Cafe Specific Cost Coding Guide
I. Introduction
Our Cafe Specific Cost Coding Guide is designed to provide a standardized framework for categorizing and tracking costs associated with our cafe operations. By implementing a consistent cost coding system, we aim to improve our ability to analyze expenses, identify cost-saving opportunities, and make informed business decisions.
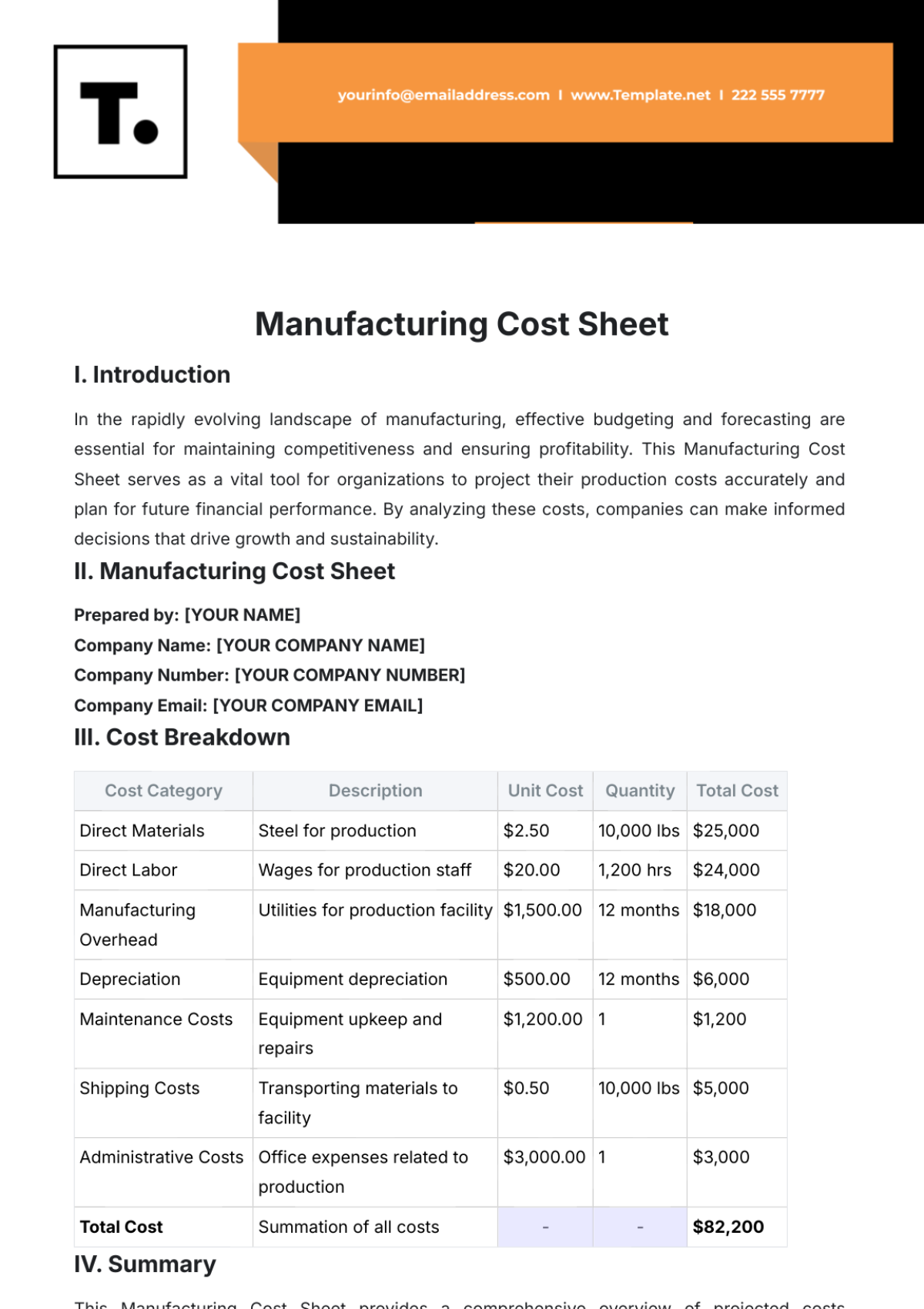
II. Cost Code Structure
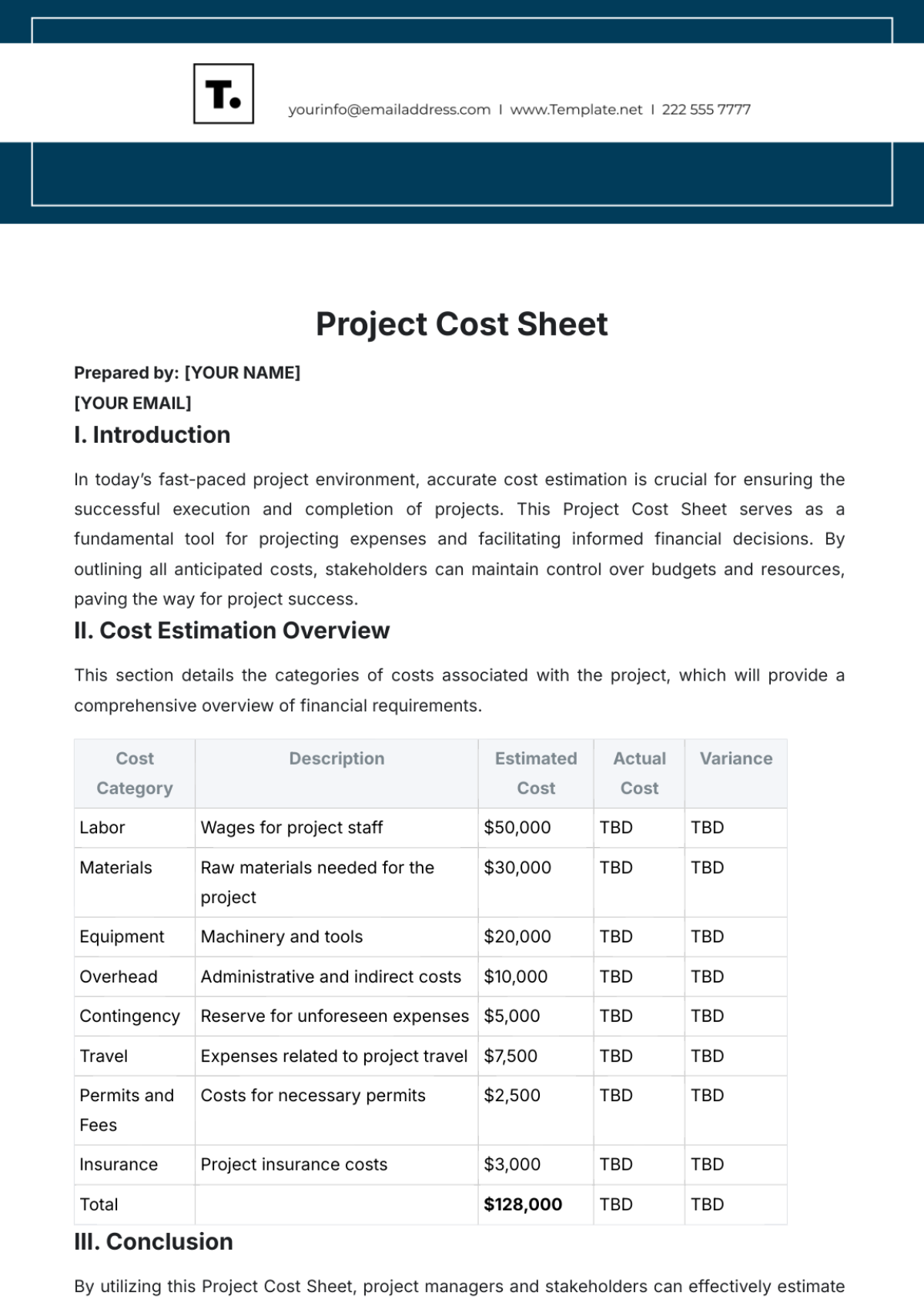
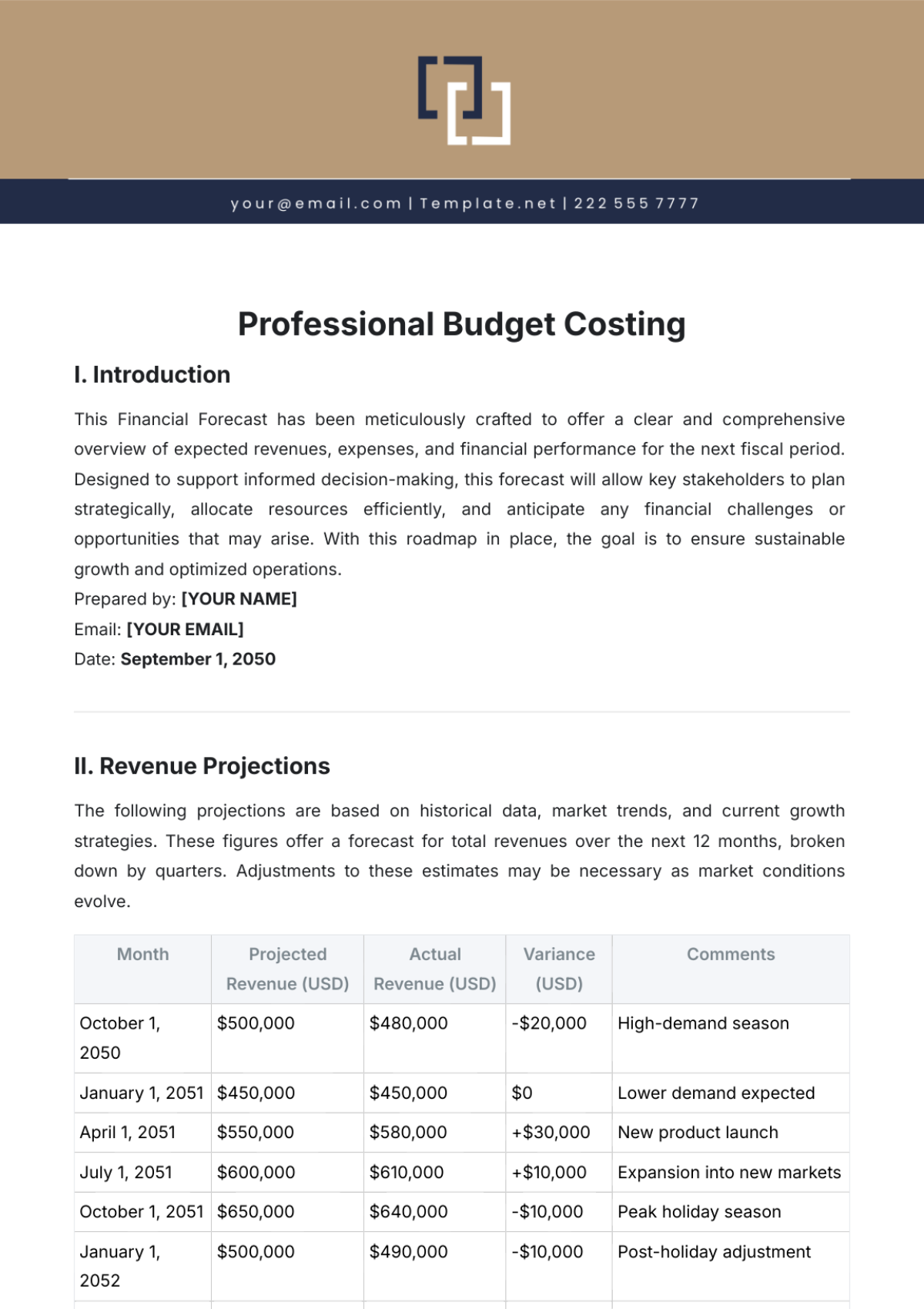
Our cost coding system is structured into three main categories: Food Costs, Labor Costs, and Overhead Costs. Each category is further divided into subcategories to provide a detailed breakdown of expenses. The following table outlines our cost code structure:
Category | Subcategory |
|---|---|
Food Costs | Ingredients |
Packaging | |
Labor Costs | Front-of-House Staff |
Back-of-House Staff | |
Management | |
Overhead Costs | Rent |
Utilities | |
Marketing |
III. Food Costs
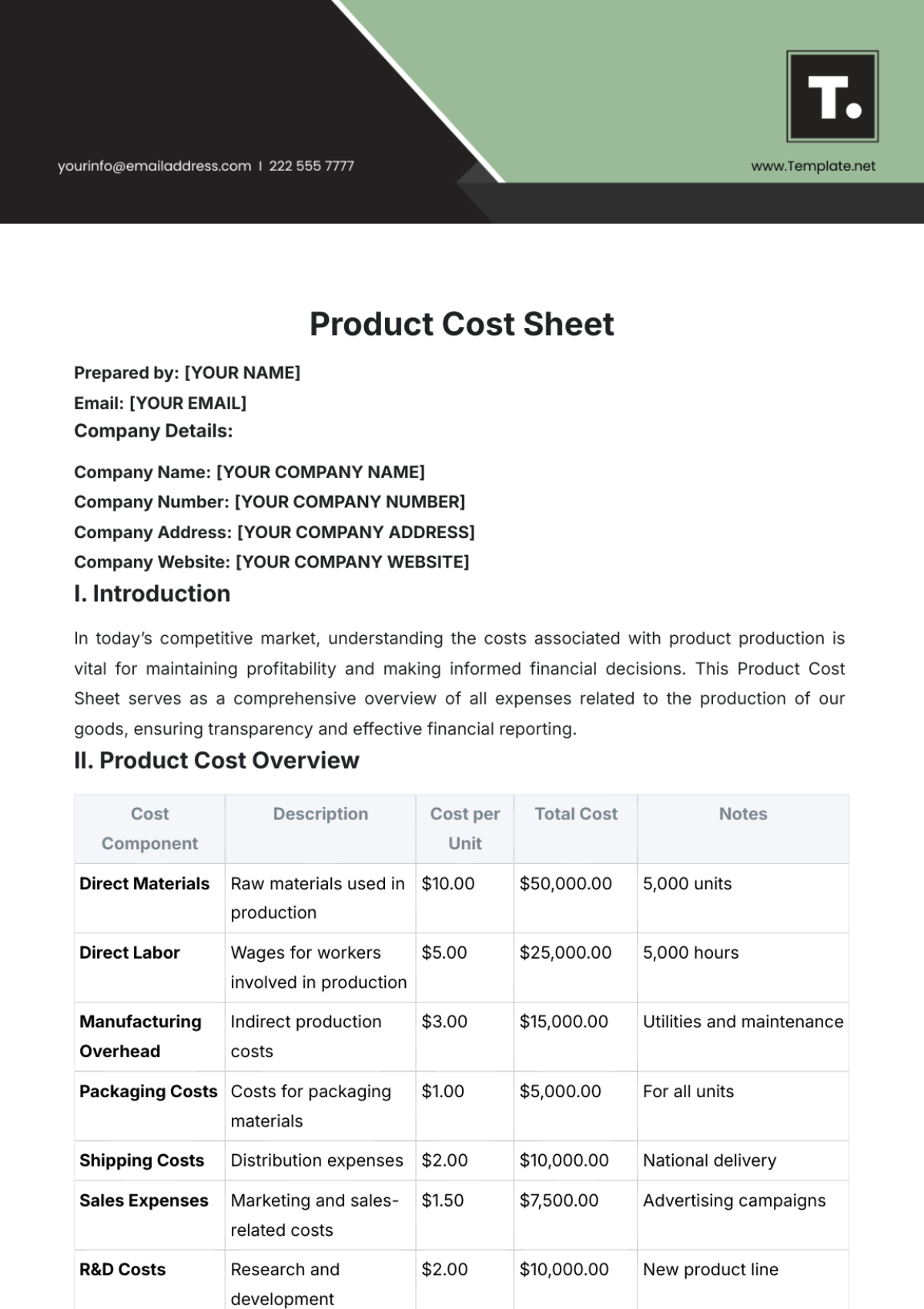
Our food costs are categorized into two main subcategories: Ingredients and Packaging. These categories encompass the costs associated with the raw materials used in food preparation as well as the packaging materials used for serving and storage. The following table provides examples of cost codes within each subcategory:
Subcategory | Cost Code |
|---|---|
Ingredients | Coffee Beans |
Baked Goods | |
Dairy Products | |
Packaging | Disposable Cups |
Food Containers | |
Wrapping Materials |
IV. Labor Costs
Our labor costs are divided into three subcategories: Front-of-House Staff, Back-of-House Staff, and Management. These categories encompass the wages and salaries of our staff involved in customer service, food preparation, and managerial roles. The following table provides examples of cost codes within each subcategory:
Subcategory | Cost Code |
|---|---|
Front-of-House Staff | Barista Wages |
Server Wages | |
Back-of-House Staff | Chef Wages |
Kitchen Helper Wages | |
Management | Manager Salary |
Supervisor Salary |
V. Overhead Costs
Our overhead costs are divided into three subcategories: Rent, Utilities, and Marketing. These categories encompass the costs associated with maintaining our physical location, utilities usage, and marketing efforts. The following table provides examples of cost codes within each subcategory:
Subcategory | Cost Code |
|---|---|
Rent | Rent Expense |
Utilities | Electricity Bill |
Water Bill | |
Internet Bill | |
Marketing | Advertising Costs |
Promotional Events | |
Printing Materials |
VI. Cost Code Usage
Effective utilization of cost codes is essential for accurate expense tracking and financial analysis. To ensure consistency and accuracy, the following guidelines should be followed when assigning cost codes to expenses:
Identify the Nature of the Expense: Determine the category and subcategory to which the expense belongs (e.g., Food Costs, Labor Costs, Overhead Costs).
Select the Appropriate Cost Code: Choose the specific cost code that best represents the nature of the expense within the identified category and subcategory.
Avoid Overlapping Codes: Each expense should be assigned a single cost code to prevent duplication or confusion in reporting.
Use Descriptive Labels: Assign descriptive labels to cost codes to provide clarity and facilitate easy identification during reporting and analysis.
Consistent Application: Ensure that cost codes are consistently applied across all expenses to maintain uniformity and accuracy in reporting.
Review and Update Regularly: Periodically review and update cost codes to reflect changes in expense categories or to accommodate new types of expenses.
VII. Cost Code Reporting and Analysis
Accurate and meaningful cost reporting and analysis rely on the consistent use of cost codes. The following steps outline how to generate cost reports using cost codes:
Compile Expense Data: Collect all relevant expense data, ensuring that each expense is assigned the appropriate cost code.
Generate Cost Reports: Use accounting software or spreadsheet tools to generate cost reports, categorizing expenses based on the assigned cost codes.
Analyze Cost Reports: Review cost reports to identify trends, anomalies, and areas where cost-saving measures can be implemented.
Compare Actual vs. Budgeted Costs: Compare actual expenses to budgeted costs to assess financial performance and make necessary adjustments.
Use Reports for Decision-Making: Utilize cost reports to make informed decisions regarding budget allocation, pricing strategies, and operational improvements.
By adhering to these guidelines, we can effectively track and analyze our expenses, enabling us to make informed decisions that contribute to the overall success of our cafe.