Free Small Business SWOT Analysis
Prepared By: [Your Name]
Company: [Your Company Name]
Date: May 20, 2050
Overview
This SWOT analysis was conducted by our team to evaluate [Your Company Name]'s current business environment, identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. The insights gained aim to support strategic decision-making and long-term growth.
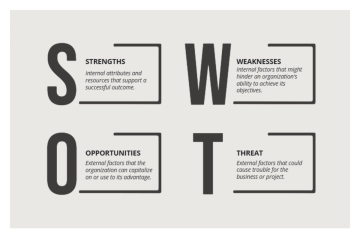
SWOT Analysis
Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|
Premium, locally sourced products | Limited marketing reach |
Strong community engagement | High employee turnover |
Prime downtown location | Seasonal revenue fluctuations |
Sustainability-focused branding | Reliance on in-store sales |
Opportunities | Threats |
|---|---|
Expanding into e-commerce | Economic uncertainty affecting demand |
Collaborations with local businesses | Rising competition in the local area |
Introducing new menu options | Volatile supply chain costs |
Accessing sustainability grants | Labor shortages hindering operations |
Strategic Recommendations
Expand Online Presence: Build a user-friendly e-commerce platform for packaged products and merchandise.
Strengthen Employee Engagement: Implement training programs and offer competitive compensation to reduce turnover.
Diversify Revenue Streams: Introduce subscription-based coffee deliveries and seasonal product lines.
Leverage Brand Strengths: Promote the company’s sustainability initiatives and community-focused activities in marketing efforts.
This analysis provides actionable insights to guide [Your Company Name] in leveraging its strengths, addressing weaknesses, and capitalizing on growth opportunities while mitigating potential risks.
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
The Small Business SWOT Analysis Template from Template.net is a versatile, editable, and customizable tool designed to help you evaluate your business's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Easily editable in our AI Editor Tool, this template lets you personalize every aspect, ensuring a comprehensive analysis that suits your business needs perfectly.