Medication Study Guide
Prepared by | [YOUR NAME] |
Company Name | [YOUR COMPANY NAME] |
Company Address | [YOUR COMPANY ADDRESS] |
Company Website | [YOUR COMPANY WEBSITE] |
Company Email | [YOUR COMPANY EMAIL] |
Company Phone | [YOUR COMPANY NUMBER] |
Company Social Media | [YOUR COMPANY SOCIAL MEDIA] |
I. Introduction
A. Overview
This guide provides comprehensive information on various medications, their uses, side effects, and proper administration. It is designed to aid students, healthcare professionals, and patients in understanding medications better.
B. Importance
Understanding medications is crucial for effective treatment, patient safety, and overall healthcare outcomes. This guide aims to educate and inform on the correct use of medications.
II. Types of Medications
A. Prescription Medications
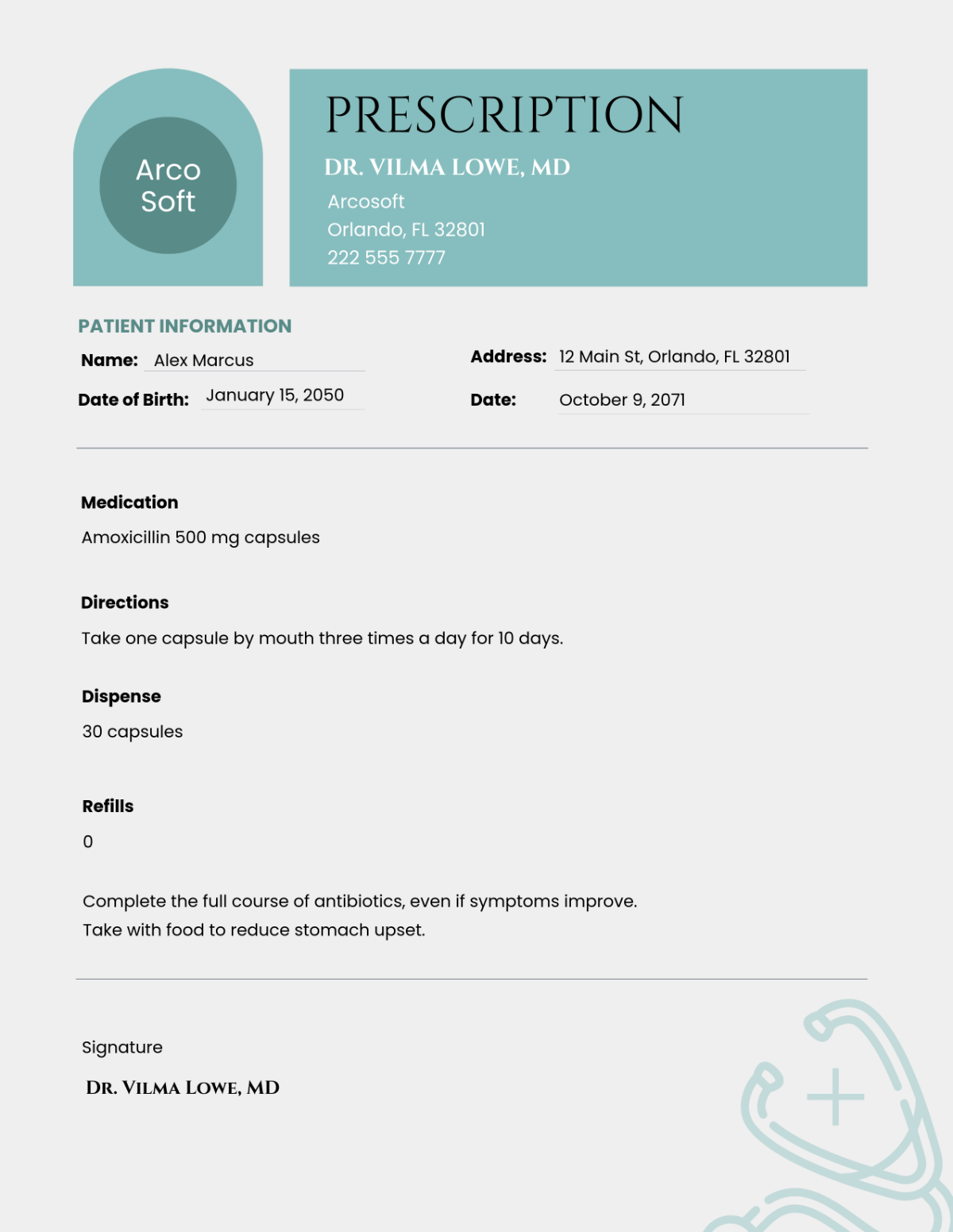
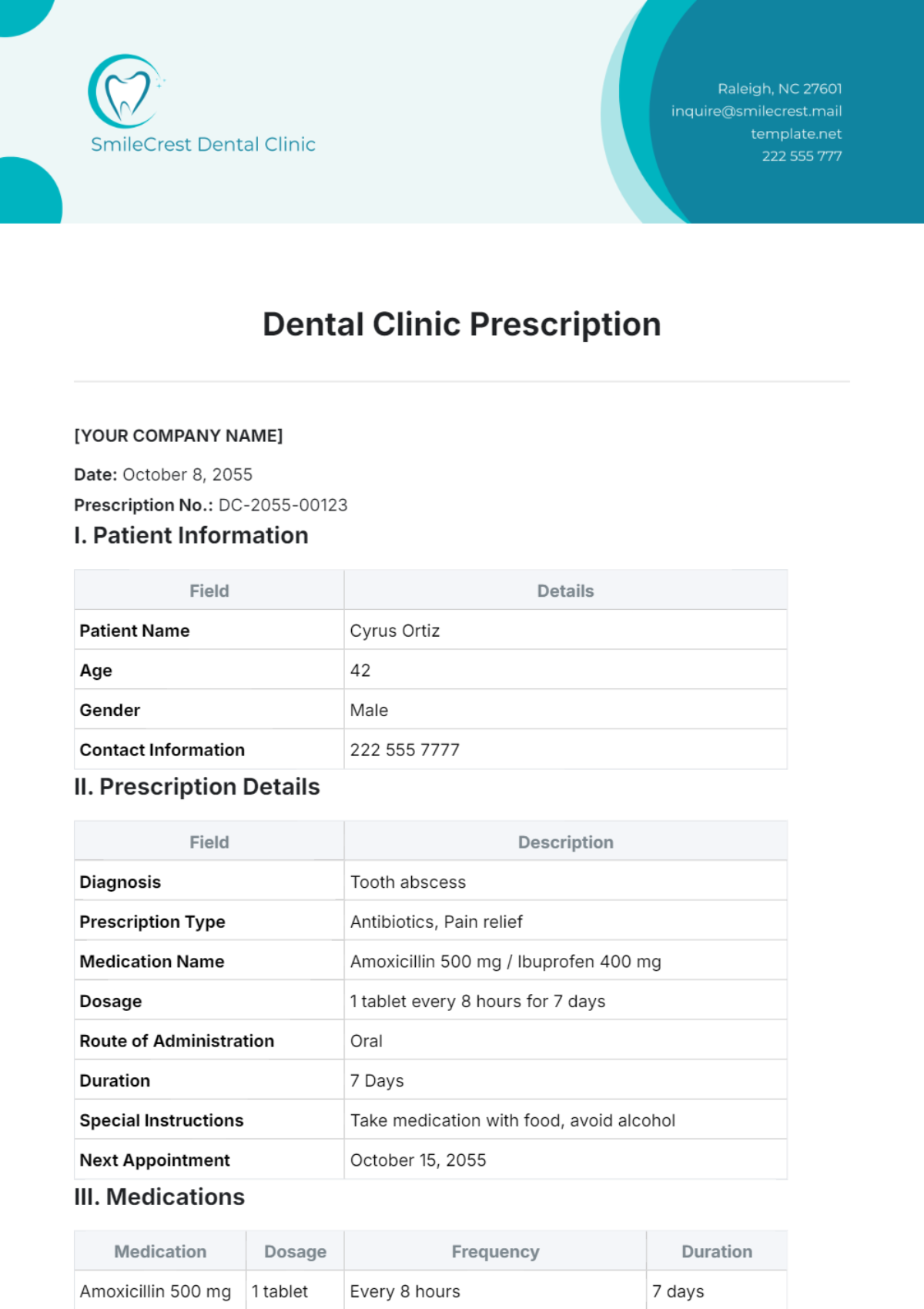
Antibiotics: Used to treat bacterial infections.
Antidepressants: Used to treat depression and anxiety disorders.
Antihypertensive: Used to manage high blood pressure.
B. Over-the-Counter (OTC) Medications
Pain Relievers: Such as acetaminophen and ibuprofen.
Cough and Cold Remedies: Including decongestants and antihistamines.
Antacids: Used to relieve heartburn and indigestion.
III. Medication Administration
A. Routes of Administration
Oral: Tablets, capsules, and liquids taken by mouth.
Topical: Creams, ointments, and patches applied to the skin.
Inhalation: Inhalers and nebulizers for respiratory conditions.
B. Dosage and Timing
Dosage Instructions: Following prescribed amounts and intervals.
Missed Doses: Guidelines on what to do if a dose is missed.
Timing: Importance of taking medication at the same time each day.
IV. Side Effects and Interactions
A. Common Side Effects
Gastrointestinal Issues: Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
Allergic Reactions: Rash, itching, and swelling.
Drowsiness or Dizziness: Particularly with certain pain relievers and antihistamines.
B. Drug Interactions
Food Interactions: Foods that may affect medication absorption.
Medication Interactions: Potential interactions between different drugs.
Alcohol and Substance Use: Effects on medication efficacy and safety.
V. Special Considerations
A. Pediatric Patients
Dosage Adjustments: Based on age and weight.
Administration Tips: Making medication palatable for children.
B. Geriatric Patients
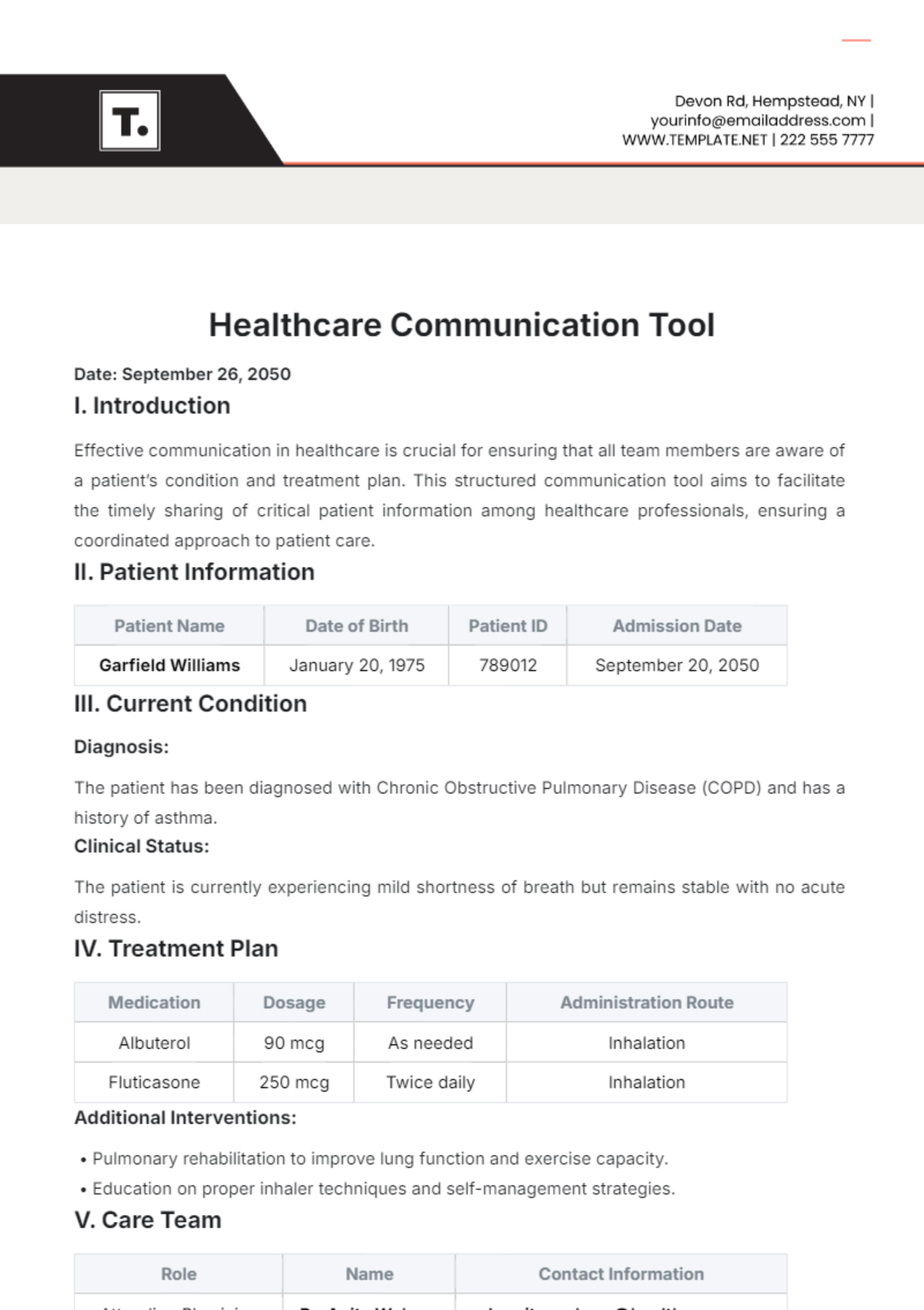
Polypharmacy Risks: Managing multiple medications.
Sensitivities: Adjusting doses due to age-related changes in drug metabolism.
VI. Case Studies
A. Effective Medication Management
Case | Description |
|---|---|
Case 1 | [Patient A] successfully manages diabetes through a combination of insulin therapy and lifestyle adjustments. |
Case 2 | [Patient B] overcomes depression with the aid of antidepressant medication alongside therapy sessions. |
B. Medication Errors and Prevention
Case 3: [Patient C] experiencing adverse effects due to incorrect dosing and the steps taken to rectify the situation.
VII. Resources and References
A. Additional Reading
Books: "Goodman & Gilman's: The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics"
Articles: "Current Trends in Medication Safety" by the FDA
B. Useful Websites
[YOUR COMPANY WEBSITE]
[YOUR COMPANY SOCIAL MEDIA]
VIII. Glossary
Pharmacokinetics: The study of how drugs move through the body.
Pharmacodynamics: The study of how drugs affect the body.
Contraindications: Specific situations where a drug should not be used.
IX. Action Plan
A. Individual Actions
Medication Adherence: Importance of following prescribed treatment plans.
Reporting Side Effects: Notifying healthcare providers of any adverse reactions.
B. Organizational Actions
Patient Education Programs: Developing initiatives to educate patients on medication use.
Medication Safety Policies: Implementing procedures to prevent medication errors.
X. Conclusion
A. Summary
Medications play a crucial role in healthcare, and understanding their proper use is essential. This guide provides the necessary information to ensure safe and effective medication management.
B. Call to Action
We strongly recommend that healthcare professionals, patients, and caregivers actively utilize this guide as a valuable resource for enhancing the practices associated with medication management and for achieving better outcomes in treatment.