Cost Analysis
Prepared By : | [Your Name] |
Company : | [Your Company Name] |
Department : | [Your Department] |
I. Introduction
A. Objective
The objective of this Cost Analysis is to thoroughly examine the expenses associated with the Project, aiming to provide stakeholders with insights into its financial feasibility, efficiency, and potential risks.
B. Scope
This analysis will focus on the development of a new mobile application for a ride-sharing service the planning, design, development, and initial launch phases, encompassing the initial launch market being limited to a specific city or region, the use of existing infrastructure for backend support, and a fixed budget for development and marketing.
C. Methodology
The analysis will employ a combination of methods, tools, and data sources may include cost-benefit analysis, comparative analysis, bottom-up estimation, expert judgment, spreadsheet software, project management software, financial modeling software, internal financial records, market research reports, supplier quotations, government databases, and stakeholder interviews., ensuring comprehensive coverage and accuracy in cost assessment.
II. Cost Identification
Direct Costs
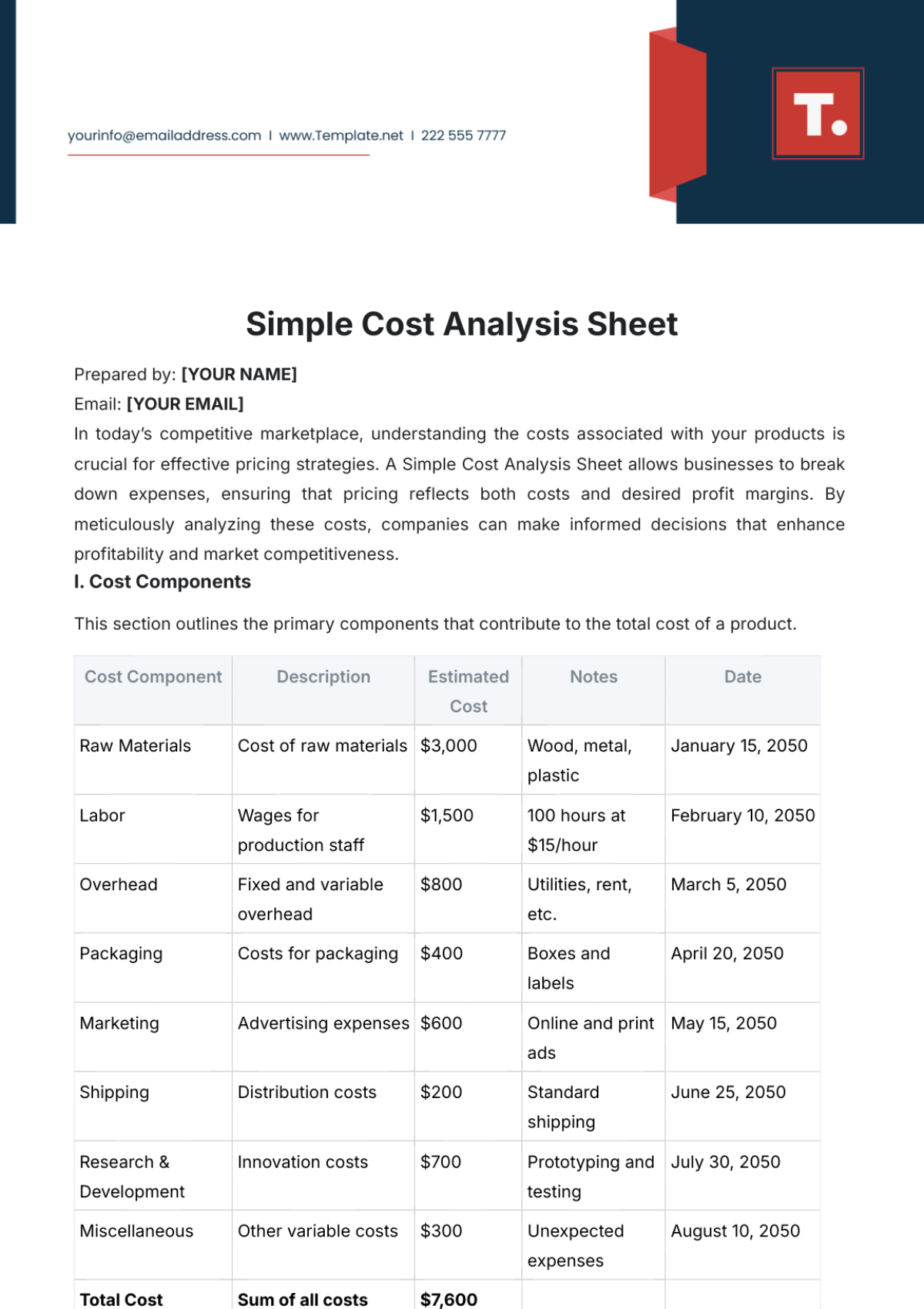
1. Raw Materials: The cost of raw materials required for [Project].
2. Labor Expenses: Salaries and wages for personnel involved in [Project].
3. Equipment Costs: Costs of acquiring essential equipment.
4. Transportation: Transportation costs for materials, equipment, or personnel.
Indirect Costs
1. Overheads: Administrative expenses, utilities, and other indirect costs.
2. Marketing and Advertising: Expenses for promoting [Project].
3. Insurance: Insurance premiums for coverage related to the project.
III. Cost Estimation
Cost Components Breakdown
The total cost comprises:
Direct Costs: The sum of all direct costs associated with the project, including raw materials, labor expenses, equipment costs, and transportation expenses.
Indirect Costs: The sum of all indirect costs, encompassing overhead expenses, marketing and advertising expenses, insurance premiums, and other administrative costs.
Cost Estimation Methods
1. Raw Materials: Estimated based on market prices and required quantities.
2. Labor Expenses: Calculated using hourly rates and projected work hours.
3. Equipment Costs: Obtained from quotations or market research.
4. Transportation: Based on distance, transport type, and fuel expenses.
IV. Cost Analysis
A. Total Cost Calculation
Total Cost = Direct Costs + Indirect Costs
B. Cost Efficiency Assessment
Analyzing the cost per unit of output or deliverable to assess efficiency.
Conducting a cost-benefit analysis to determine the project's viability.
C. Risk Analysis
1. Identify risks like supply chain disruptions, shortages, and regulatory changes.
2. Assess the financial impact of identified risks on cost projections.
V. Cost Comparison
A. Alternative Scenarios
1. Scenario 1: A phased development approach focusing on core features initially, reducing upfront costs with the option for future expansions.
2. Scenario 2: An aggressive expansion strategy with heavy investments in marketing, technology upgrades, and infrastructure, leading to higher upfront costs and increased risks.
B. Comparison Table
Scenario | Total Cost ($) | Cost Efficiency | Risk Level |
|---|---|---|---|
Current Plan | [$250,000] | High | Medium |
Scenario 1 | [$220,000] | Medium | Low |
Scenario 2 | [$270,000] | Low | High |
VI. Sensitivity Analysis
A. Key Variables
Key variables influencing costs include:
Material Costs
Labor Expenses
Equipment Costs
Transportation Costs
Overhead Expenses
Market Demand
Regulatory Requirements
Economic Factors
Technology Costs
Marketing Expenses
B. Scenario Analysis
Analyze the impact of variations in key variables on total costs.
VII. Conclusion and Recommendations
Summary of Findings
The analysis revealed :
Project costs are on a budget, demonstrating effective management.
Labor expenses dominate, emphasizing the need for efficiency.
Scenario 1 indicates cost savings with moderate risk.
Scenario 2 reveals higher costs and risks.
Market demand and regulations significantly impact costs.
Recommendations
Based on the findings, stakeholders are advised to :
Enhance labor efficiency to reduce costs.
Optimize procurement processes for materials and equipment.
Implement contingency plans to mitigate risks.
Stay vigilant to market trends and regulatory changes.
Invest strategically in marketing efforts to boost returns.