Root Cause Analysis
Prepared By : | [YOUR NAME] |
Company : | [YOUR COMPANY NAME] |
Department : | [YOUR DEPARTMENT] |
I. Executive Summary
A. Issue Description
In this section, provide a succinct overview of the problem under investigation, such as detailing recurring system failures (machinery breakdowns, software glitches) that hinder production, and discuss their impact, historical patterns, and key characteristics.
B. Impact Analysis
In this analysis, you explore the wider impact of the problem, which extends past immediate production issues to affect multiple business areas. System failures, for instance, disrupt production, increase maintenance costs, lower product quality, and cause delivery delays and customer dissatisfaction, potentially leading to financial losses from downtime.
C. Key Findings Summary
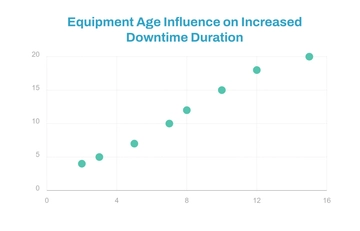
This section summarizes key insights from your analysis, emphasizing crucial findings such as equipment downtime's major role in production losses, supported by data. It also covers secondary contributors identified during the RCA, like poor maintenance or old equipment.
II. Problem Statement
A. Specific Problem
The frequent malfunctions of equipment are consistently resulting in disruptions to the planned production schedules, which are consequently harming the overall efficiency of the operational processes.
B. Symptoms and Implications
Operational Disruptions: The recurring breakdowns of critical machinery, such as CNC milling machines in the machining department or conveyor systems in the assembly line, lead to unexpected downtimes, halting production lines and causing delays in fulfilling orders.
Increased Maintenance Costs: Each instance of equipment failure necessitates immediate repairs or replacements, contributing significantly to maintenance expenditures and reducing budget predictability.
Production Losses: Downtimes directly translate to production losses, affecting output targets and potentially jeopardizing contractual obligations or customer commitments.
Quality Control Challenges: Rushed restarts or temporary workarounds post-failure can compromise product quality, leading to rework, waste, and potential customer dissatisfaction.
Employee Frustration and Burnout: Continuous disruptions create a stressful work environment for frontline staff, impacting morale, and productivity, and potentially increasing employee turnover rates.
Customer Impact: Delays in order fulfillment or compromised product quality due to production interruptions can result in dissatisfied customers, damaging long-term relationships and brand reputation.
III. Methodology
A. Data Collection
Specifies sources and types of data collected for the Root Cause Analysis (RCA).
Sources: Data sources can include equipment logs, maintenance records, production diagrams, incident reports, and interviews with personnel for insights into equipment performance and issues.
Types of Data: The gathered data includes quantitative aspects (like downtime duration and frequency of breakdowns) and qualitative elements (such as descriptions of equipment symptoms and maintenance actions recorded).
B. Analysis Techniques:
Describes the methods used to analyze collected data for root cause identification.
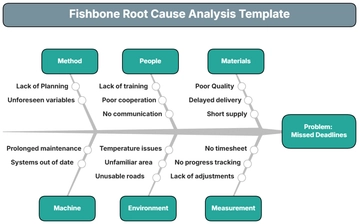
Fishbone Diagrams (Ishikawa Diagrams): Used to visually identify potential causes of equipment failures across categories such as people, process, equipment, materials, environment, and management.
Pareto Analysis: Helps prioritize root causes by identifying the most significant contributors to equipment failures based on frequency or impact, guiding focused remediation efforts.
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA): Systematically evaluates failure modes, their causes, and potential effects on production processes, highlighting critical areas for intervention and improvement.
Statistical Analysis: Utilizes statistical tools like trend analysis, correlation analysis, or regression analysis to identify patterns, correlations, or anomalies in data sets related to equipment failures and production disruptions.
C. Team Involvement
Lists team members, their roles, and contributions to the RCA process.
Data Analyst: Responsible for data collection, cleaning, and analysis using statistical and visualization tools to derive insights from the collected data sets.
Subject Matter Experts (SMEs): Provide domain-specific knowledge related to equipment functionality, maintenance practices, production workflows, and potential failure modes, guiding the analysis and root cause identification process.
Maintenance Technicians/Engineers: Provide insights on equipment history, maintenance records, failure trends, and operational challenges to support validation of analysis outcomes and recommended solutions.
Operations Managers/Supervisors: Offer insights on how equipment failures affect production schedules, resource allocation, and customer commitments, linking root cause analysis outcomes to strategic business goals.
IV. Findings
Detail the findings from the analysis conducted, focusing on identifying the root causes.
Event | Causes | Impacts |
|---|---|---|
Equipment Breakdowns | Cause A: Inadequate preventive maintenance practices. Cause B: Age-related wear and tear | Impact A: Increased production delays due to unexpected breakdowns. Impact B: Escalating maintenance costs for emergency repairs |
Product Quality Issues | Cause C: Lack of operator training on equipment handling and maintenance procedures | Impact C: Decline in product quality due to improper equipment usage |
V. Conclusion
The analysis has identified critical equipment failures as the root causes of the operational disruptions and quality issues observed during the RCA process. Key takeaways include:
Dependency on Reactive Maintenance: The dependence on reactive maintenance strategies has led to a significant increase in downtime and production delays, along with escalated maintenance expenses owing to the necessity for emergency repairs.
Skills and Knowledge Gap: Inadequate training of operators, coupled with a lack of awareness concerning the proper handling and maintenance procedures for equipment, plays a significant role in leading to failures of the equipment and issues related to the quality of the products produced.
VI. Recommendations
Implement Specific Controls:
Regular Maintenance Schedules: Establish and adhere to proactive maintenance schedules, including routine inspections, lubrication, and component replacements to prevent unexpected failures.
Equipment Condition Monitoring: Deploy sensor-based monitoring systems or predictive maintenance technologies to detect early signs of equipment deterioration and schedule maintenance proactively.
Propose Changes in Procedures or Policies:
Revised Equipment Usage Guidelines: Develop and communicate clear guidelines and best practices for equipment operation, maintenance, and troubleshooting to reduce operator errors and equipment stress.
Incident Reporting and Analysis: Implement a structured incident reporting system to capture equipment failures, analyze root causes, and initiate corrective actions systematically.
Identify Training or Development Needs:
Operator Training Programs: Design and conduct comprehensive training programs for equipment operators, focusing on safety protocols, maintenance tasks, troubleshooting techniques, and equipment-specific knowledge.
Continuous Learning Initiatives: Encourage ongoing learning and skills development through regular training updates, knowledge-sharing sessions, and certifications relevant to equipment handling and maintenance best practices.
VII. Appendices
Appendix A - Data Files
This appendix includes raw data used in the Root Cause Analysis (RCA). Examples of data sources include:
Equipment Logs: Detailed logs capturing equipment performance metrics, downtime events, and maintenance activities.
Maintenance Records: Records documenting past maintenance schedules, repairs, parts replacements, and service histories.
Production Reports: Data indicating production output, efficiency metrics, and performance trends over specific periods.
Incident Reports: Reports documenting equipment failures, breakdown events, and associated impacts on operations.
Quality Control Data: Information related to product quality metrics, defects, rejections, and quality assurance processes.
Appendix B - Interview Notes
This appendix contains summarized notes from interviews conducted with relevant personnel involved in equipment operations, maintenance, and management. Interviewees may include:
Equipment Operators: Insights into daily equipment usage, observations of equipment behavior, and challenges faced during operations.
Maintenance Technicians/Engineers: Information on equipment maintenance, past failures, repair methods, and improvement suggestions.
Production Supervisors/Managers: Perspectives on production schedules, impacts of equipment failures on workflows, resource allocation challenges, and operational priorities.
Quality Assurance Personnel: Feedback on product quality, inspection procedures, quality control, and equipment performance issues.