Free Health & Safety Legal User Guide

I. Introduction to Health and Safety Compliance
This guide provides an essential overview of health and safety laws, critical for maintaining a safe workplace. Understanding these laws is vital for both employers and employees to ensure a secure and healthy working environment, complying with legal standards, and mitigating workplace risks.
Purpose of the Guide
The purpose of this guide is to elucidate the objectives and importance of health and safety compliance. It serves as a comprehensive resource for navigating complex legal requirements, offering clear explanations and practical guidance to ensure that your organization remains compliant and safe.
II. Understanding Legal Framework and Regulations
This section delves into the key health and safety legislation impacting workplaces. Understanding these laws is crucial for legal compliance and ensuring workplace safety. It outlines major regulations and their practical implications in various work settings.
A. Key Health and Safety Legislation
The core of workplace safety lies in understanding key legislation like OSHA. These laws cover a range of safety aspects, from hazard communication to emergency preparedness. Familiarity with these laws is crucial for legal compliance and creating a safe work environment.
Legislation | Description | Key Provisions |
Occupational Safety and Health Act (OSHA) | Establishes employer responsibilities to ensure a safe and healthy workplace. | Mandates hazard assessment and control. Requires recordkeeping of workplace injuries and illnesses. Provides rights to workers for safe working conditions. |
Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) | Prohibits discrimination based on disability and requires reasonable accommodations in the workplace. | Ensures equal employment opportunities. Requires modifications to the workplace for accessibility. Mandates accommodations for disabled employees. |
Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) | Sets standards for wages, overtime, and youth employment in the private sector and government. | Establishes minimum wage. Regulates overtime pay. Sets working hours and conditions for minors. |
B. Application to the Workplace
Applying these laws effectively in the workplace involves recognizing their relevance to various operations and scenarios. This section explores how different regulations impact day-to-day work, ensuring that legal standards are seamlessly integrated into your business practices.
Legislation | Application in Workplace | Examples of Implementation |
Occupational Safety and Health Act (OSHA) | Ensuring workplace safety through regular risk assessments and compliance with safety standards. | Conducting safety training sessions. Implementing emergency response plans. Regular safety audits and equipment checks. |
Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) | Making workplaces accessible and inclusive for all employees, regardless of disability. | Installing ramps and elevators. Modifying workstations for accessibility. Providing assistive technologies and flexible work arrangements. |
Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) | Complying with wage and hour laws, and ensuring ethical employment of minors. | Maintaining accurate payroll records. Ensuring proper compensation for overtime. Adhering to regulations for hiring and working hours of minors. |
III. Risk Assessment and Management
Essential to workplace safety, this section guides through conducting risk assessments and managing identified risks. It details the process of evaluating potential hazards and implementing effective control measures, crucial for mitigating workplace risks.
A. Conducting Risk Assessments
Risk assessment is the backbone of workplace safety, identifying potential hazards and their implications. It's a systematic process that evaluates the likelihood and severity of risks, forming the basis for implementing effective safety measures.
Step | Process Description | Implementation in Workplace |
Hazard Identification | Recognizing potential sources of harm in the workplace. | Regularly inspecting the workplace to identify new and existing hazards. |
Risk Evaluation | Determining the likelihood and severity of identified hazards. | Using risk matrices to assess the potential impact of each hazard. Considering both the probability of occurrence and potential consequences. |
Control Implementation | Deciding on measures to mitigate or eliminate the risk. | Prioritizing risks based on their severity and likelihood, then implementing appropriate control measures such as redesigning work processes or providing safety equipment. |
Record-Keeping | Documenting the findings of the risk assessment. | Maintaining detailed records of all identified risks, their evaluations, and the control measures implemented. |
Review and Update | Regularly revisiting the risk assessment to ensure it remains current. | Reviewing and updating the assessments after significant changes in the workplace, introduction of new equipment, or in response to an incident. |
B. Mitigating and Managing Risks
Effective risk management requires strategic actions to minimize identified risks. This section delves into various strategies, including preventive measures and emergency response planning, ensuring that risks are managed proactively and effectively.
Strategy | Description | Application Examples |
Engineering Controls | Implementing physical modifications to reduce risks. | Installing guardrails, improving ventilation, using soundproofing materials. |
Administrative Controls | Changing work procedures to minimize risk exposure. | Rotating job assignments, implementing work-rest cycles, providing training. |
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) | Using equipment to protect employees from hazards. | Providing helmets, safety glasses, gloves, or other protective gear as needed. |
Emergency Preparedness | Preparing for and responding effectively to emergencies. | Developing and practicing emergency response plans, including evacuation routes and procedures. |
IV. Health & Safety Policies and Procedures
This section outlines the legal obligations of employers and the rights and duties of employees under health and safety laws. Understanding these roles is vital for ensuring a collaborative and compliant approach to workplace safety.
A. Employer Obligations
Employers play a pivotal role in workplace safety, holding numerous responsibilities under health and safety laws. These include providing safe equipment, ensuring proper training, and maintaining compliance with safety protocols, fundamental for a safe work environment.
Obligation | Description | Implementation Examples |
Provide a Safe Work Environment | Ensuring the workplace is free from recognized hazards. | Regular maintenance of equipment, ensuring clean and unobstructed work areas. |
Conduct Regular Safety Training | Offering training to employees on health and safety practices. | Organizing orientation sessions for new hires, periodic safety workshops, and emergency drills. |
Implement Health and Safety Policies | Developing and enforcing safety policies and procedures. | Creating a comprehensive safety manual, establishing clear protocols for reporting hazards. |
Ensure Compliance with Safety Laws | Adhering to all relevant health and safety regulations. | Staying updated with legislative changes, conducting internal audits for compliance. |
B. Employee Rights and Duties
Employees are not just beneficiaries of safety measures but also active participants. Their rights to a safe workplace and duties in adhering to safety practices are crucial for fostering a collaborative safety culture.
Right/Duty | Description | Application in Workplace |
Right to a Safe Workplace | Working in an environment free of serious recognized hazards. | Employees should expect hazard-free conditions and should report unsafe conditions. |
Duty to Follow Safety Rules | Adhering to established health and safety protocols. | Following the safety guidelines and procedures outlined in the company’s safety manual. |
Right to Receive Safety Training | Being trained in a language they understand. | Participation in safety training sessions, workshops, and drills provided by the employer. |
Duty to Use Safety Equipment | Properly utilizing provided safety gear and equipment. | Using PPE as instructed and reporting any malfunctions or lack of equipment. |
V. Health and Safety Policies and Procedures
Focusing on the development and implementation of health and safety policies, this section emphasizes the importance of clear and effective procedures. Adherence to these policies is key for maintaining a safe and compliant work environment.
A. Developing Effective Policies
Crafting effective health and safety policies is a critical step in legal compliance. These policies should be comprehensive, well-communicated, and regularly updated to reflect changing regulations and workplace environments.
Policy | Purpose | Implementation Guidelines |
Hazard Identification and Reporting | To ensure timely recognition and reporting of potential workplace hazards. | Implement a system for employees to easily report hazards. Regularly review and address reported issues. |
Emergency Response and Evacuation | To prepare employees for emergency situations and ensure safe evacuation. | Develop clear evacuation plans and conduct regular drills. Place emergency procedure guides in visible locations. |
Accident and Incident Investigation | To analyze the causes of accidents and incidents and prevent recurrence. | Establish a procedure for investigating workplace incidents and use findings to improve safety measures. |
Health Surveillance and Monitoring | To monitor employees' health, particularly those in high-risk areas. | Conduct regular health check-ups and exposure monitoring for employees in hazardous roles. |
B. Procedure Compliance
Ensuring adherence to these policies and procedures is a shared responsibility. Non-compliance is not only a legal breach but also a potential hazard, emphasizing the need for strict adherence and regular monitoring.
Benefit/Application | Description | Examples |
Legal Compliance | Adhering to health and safety policies ensures compliance with legal standards. | Regular audits and checks to ensure policies align with current laws and regulations. |
Enhanced Safety Culture | Consistent application of policies fosters a culture focused on safety. | Encouraging employee participation in safety initiatives and discussions. |
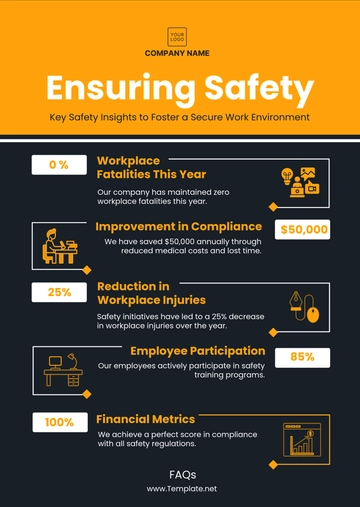
Reduced Workplace Injuries | Following procedures minimizes the risk of accidents and injuries. | Tracking and analyzing incident reports to identify trends and areas for improvement. |
Improved Employee Morale | A safe workplace boosts employee confidence and satisfaction. | Conducting surveys to gauge employee feelings about safety and addressing concerns proactively. |
Financial Savings | Preventing accidents reduces costs related to injuries and legal penalties. | Keeping records of safety measures and their impact on reducing workplace incidents. |
VI. Training and Awareness
This section highlights the importance of employee training and awareness in health and safety. It covers the creation and execution of training programs and strategies for fostering a safety-conscious workplace culture.
A. Employee Training Programs
Developing and implementing comprehensive employee training programs is a cornerstone of maintaining workplace safety. Such programs should cover a wide range of topics, from basic safety principles to specific procedures for handling hazardous materials or emergency situations. Training must be tailored to the various roles within the organization, ensuring that each employee receives relevant and practical knowledge.
Regular refreshment courses are also crucial to keep everyone up to date with the latest safety protocols and regulatory changes. The use of interactive training methods, such as workshops, simulations, and e-learning modules, can enhance engagement and retention of safety information. Tracking and documenting the completion of training sessions are essential for ensuring compliance and identifying areas where additional training may be needed.
B. Promoting Health and Safety Awareness
Promoting health and safety awareness in the workplace goes beyond formal training; it's about fostering a culture where safety is ingrained in every aspect of work life. This can be achieved through regular communication about safety topics, such as newsletters, bulletins, or safety minutes at the beginning of meetings. Creating a platform for employees to share their ideas and feedback on safety matters encourages active participation and a sense of ownership over their work environment.
Celebrating safety milestones and recognizing individuals or teams for exemplary safety practices can also reinforce the importance of a safety-first mindset. Awareness campaigns, themed around specific safety topics or observances like National Safety Month, can help keep the conversation about workplace safety fresh and relevant. Engaging employees in these activities not only educates them but also builds a community focused on maintaining a safe and healthy workplace.
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
Elevate your Health & Safety legal compliance effortlessly with Template.net's Health & Safety Legal User Guide Template. This fully editable and customizable template, powered by our Ai Editor Tool, streamlines the process of crafting comprehensive user guides. Ensure compliance with ease and precision, only with Template.net's innovative solutions.