A Level Coursework
I. Introduction
This coursework aims to evaluate students' comprehension of key biological concepts related to cellular respiration. The study investigates the relationship between glucose metabolism and ATP production, with a focus on the role of mitochondria in aerobic respiration. Understanding these processes is crucial for A Level students as it forms the foundation for advanced studies in biology and related fields.
II. Background Study
A. Literature Review
The literature review explores seminal studies on cellular respiration, highlighting the contributions of researchers such as Otto Warburg and Hans Krebs.
It discusses the biochemical pathways involved in glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
Gaps in the literature regarding the regulation of mitochondrial function and its implications for human health are identified for further investigation.
B. Theoretical Framework
The coursework adopts a bioenergetics perspective, emphasizing the conservation and transfer of energy during cellular respiration.
Theoretical concepts from biochemistry and molecular biology, such as enzyme kinetics and electron transport chain, provide a framework for analyzing experimental data.
III. Research Methodology
A. Research Design
A laboratory-based approach is employed to investigate the effect of substrate concentration on the rate of cellular respiration.
Experimental groups are exposed to varying concentrations of glucose, while control groups receive standard conditions.
B. Data Collection
Data on oxygen consumption rates are collected using a respirometer apparatus over specified time intervals.
Precautions are taken to control environmental factors such as temperature and pH, ensuring the reliability of results.
C. Data Analysis
Statistical analysis involves calculating mean rates of oxygen consumption for each experimental condition.
Graphical representation of data allows for visual interpretation of trends and comparisons between experimental groups.
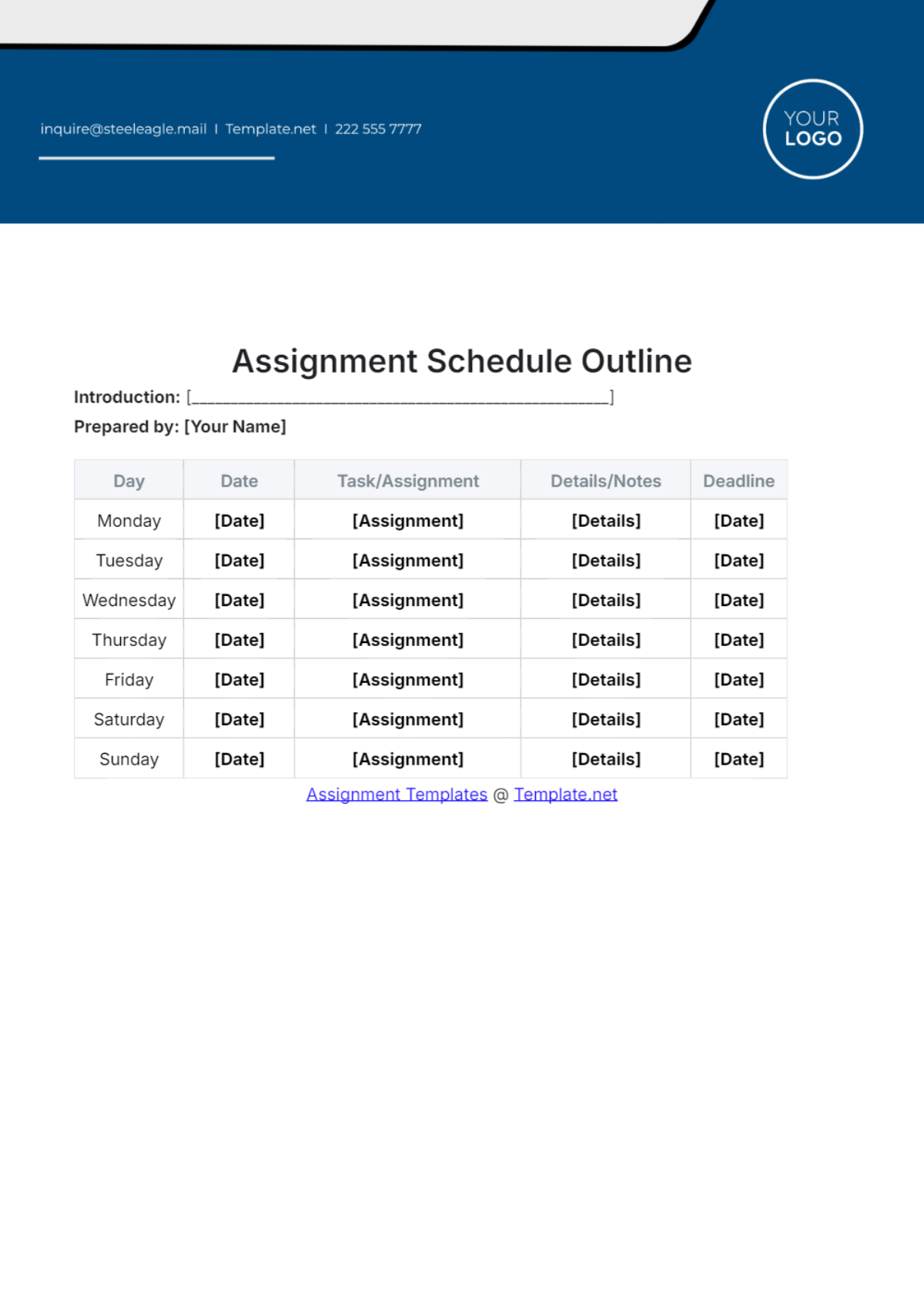
Data Analysis Summary Table:
Analysis Method | Findings |
|---|---|
Statistical Tests | Glucose concentration significantly affects oxygen consumption rates. |
Qualitative Coding | Common patterns observed in oxygen consumption kinetics. |
IV. Results and Discussion
A. Key Findings
Higher concentrations of glucose correlate with increased rates of oxygen consumption, indicating enhanced metabolic activity.
The rate of oxygen consumption reaches a plateau at saturating substrate concentrations, suggesting substrate inhibition or metabolic saturation.
Summary of Key Findings Table:
Finding | Description |
|---|---|
Increased Glucose Concentration | Leads to higher rates of oxygen consumption |
Saturation Effect | Plateau observed at high glucose concentrations |
B. Discussion
The findings support the hypothesis that glucose availability influences cellular respiration rates.
Implications for metabolic regulation and energy homeostasis are discussed in the context of cellular physiology and human health.
V. Conclusion
The coursework findings underscore the significance of substrate concentration in regulating cellular metabolism. Understanding the principles of cellular respiration provides insights into broader biological processes and offers potential applications in medical research and biotechnology.
VI. Recommended Reading
Explore these fictional resources to deepen your understanding of cellular respiration and related topics:
"The Powerhouse of the Cell: A Comprehensive Guide to Mitochondrial Function" by Dr. Emily Biochemist
"Bioenergetics: Unraveling the Mysteries of ATP Synthesis" by Professor Alexander Metabolic
"Cellular Respiration Demystified: From Glycolysis to Oxidative Phosphorylation" by Dr. Sarah Respirologist
VII. Appendices
Appendix A: Raw data tables of oxygen consumption rates under different glucose concentrations.
Appendix B: Detailed protocols for experimental procedures and data analysis.