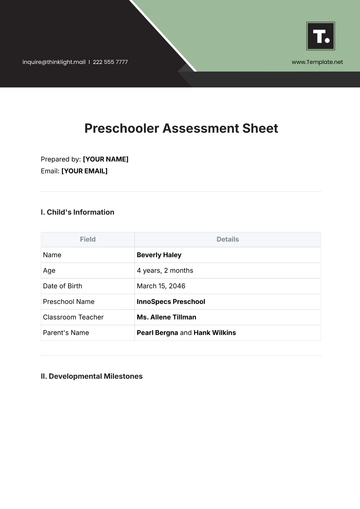
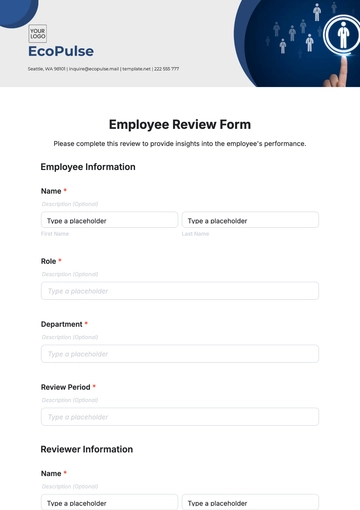
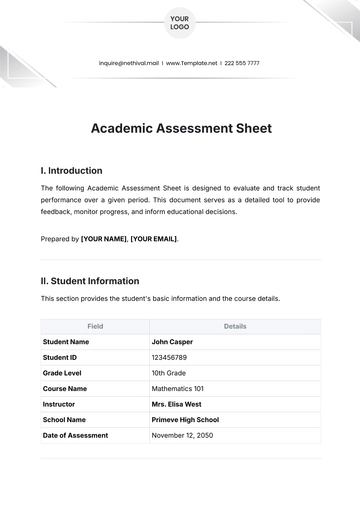
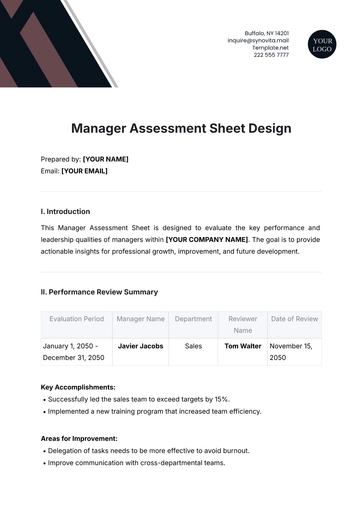
Free Food And Agriculture Country Fact Sheet

Created by: [YOUR NAME]
Company: [YOUR COMPANY NAME
Department: [YOUR DEPARTMENT]
I. Introduction

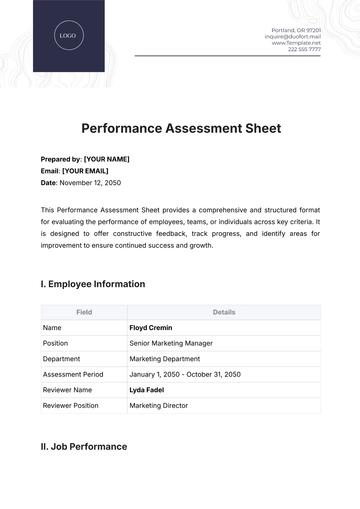
Kenya's agriculture sector is a vital pillar of the country's economy, contributing significantly to employment, exports, and food security. The sector is characterized by diverse agricultural activities, with smallholder farming and livestock rearing playing pivotal roles in sustaining livelihoods and meeting domestic needs.
II. Key Exports
Tea: Kenya is celebrated globally for its high-quality tea, with tea production being a major export earner for the country.
Coffee: Kenyan coffee is esteemed for its distinctive flavors and commands premium prices in international markets.
Flowers: The floriculture industry in Kenya is a major contributor to the country's export earnings, particularly in the production of roses and other cut flowers.
III. Staple Crops
Maize: Maize cultivation is widespread across Kenya and serves as a staple food crop for many households.
Wheat: Wheat farming supports the production of flour and baked goods, addressing domestic consumption needs.
Potatoes: Potatoes are grown extensively in various regions of Kenya, providing an essential dietary component for the population.
IV. Livestock Rearing
Livestock rearing is integral to Kenya's agricultural landscape, supporting both dairy and meat production.
Dairy: Kenya's dairy sector contributes significantly to milk production, meeting the demands of the domestic market.
Meat: Cattle, goats, and sheep farming contribute to meat supply and protein needs across the country.
V. Challenges and Solutions
Kenya's agriculture sector faces several challenges that require concerted efforts and innovative solutions.
A. Challenges | |
Challenge | Description |
Climate Change Impacts | Erratic weather patterns, including droughts and floods, pose risks to agricultural productivity. |
Food Security | Ensuring adequate and equitable access to nutritious food remains a persistent challenge. |
Resource Constraints | Limited access to modern farming technologies and inputs hinders productivity gains. |
B. Solutions | |
| |
Climate-Smart Agriculture | Promoting practices that enhance resilience to climate change, such as conservation agriculture and agroforestry. |
Market Access | Improving market linkages and infrastructure to enhance farmers' access to markets and reduce post-harvest losses. |
Technology Adoption | Encouraging the adoption of innovative technologies, such as precision agriculture and mobile-based extension services, to boost productivity and efficiency. |
VI. Government Policies
Climate Resilience: The Kenyan government has adopted strategies to enhance agricultural resilience to climate change.
Food Security: Initiatives aimed at improving food production and distribution to ensure national food security.
VII. International Partnerships
Collaborations and partnerships between various international organizations and agencies have significantly contributed to the facilitation of knowledge exchange and the transfer of technology within the field of agriculture.
VIII. Conclusion
In conclusion, Kenya's agriculture sector continues to evolve, driven by innovation and sustainable practices. Despite challenges, the sector remains resilient, supported by government policies and global partnerships. As we look ahead, the future of agriculture in Kenya holds promise for further growth and development, ensuring food security and economic prosperity for generations to come.
For more information, please contact [YOUR COMPANY NAME] at [YOUR COMPANY EMAIL] or visit our website at [YOUR COMPANY WEBSITE].
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
Explore the Food And Agriculture Country Fact Sheet Template on Template.net. This editable and customizable document is ideal for presenting detailed insights. Effortlessly tailor content using our Ai Editor Tool for precision and clarity. Enhance reports with ease and showcase agricultural prowess effectively. Access this comprehensive tool today for impactful presentations and insightful analysis of food and agriculture data.
You may also like
- Attendance Sheet
- Work Sheet
- Sheet Cost
- Expense Sheet
- Tracker Sheet
- Student Sheet
- Tracking Sheet
- Blank Sheet
- Information Sheet
- Sales Sheet
- Record Sheet
- Price Sheet
- Plan Sheet
- Score Sheet
- Estimate Sheet
- Evaluation Sheet
- Checklist Sheet
- Bid Sheet
- Call Log Sheet
- Bill Sheet
- Assessment Sheet
- Task Sheet
- School Sheet
- Work From Home Sheet
- Summary Sheet
- Construction Sheet
- Cover Sheet
- Debt Spreadsheet
- Debt Sheet
- Client Information Sheet
- University Sheet
- Freelancer Sheet
- Bookkeeping Sheet
- Itinerary Spreadsheet
- Scorecard Sheet
- Run Sheet
- Monthly Timesheet
- Event Sheet
- Advertising Agency Sheet
- Missing Numbers Worksheet
- Training Sheet
- Production Sheet
- Mortgage Sheet
- Answer Sheet
- Excel Sheet