Incident Root Cause Analysis
Prepared by: [Your Name]
Date: January 1, 2060
I. Introduction
Incident Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is a methodical approach designed to identify the fundamental causes of an incident or problem rather than merely addressing the symptoms. This analysis aims to uncover the root causes to prevent recurrence and improve overall system reliability and safety. This comprehensive report outlines the steps taken during the analysis, the findings, and the recommended corrective actions.
II. Incident Description
A. Incident Overview
The incident occurred on August 15, 2050, at the [Your Company Name]. A significant explosion resulted in severe damage to the production line, injury to three employees, and a temporary halt in operations. The explosion was initially attributed to equipment failure, but a detailed Root Cause Analysis (RCA) was conducted to understand the deeper issues.
B. Incident Impact
Damage: Extensive damage to the production line is estimated at $1 million.
Injuries: Three employees sustained injuries, two of whom required hospitalization.
Operational Disruption: Production was halted for two weeks, leading to financial losses and a backlog of orders.
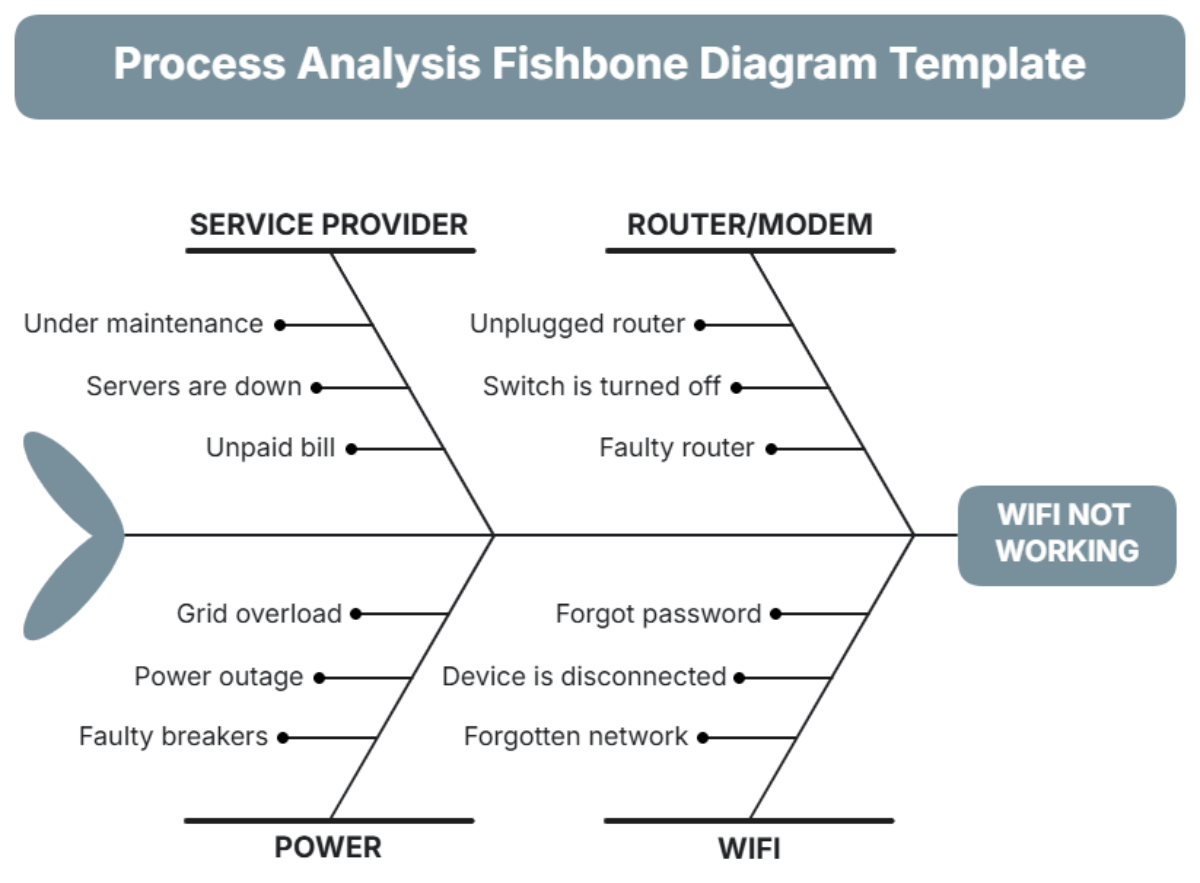
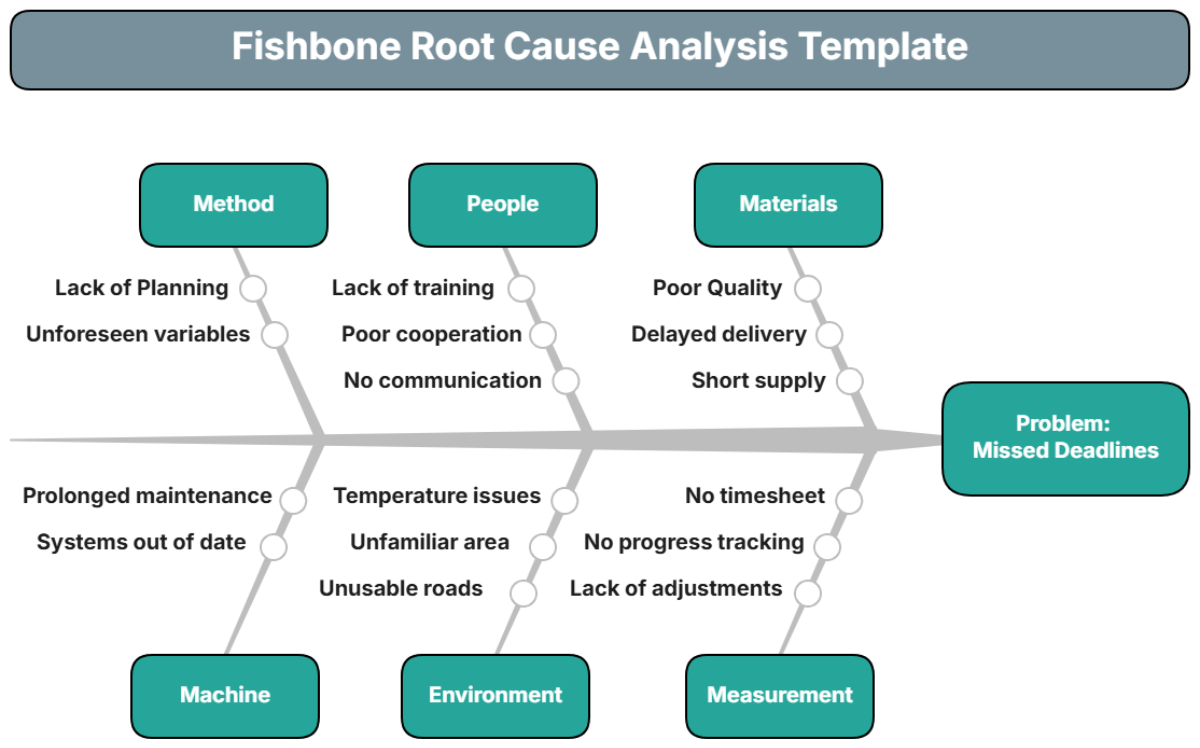
III. Root Cause Identification
To fully understand the incident and prevent future occurrences, it is essential to identify both the immediate and underlying causes. The following details outline the root causes identified through the analysis:
A. Immediate Causes
Equipment Failure: The explosion was triggered by a malfunctioning pressure valve, which was operating beyond its recommended pressure range.
Maintenance Negligence: The equipment had not undergone its scheduled maintenance due to incomplete maintenance records and an understaffed maintenance team.
B. Underlying Causes
Inadequate Safety Protocols: The facility lacked comprehensive safety procedures for high-risk equipment, with outdated safety guidelines that were not regularly reviewed.
Training Deficiencies: Operators were inadequately trained to handle equipment failures, with infrequent and outdated training programs that did not reflect current best practices.
Poor Communication Channels: There was a lack of effective communication between the maintenance and operations teams, with equipment issues not consistently relayed to maintenance personnel.
IV. Corrective Actions
To address the issues identified in the Root Cause Analysis, the following corrective actions have been implemented:
A. Immediate Actions
Emergency Repairs: Immediate repairs were carried out on the damaged equipment by a temporary team brought in to expedite the process.
Incident Reporting: All incident details were documented and communicated to relevant stakeholders. A preliminary report was issued within 24 hours of the incident.
B. Long-Term Actions
Review and Update Safety Protocols: A comprehensive review and revision of safety procedures will be conducted by engaging safety experts to update guidelines and ensure regular reviews.
Enhance Maintenance Procedures: A robust maintenance schedule with clear records will be implemented by introducing automated tracking systems for maintenance schedules and compliance.
Improve Training Programs: An updated training program for equipment operators will be developed and implemented, including regular training sessions and simulations to prepare staff for emergencies.
Strengthen Communication Channels: Communication protocols between operations and maintenance teams will be improved by establishing a standardized reporting system for equipment issues and conducting regular inter-departmental meetings.
V. Implementation Plan
To effectively address the identified root causes and ensure the successful implementation of the corrective actions, the following plan outlines the key tasks, responsible parties, and timelines for completion.
Action Item | Responsible Party | Timeline | Status |
|---|---|---|---|
Review and Update Safety Protocols | Safety Officer | August 2050 | In Progress |
Enhance Maintenance Procedures | Maintenance Manager | September 2050 | Not Started |
Improve Training Programs | HR Department | October 2050 | Not Started |
Strengthen Communication Channels | Operations Manager | November 2050 | Not Started |
VI. Follow-Up
To ensure the effectiveness of the implemented changes and to continuously improve, a robust follow-up process will be established, including regular monitoring and evaluation, feedback mechanisms, and trend analysis.
Monitoring and Evaluation: To ensure the effectiveness of implemented changes, regular audits will be conducted every quarter, with comprehensive annual reviews.
Feedback Mechanism: A feedback system will be established to continuously gather input from employees on the new protocols. This will include anonymous feedback forms and regular team meetings.
Review of Incident Trends: Incident trends will be analyzed annually to identify any recurring issues or areas needing further improvement. This will involve a review of incident reports and RCA outcomes.
VII. Conclusion
The Incident Root Cause Analysis for the explosion has revealed several critical areas for improvement. By addressing the root causes identified, implementing corrective actions, and establishing a robust follow-up plan, the facility aims to enhance safety, prevent future incidents, and ensure operational excellence.