I. Introduction
A. Purpose of the Analysis
The purpose of this Architecture Gap Analysis is to identify discrepancies between the current state of architectural projects at [Your Company Name] and the desired future state. This analysis aims to highlight areas of improvement in design, structural integrity, and functional efficiency to ensure that [Your Company Name] remains competitive and meets the highest industry standards.
B. Scope of the Analysis
This analysis covers all major architectural projects undertaken by [Your Company Name]. It includes an evaluation of current architectural designs, resource capabilities, and performance metrics, compared against the envisioned future state of these elements. The scope extends to assessing human, technological, and financial resources, as well as project completion times, cost efficiency, and client satisfaction.
C. Objectives
The objectives of this gap analysis are:
To provide a comprehensive overview of the current architectural state.
To define the desired future state of architecture at [Your Company Name].
To identify gaps in design, structural integrity, and functional efficiency.
To propose actionable recommendations to bridge these gaps.
To develop an implementation plan for achieving the desired future state.
D. Methodology
The methodology for this gap analysis includes a combination of qualitative and quantitative approaches. Data is collected through internal documentation review, interviews with key stakeholders, and analysis of performance metrics. Comparative analysis is used to identify gaps, and root cause analysis helps in understanding underlying issues. Recommendations are developed based on industry best practices and expert insights.
II. Current State Assessment
A. Overview of Current Architecture
Architectural Design
The current architectural designs at [Your Company Name] exhibit a blend of contemporary and traditional styles. While many projects have received acclaim for their aesthetic appeal, there are concerns regarding the consistency and innovation in design elements.
Structural Integrity
Structural integrity plays a crucial role in the success of architectural projects, ensuring stability and safety. Recent evaluations and audits have demonstrated that, although a majority of buildings are compliant with established safety regulations and standards, there are sporadic instances where the materials employed and the methods of construction have fallen short. These shortcomings occasionally result in various minor structural problems.
Functional Efficiency
Functional efficiency relates to the effectiveness with which architectural designs fulfill their intended functions. Client feedback indicates that although residential projects tend to succeed in achieving functional effectiveness, some commercial projects have faced challenges related to the optimal use of space and ensuring easy access.
B. Current Resources and Capabilities
Human Resources
[Your Company Name] employs a team of skilled architects, engineers, and support staff. However, there is a noted shortage of specialized roles such as sustainability experts and advanced materials engineers.
Technological Resources
The technological infrastructure within the organization encompasses sophisticated design software along with various simulation tools. Despite these advanced technologies, their integration into the regular workflows of the organization is less than ideal. This inadequate integration results in a suboptimal usage of the accessible resources, causing them to be underutilized.
Financial Resources
From an economic standpoint, [Your Company Name] maintains a stable financial position, supported by consistent revenue flows derived from projects that are currently in progress. Nevertheless, it is important to note that there are periodic budgetary restrictions that somewhat restrain the company's capacity to allocate funds toward the acquisition of the latest technological advancements and superior-quality materials.
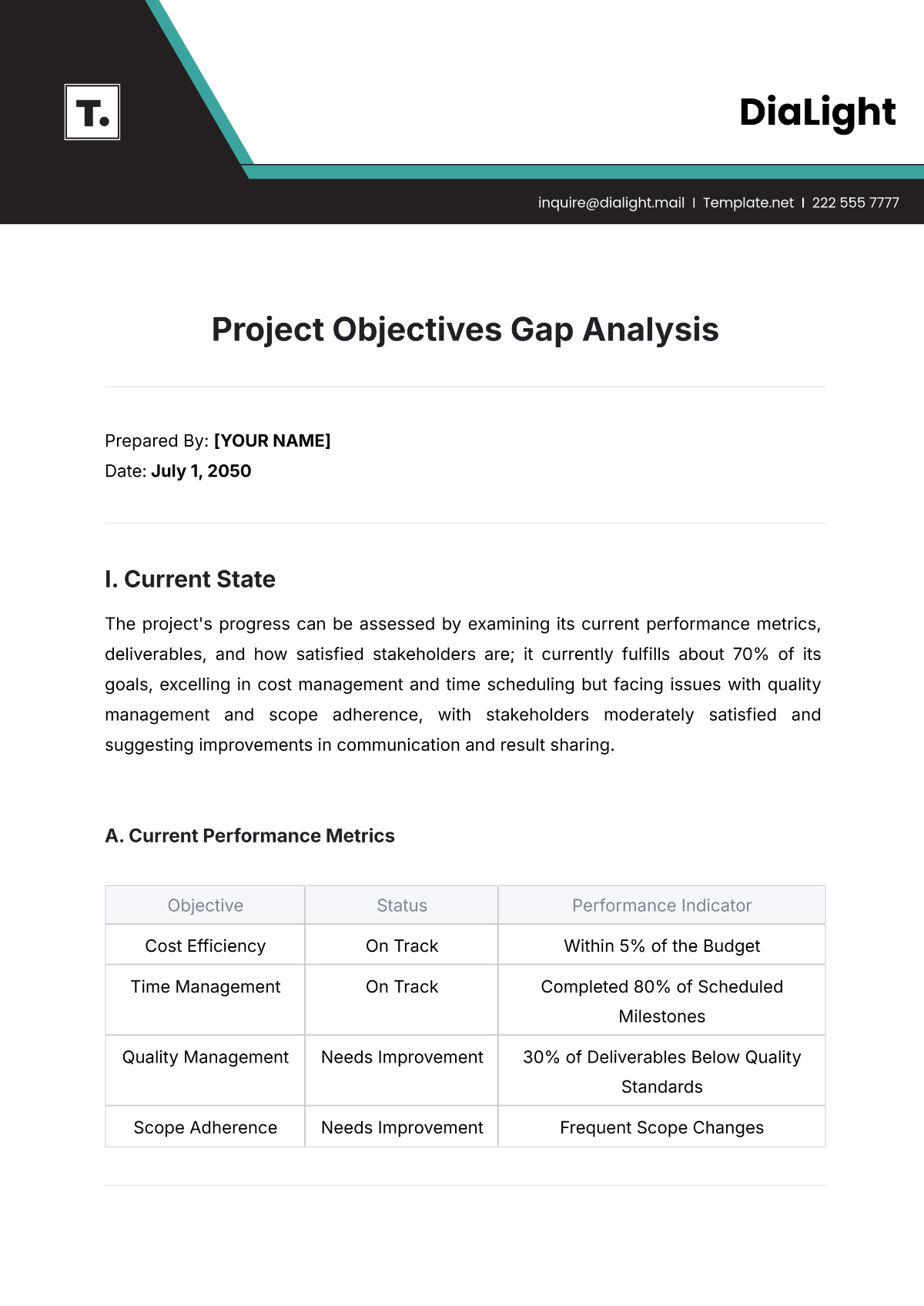
C. Current Performance Metrics
Project Completion Times
Average Project Completion Times Table
Project Type | Average Completion Time (Months) |
|---|---|
Residential | 12 |
Commercial | 18 |
Institutional | 24 |
Cost Efficiency
Cost efficiency is measured by comparing actual project costs against budgeted costs. Current data shows that while residential projects are completed within budget, commercial and institutional projects often exceed budget due to unforeseen complications.
Client Satisfaction
Client satisfaction is assessed through post-project surveys. Residential projects have a high satisfaction rate of 90%, whereas commercial and institutional projects have lower satisfaction rates of 75% and 70%, respectively.
III. Desired Future State
A. Vision for the Future Architecture
The vision for [Your Company Name] is to be a leading architectural firm recognized for innovative design, structural excellence, and unparalleled functional efficiency. This involves adopting sustainable practices, utilizing advanced materials, and ensuring all projects meet the highest standards of safety and usability.
B. Target Architectural Design
The target state for architectural design involves creating more innovative and sustainable designs that reflect modern trends and client needs. This includes incorporating green building practices, smart building technologies, and adaptive reuse of structures.
C. Desired Structural and Functional Improvements
The aim to enhance structural integrity involves incorporating advanced materials and employing sophisticated construction techniques in order to increase both durability and safety. From a functional perspective, the objective is to maximize the use of available space and to guarantee that all designs are not only user-friendly but also accessible to everyone.
D. Future Resource and Capability Requirements
Human Resources
The future state requires a more diversified team with expertise in sustainable design, advanced materials, and smart building technologies. This includes hiring additional sustainability experts, materials scientists, and technology integration specialists.
Technological Resources
Investments in state-of-the-art design software, Building Information Modeling (BIM), and simulation tools are crucial. Additionally, training staff to fully utilize these technologies will enhance overall efficiency and innovation.
Financial Resources
Adequate financial resources are necessary to support technological upgrades, staff training, and the adoption of new materials and practices. This involves increasing project budgets and exploring additional funding sources such as grants and partnerships.
E. Future Performance Metrics
Improved Project Completion Times
Target Project Completion Times Table
Project Type | Target Completion Time (Months) |
|---|---|
Residential | 10 |
Commercial | 15 |
Institutional | 20 |
Enhanced Cost Efficiency
The objective is to successfully finish all projects within the allocated budgetary constraints by enhancing both planning and risk management procedures. To achieve this, it is essential to adopt cost estimation techniques that are more precise and to implement more effective contingency planning strategies.
Increased Client Satisfaction
Targeting a client satisfaction rate of 95% across all project types through improved design, structural integrity, and functional efficiency. Enhanced communication and feedback mechanisms will also be implemented to better meet client expectations.
IV. Gap Identification
A. Comparison of Current State and Desired Future State
Comparing the current and desired states reveals significant gaps in design innovation, structural integrity, and functional efficiency. While the current state shows competence in basic architectural practices, the desired state aims for excellence and leadership in the field.
B. Identification of Gaps in Architectural Design
Current designs lack consistent innovation and sustainability. The desired state emphasizes the need for more creative and eco-friendly solutions, highlighting a gap in design philosophy and execution.
C. Identification of Gaps in Structural Integrity
While most structures meet basic safety standards, there are gaps in using advanced materials and construction techniques that could significantly enhance durability and safety.
D. Identification of Gaps in Functional Efficiency
Many commercial enterprises encounter difficulties with regard to the optimization of space utilization and ensuring easy accessibility, which highlights existing deficiencies in the functional elements of architectural and interior design. Moving forward, it will be essential to devote greater consideration to enhancing the user experience and improving the practical usability of these spaces to meet future needs effectively.
E. Identification of Resource Gaps
Human Resources
There exists a notable shortage of highly specialized roles, including those of sustainability experts and advanced materials engineers, roles which are crucial for realizing the anticipated future state.
Technological Resources
While there are advanced technologies available, the level of their integration into everyday workflows remains inadequate. Consequently, there is a significant need for enhanced adoption of these technologies, coupled with improved training programs to facilitate their integration.
Financial Resources
Financial limitations are currently constraining the ability to invest in innovative technologies and new materials. It is essential to procure additional funding in order to facilitate and support the transition toward achieving the envisioned future state.
F. Identification of Performance Gaps
Performance gaps are evident in project completion times, cost efficiency, and client satisfaction, particularly for commercial and institutional projects. These gaps highlight the need for improved planning, resource allocation, and client engagement strategies.
V. Gap Analysis
A. Root Cause Analysis of Gaps
Architectural Design Issues
The primary cause of design gaps is a reliance on traditional design approaches and insufficient emphasis on innovation and sustainability. Limited exposure to global trends and best practices also contributes to this issue.
Structural Integrity Concerns
Structural gaps arise from the use of conventional materials and construction methods. There is a lack of investment in research and adoption of advanced materials that could enhance structural performance.
Functional Efficiency Challenges
Functional gaps are primarily due to inadequate user-centric design processes. The design teams often prioritize aesthetic appeal over practical usability, leading to issues in space utilization and accessibility.
B. Resource and Capability Deficiencies
Human resource deficiencies are evident in the lack of specialized roles. Technological gaps result from underutilization of available tools and insufficient training. Financial constraints hinder the ability to invest in necessary upgrades and innovations.
C. Performance Shortcomings
Performance gaps stem from inefficient project management practices, leading to delays and cost overruns. Additionally, the lack of robust client feedback mechanisms results in lower client satisfaction rates.
VI. Recommendations
A. Strategies to Address Architectural Design Gaps
To bridge design gaps, [Your Company Name] should:
Adopt a design thinking approach that emphasizes innovation and sustainability.
Encourage continuous learning and exposure to global architectural trends.
Implement green building practices and smart technologies in all projects.
B. Strategies to Improve Structural Integrity
Improving structural integrity requires:
Investing in research and development of advanced materials.
Training construction teams in modern building techniques.
Implementing rigorous quality control measures throughout the construction process.
C. Strategies to Enhance Functional Efficiency
To enhance functional efficiency:
Adopt a user-centric design process that prioritizes practical usability.
Conduct thorough space utilization studies during the design phase.
Ensure all designs meet accessibility standards and client needs.
D. Resource and Capability Development Plans
Human Resources
Recruitment and training plans should focus on:
Hiring sustainability experts, materials scientists, and technology integration specialists.
Providing ongoing professional development and training for existing staff.
Technological Investments
Invest in state-of-the-art design software, BIM, and simulation tools. Ensure all staff are trained to fully utilize these technologies.
Financial Planning
Secure additional funding through grants, partnerships, and increased project budgets. Implement robust financial planning and management processes to ensure efficient use of resources.
E. Performance Improvement Initiatives
To improve performance:
Implement effective project management practices to reduce completion times and costs.
Develop comprehensive client feedback mechanisms to enhance satisfaction rates.
Monitor and evaluate performance regularly to identify and address issues promptly.
VII. Implementation Plan
A. Action Plan
The action plan includes short-term and long-term actions to address identified gaps and achieve the desired future state. Key steps involve resource allocation, risk management, and regular monitoring and evaluation to ensure successful implementation. This plan will be detailed in the following section to provide a clear roadmap for [Your Company Name] to transition from the current state to the desired future state.
By following this detailed analysis and implementing the recommended strategies, [Your Company Name] will be well-positioned to achieve its vision of becoming a leading architectural firm known for innovation, structural excellence, and unparalleled functional efficiency.
VIII. Conclusion
A. Summary of Findings
This gap analysis for [Your Company Name] has identified significant discrepancies between the current state and the desired future state in architectural design, structural integrity, functional efficiency, resources, and performance metrics. The analysis revealed a need for increased innovation, advanced materials, improved usability, enhanced technology integration, and better financial management.
B. Summary of Recommendations
To bridge these gaps, we recommend adopting a design thinking approach, investing in advanced materials and technologies, enhancing user-centric design processes, recruiting specialized talent, and securing additional financial resources. Implementing these strategies will help achieve improved project completion times, cost efficiency, and client satisfaction.
C. Expected Outcomes
By addressing the identified gaps and implementing the recommended strategies, [Your Company Name] is expected to enhance its architectural designs, structural integrity, and functional efficiency. This will lead to higher project quality, increased client satisfaction, and a stronger market position.
D. Final Remarks
This gap analysis provides a clear roadmap for [Your Company Name] to transition from its current state to the desired future state. By focusing on innovation, sustainability, and efficiency, the company can achieve its vision of becoming a leading architectural firm.