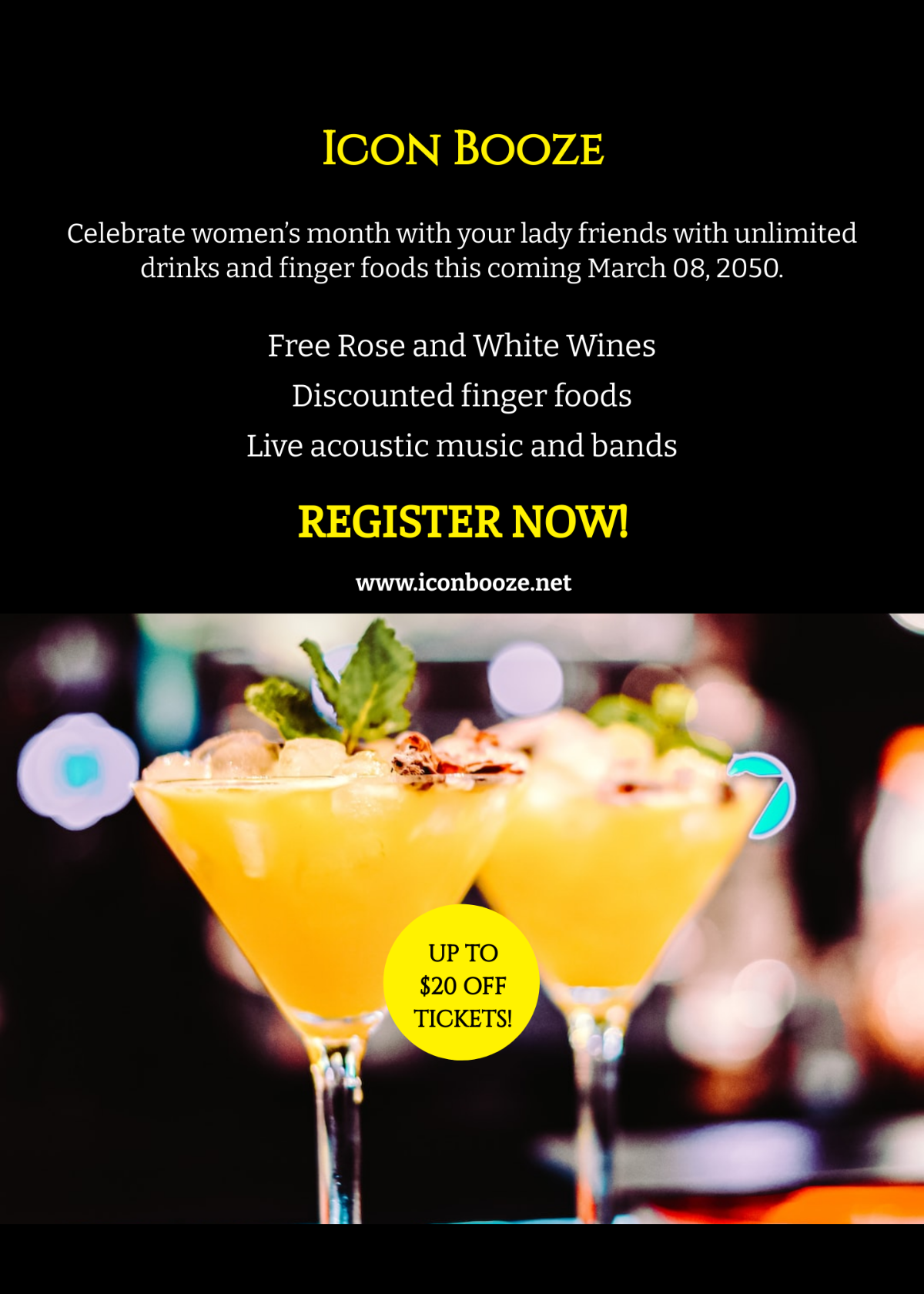
Free Architect Article
Elevate your architectural writing with our premium Architect Article Template from Template.net. This customizable and editable template is meticulously crafted to suit your professional needs. Seamlessly organize your ideas and insights with ease using our intuitive AI Editor Tool. Empower your content creation process and captivate your audience with polished, professional articles.