Restaurant Specific Cost Coding Guide
I. Introduction
Welcome to [Your Company Name]'s Restaurant Specific Cost Coding Guide. This guide is designed to help restaurant owners and managers accurately categorize and manage their expenses. Proper cost coding is essential for financial reporting, budgeting, and overall financial health. By using this guide, you will be able to streamline your accounting processes, reduce errors, and gain better insights into your financial performance. With accurate cost coding, you can make more informed decisions that contribute to the profitability and sustainability of your restaurant.
This guide covers a comprehensive range of cost categories, each with unique codes for easy identification and tracking. Whether you are managing food and beverage costs, labor expenses, or marketing budgets, this guide provides the structure you need to maintain financial clarity. Additionally, we include practical examples and detailed explanations to ensure that every member of your team can effectively implement these codes.
II. Cost Coding Structure
A. Overview of Cost Coding
Cost coding involves assigning a unique identifier to each expense category, allowing for systematic tracking and reporting. This process is critical for ensuring that all expenses are accounted for and can be analyzed accurately. Our structure includes primary and secondary categories, designed to cover all aspects of restaurant operations. By implementing a consistent coding system, you can easily track spending patterns, identify cost-saving opportunities, and ensure compliance with financial regulations.
A well-structured cost coding system helps in creating detailed financial reports, which are essential for internal reviews and external audits. It also supports better communication between different departments within your organization, ensuring that everyone understands where resources are being allocated. Implementing this system will also aid in setting benchmarks and comparing performance across different periods.
B. Primary Categories
The primary categories represent broad expense areas. Each primary category is assigned a two-digit code, which simplifies the process of categorizing and reporting expenses. These categories cover the major cost drivers in a restaurant, providing a clear overview of where your money is being spent. Understanding these categories helps in setting up budgets and controlling costs more effectively.
Category | Code |
|---|---|
Food Costs | 10 |
Beverage Costs | 20 |
Labor Costs | 30 |
Occupancy Costs | 40 |
Operating Costs | 50 |
Marketing Costs | 60 |
Administrative Costs | 70 |
Miscellaneous Costs | 80 |
1. Food Costs (10)
Food costs encompass all expenses related to the purchase and preparation of food items. This category is crucial as it directly impacts your restaurant's profitability. Accurate tracking of food costs helps in pricing menu items appropriately and managing inventory effectively.
2. Beverage Costs (20)
Beverage costs include all expenses related to the purchase and preparation of drinks. This category is essential for restaurants and bars, where beverages can be a significant revenue stream. Proper coding and tracking of beverage costs can help in managing supply levels and identifying popular items.
3. Labor Costs (30)
Labor costs cover all expenses related to employee compensation. This includes wages, benefits, payroll taxes, and training expenses. Labor costs are often one of the largest expense categories for restaurants, making it critical to monitor and manage these costs closely.
4. Occupancy Costs (40)
Occupancy costs include expenses related to the physical space your restaurant occupies. This encompasses rent, utilities, property insurance, and property taxes. Managing occupancy costs is vital for maintaining profitability, especially in high-rent areas.
5. Operating Costs (50)
Operating costs cover a wide range of day-to-day expenses necessary for running your restaurant. This includes kitchen supplies, cleaning supplies, uniforms, and small wares. Keeping track of these costs helps in managing operational efficiency and ensuring that the restaurant runs smoothly.
6. Marketing Costs (60)
Marketing costs include all expenses related to promoting your restaurant. This can encompass advertising, promotions, public relations, social media, and loyalty programs. Effective marketing is crucial for attracting and retaining customers, making this category important for driving revenue growth.
7. Administrative Costs (70)
Administrative costs cover expenses related to the general management and administration of your restaurant. This includes office supplies, legal and professional fees, accounting services, licensing, and IT services. Proper management of administrative costs helps in ensuring that your restaurant operates efficiently and complies with regulatory requirements.
8. Miscellaneous Costs (80)
Miscellaneous costs cover any expenses that do not fit into the other primary categories. This can include bank charges, credit card fees, and other unexpected expenses. Tracking these costs helps in maintaining a comprehensive understanding of all expenses.
C. Secondary Categories
Secondary categories provide more detailed expense tracking within each primary category. Each secondary category is represented by a four-digit code, where the first two digits correspond to the primary category. This detailed coding allows for precise tracking and analysis of specific expense types.
1. Food Costs (10)
Subcategory | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
Produce | 1010 | Includes all fresh fruits and vegetables. |
Meat and Poultry | 1020 | Covers all meat and poultry purchases. |
Seafood | 1030 | Includes all types of seafood. |
Dairy | 1040 | Covers milk, cheese, butter, and other dairy products. |
Dry Goods | 1050 | Includes grains, rice, pasta, and other non-perishable items. |
Bakery Products | 1060 | Covers bread, pastries, and other baked goods. |
Beverages (Non-Alcoholic) | 1070 | Includes soft drinks, coffee, tea, and juices. |
Condiments and Spices | 1080 | Covers all condiments, spices, and seasonings. |
Prepared Food | 1090 | Includes pre-prepared items like soups and salads. |
2. Beverage Costs (20)
Subcategory | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
Alcoholic Beverages | 2010 | Includes beer, wine, spirits, and other alcoholic drinks. |
Non-Alcoholic Beverages | 2020 | Covers soft drinks, juices, water, and other non-alcoholic beverages. |
Beverage Supplies | 2030 | Includes items like glassware, straws, and napkins used in beverage service. |
3. Labor Costs (30)
Subcategory | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
Salaries and Wages | 3010 | Covers regular and overtime wages for all employees. |
Employee Benefits | 3020 | Includes health insurance, retirement plans, and other benefits. |
Payroll Taxes | 3030 | Covers employer-paid taxes such as Social Security and Medicare. |
Training and Development | 3040 | Includes costs for employee training programs and materials. |
4. Occupancy Costs (40)
Subcategory | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
Rent | 4010 | Covers monthly rental payments for restaurant premises. |
Utilities | 4020 | Includes electricity, water, gas, and other utility expenses. |
Property Insurance | 4030 | Covers insurance policies for the restaurant property. |
Property Taxes | 4040 | Includes taxes levied on the property by local authorities. |
Repairs and Maintenance | 4050 | Covers costs for repairing and maintaining the property. |
5. Operating Costs (50)
Subcategory | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
Kitchen Supplies | 5010 | Includes utensils, cookware, and other kitchen essentials. |
Cleaning Supplies | 5020 | Covers detergents, disinfectants, and other cleaning products. |
Uniforms | 5030 | Includes uniforms and aprons for staff. |
Small wares | 5040 | Covers small kitchen equipment and tools. |
Linens and Laundry | 5050 | Includes tablecloths, napkins, and laundry services. |
6. Marketing Costs (60)
Subcategory | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
Advertising | 6010 | Covers print, online, and media advertising expenses. |
Promotions | 6020 | Includes costs for special offers and discounts. |
Public Relations | 6030 | Covers PR campaigns and events. |
Social Media | 6040 | Includes expenses for social media marketing and management. |
Loyalty Programs | 6050 | Covers costs for customer loyalty and rewards programs. |
7. Administrative Costs (70)
Subcategory | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
Office Supplies | 7010 | Includes pens, paper, and other office essentials. |
Legal and Professional Fees | 7020 | Covers costs for legal services and consulting. |
Accounting Services | 7030 | Includes fees for accounting and bookkeeping services. |
Licensing and Permits | 7040 | Covers fees for business licenses and permits. |
IT Services | 7050 | Includes costs for IT support and software. |
8. Miscellaneous Costs (80)
Subcategory | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
Bank Charges | 8010 | Covers fees charged by banks for account maintenance and transactions. |
Credit Card Fees | 8020 | Includes fees for processing credit card payments. |
Miscellaneous Expenses | 8030 | Covers any other expenses that do not fit into the above categories. |
III. Implementation Guide
A. Setting Up Cost Codes
Identify All Expense Types: Review all current and anticipated expenses to ensure comprehensive coverage. Start by listing out every type of expense your restaurant incurs, from food and beverages to cleaning supplies and marketing costs.
Assign Codes: Use the provided coding structure to assign codes to each expense type. Make sure that each category and subcategory has a unique code, and ensure that the codes are easy to understand and use.
Integrate with Accounting Software: Ensure your accounting software can handle the coding structure for seamless tracking. Most modern accounting systems allow for custom coding structures, so configure your system to match the codes outlined in this guide.
B. Training Staff
Conduct Training Sessions: Train relevant staff on the importance of cost coding and how to apply codes correctly. Organize workshops or training sessions to explain the coding system and demonstrate how to use it in everyday tasks.
Provide Reference Materials: Supply this guide and other reference materials to ensure consistency. Make sure that all staff have access to these materials and understand how to use them.
C. Monitoring and Reporting
Regular Reviews: Conduct regular reviews of expense reports to ensure proper coding. Schedule periodic audits to check that expenses are being coded correctly and address any discrepancies.
Adjust as Needed: Update codes and categories as new expense types arise or business needs change. The cost coding system should be flexible enough to accommodate changes in your business operations.
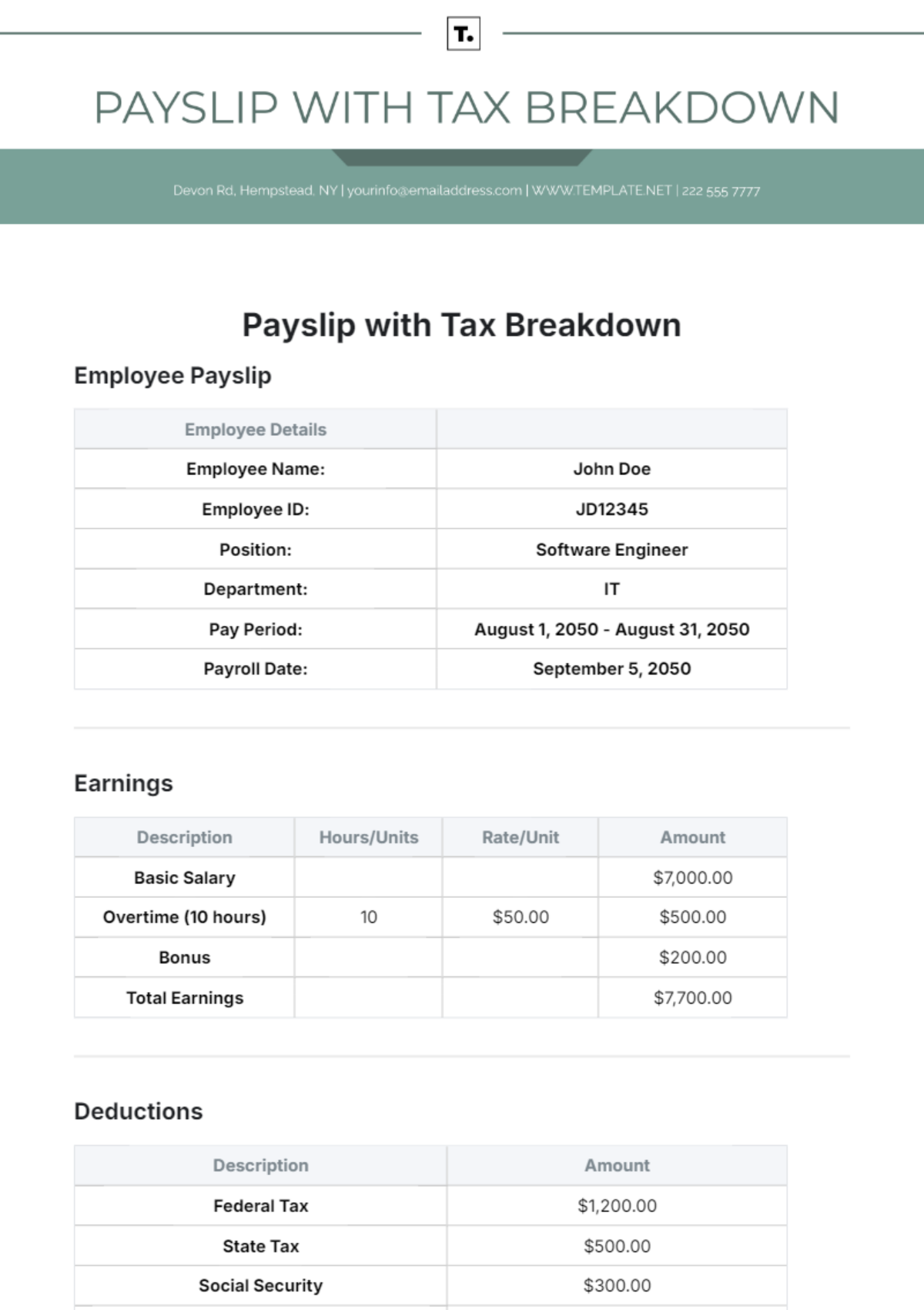
IV. Sample Cost Report
A. Monthly Cost Summary
A sample monthly cost summary provides a high-level overview of expenses categorized by primary categories. This helps in identifying major expense areas and making informed financial decisions.
Category | Code | Amount |
|---|---|---|
Food Costs | 10 | [$00,000] |
Beverage Costs | 20 | [$00,000] |
Labor Costs | 30 | [$00,000] |
Occupancy Costs | 40 | [$00,000] |
Operating Costs | 50 | [$00,000] |
Marketing Costs | 60 | [$00,000] |
Administrative Costs | 70 | [$00,000] |
Miscellaneous Costs | 80 | [$00,000] |
B. Detailed Expense Report (Food Costs)
A detailed expense report for food costs breaks down the total food expense into specific subcategories. This provides a more granular view, allowing for better cost management and identification of savings opportunities.
Subcategory | Code | Amount |
|---|---|---|
Produce | 1010 | [$0,000] |
Meat and Poultry | 1020 | [$0,000] |
Seafood | 1030 | [$0,000] |
Dairy | 1040 | [$0,000] |
Dry Goods | 1050 | [$0,000] |
Bakery Products | 1060 | [$0,000] |
Beverages (Non-Alcoholic) | 1070 | [$0,000] |
Condiments and Spices | 1080 | [$0,000] |
Prepared Food | 1090 | [$0,000] |
V. Conclusion
Proper cost coding is vital for effective financial management in the restaurant industry. By following [Your Company Name]'s Restaurant Specific Cost Coding Guide, you can achieve greater accuracy in tracking expenses, making informed financial decisions, and improving overall profitability. Accurate cost coding not only helps in day-to-day financial management but also plays a crucial role during financial audits and when applying for loans or investments. It provides a clear picture of where money is being spent and helps in identifying areas where costs can be reduced.
Implementing this guide will help you streamline your accounting processes, reduce errors, and gain better insights into your financial performance. For further assistance, please contact [Your Company Name] at [Your Company Email]. We are here to support you in achieving financial excellence and ensuring the success of your restaurant.