for years, this guide is intended to be a valuable resource for understanding your role in maintaining a safe and healthy work environment. Your well-being is our priority, and through this guide, we strive to foster a culture of safety that is embraced by all.
Understanding Health & Safety
What is Health & Safety?
Health and Safety in the workplace is a multidisciplinary field concerned with the safety, health, and welfare of people at work. The goal is to create an environment where employees are protected from hazards that could result in injury or illness. This includes implementing policies and procedures that address issues ranging from workplace ergonomics to emergency response. Understanding and adhering to these practices not only ensures compliance with legal requirements but also fosters a culture of safety that benefits everyone in the organization.
Key Health & Safety Legislation
Legislation | Purpose | Employee Implication |
Occupational Safety Act 2051 | To ensure safe working conditions by setting and enforcing standards | Mandatory training and compliance with safety procedures |
Health & Welfare Regulation 2050 | To protect employees from health hazards in the workplace | Regular health screenings and access to wellness programs |
Emergency Response Act 2052 | To establish procedures for dealing with workplace emergencies | Participation in emergency drills and understanding evacuation routes |
Workplace Hazards
Identifying Hazards
Understanding and identifying hazards is the first step in creating a safe workplace. Hazards can be classified into several categories:
Physical Hazards: These include conditions that can cause injury or harm, such as slips, trips, falls, noise, and vibration.
Chemical Hazards: These involve exposure to chemicals, which can lead to health issues like skin irritation, respiratory problems, and poisoning.
Biological Hazards: These are hazards that come from living organisms, such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi, potentially causing infections or diseases.
Ergonomic Hazards: These relate to workplace conditions that can cause musculoskeletal injuries, like repetitive strain or poor posture.
Psychosocial Hazards: These include workplace stress, violence, and other issues affecting mental well-being.
Reporting Procedures
It is crucial for employees to report any hazards they identify to prevent accidents and injuries. Here's a step-by-step guide on reporting:
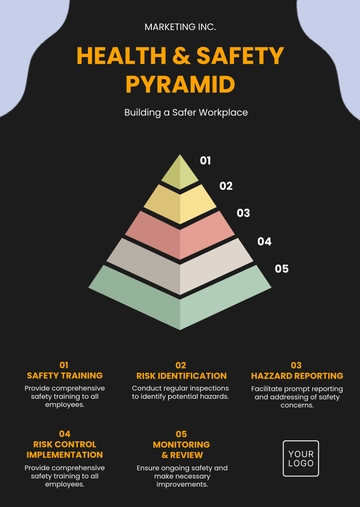
Identify the Hazard: Take note of any potential hazard you observe in the workplace.
Document the Hazard: Record the details of the hazard, including the location, time, and nature of the risk.
Report to Supervisor: Immediately inform your supervisor or the designated safety officer about the hazard.
Follow-Up: Keep track of the report and ensure that appropriate action is taken to mitigate the risk.
Risk Assessment and Management
Conducting a Risk Assessment
Risk assessment is a systematic process of evaluating potential risks that could be involved in a projected activity or undertaking. In the workplace, this involves:
Identifying Hazards: Walk through the workplace to identify potential hazards in each area. This could include anything from exposed wiring to ergonomic risks in office settings.
Determining Who Might Be Harmed and How: Consider which employees, contractors, or visitors might be at risk and how they might be harmed.
Evaluating Risks and Deciding on Precautions: Determine the likelihood and severity of each risk. Decide on measures to effectively prevent or control the harm.
Recording Findings: Document the hazards, their associated risks, and the measures to mitigate these risks.
Reviewing Assessment and Updating if Necessary: Regularly review the risk assessment to ensure the measures are still effective, especially when changes occur in the workplace.
Implementing Control Measures
Risk Identified | Control Measures | Responsibility |
Slippery Floors | Regular cleaning and non-slip mats | Facilities Team |
Chemical Exposure | Proper ventilation, protective gloves, and eyewear | Lab Technicians |
Repetitive Strain Injury | Ergonomic workstations, regular breaks | Office Managers |
Noise Pollution | Sound-proofing, providing earplugs | Construction Supervisors |
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Types of PPE
PPE Type | Use | Maintenance Guidelines |
Safety Helmets | Protects against head injuries | Inspect for cracks or wear before use. Replace after any impact. |
Eye Protection (goggles, face shields) | Protects eyes from splashes, debris, and impacts | Clean regularly. Replace if scratched or damaged. |
Hearing Protection (earplugs, earmuffs) | Reduces risk of hearing damage in noisy environments | Check for wear and tear. Clean reusable earplugs regularly. |
Respiratory Protection (masks, respirators) | Protects from inhaling harmful substances | Fit-test before use. Replace filters as per manufacturer's guidelines. |
Protective Gloves | Shields hands from chemicals, cuts, and heat | Inspect for tears or punctures. Clean after use. |
Correct Usage of PPE
Training: Employees must receive training on the correct use of PPE. This includes how to wear, adjust, and remove it.
Inspection: Before use, PPE should be inspected for any damage or wear that could compromise safety.
Wearing PPE: Follow instructions for wearing PPE correctly. For example, ensure that helmets fit snugly and safety glasses fully cover the eyes and surrounding areas.
Maintenance and Storage: Store PPE in a clean and dry place. Follow specific maintenance guidelines for each type of PPE to ensure its effectiveness and longevity.
Emergency Procedures
Emergency Response Plan
An effective emergency response plan is essential for ensuring the safety and well-being of all employees during unforeseen events. Key components include:
Evacuation Procedures: Clearly marked escape routes and exits, regular evacuation drills, and designated assembly points.
Emergency Contacts: A list of internal and external contacts, including first aiders, fire marshals, and emergency services.
Communication Plan: Procedures for informing employees of an emergency, including alarms, public address systems, and designated communication coordinators.
Role Assignments: Designated responsibilities for key staff members during an emergency, such as evacuation coordinators and first responders.
First Aid and Medical Emergencies
First Aid Kits: Location of first aid kits in the workplace, regularly checked and restocked.
Trained Personnel: List of employees trained in first aid and CPR, along with their contact information.
Procedures for Medical Emergencies: Steps to follow in case of a medical emergency, including immediate first aid response and contacting emergency services.
Health & Safety Training
Training Programs
Program Name | Description | Duration | Frequency |
Basic Health & Safety Orientation | Introduction to workplace safety policies and procedures | 2 hours | For all new hires |
Fire Safety Training | Instruction on fire prevention, use of fire extinguishers, and evacuation procedures | 1 hour | Annually |
Ergonomics Training | Training on proper workstation setup and practices to prevent ergonomic injuries | 1 hour | Biannually |
Emergency Response Training | Detailed training on the company's emergency response plan and roles | 3 hours | Annually |
Continuous Learning
Importance: Emphasizes the need for ongoing learning and staying informed about the latest health and safety practices.
Updates: Regular updates on new health and safety regulations and best practices.
Feedback Mechanism: Encourages employees to provide feedback on training programs, contributing to continuous improvement.
Workplace Wellness
Physical Wellness Programs
Physical wellness in the workplace is vital for maintaining healthy and productive employees. The company offers several programs and initiatives to support this:
Fitness Classes: On-site yoga, aerobics, and strength training classes available during lunch breaks and after hours.
Health Screenings: Regular health check-ups, including blood pressure, cholesterol, and glucose level screenings.
Ergonomic Assessments: Professional evaluations of workstations to ensure ergonomic safety and comfort.
Mental Health Resources
Mental health is equally important for a well-balanced work life. Our initiatives include:
Counseling Services: Confidential counseling services available to employees, providing support for stress, anxiety, and other mental health issues.
Stress Management Workshops: Regular workshops on managing stress, mindfulness, and work-life balance.
Employee Assistance Program (EAP): A program offering support and resources for personal and work-related challenges.
Monitoring and Review
Health & Safety Audits
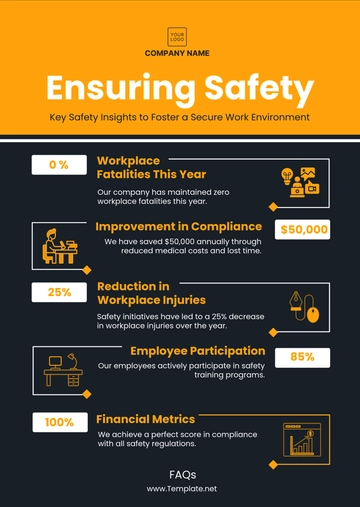
Regular health and safety audits are conducted to ensure compliance with standards and identify areas for improvement. The audit process includes:
Scheduled Inspections: Routine inspections of all workplace areas to identify and rectify potential hazards.
Employee Feedback: Gathering feedback from employees about their health and safety concerns.
Compliance Checks: Ensuring that all health and safety regulations are being met.
Feedback and Continuous Improvement
Feedback Method | Description | Frequency |
Employee Surveys | Surveys to gauge employee satisfaction with health and safety measures | Biannually |
Suggestion Box | A physical or digital platform for employees to submit safety improvement ideas | Ongoing |
Review Meetings | Regular meetings with health & safety committees to discuss issues and improvements | Quarterly |
Implementation of Suggestions: Actively incorporating employee feedback into health and safety strategies.
Continuous Education: Keeping abreast of new health and safety trends and technologies for potential implementation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this Health & Safety Awareness Guide is a testament to our organization's dedication to the highest standards of health and safety. By adhering to the guidelines and procedures outlined in this document, we can collectively ensure a safer, healthier, and more productive workplace.
Health and safety are dynamic areas, and as such, this guide is not static but a living document that will evolve with advancements in safety practices and regulations. We encourage all employees to stay engaged, provide feedback, and participate in ongoing training and wellness initiatives. Together, we can maintain a workplace environment where safety and health are integral to our everyday operations and culture.
Remember, safety in the workplace is not just the responsibility of management but of every individual. By working together and staying committed to these principles, we can achieve our goal of a safe and healthy working environment for everyone.
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
Introducing Template.net's Health & Safety Awareness Guide Template. Fully editable and customizable, this comprehensive guide empowers you to enhance safety awareness in your workplace. Utilize our Ai Editor Tool to tailor the content to your specific needs and ensure your workforce is equipped with the knowledge to promote a safe environment.