School Analysis Guide
I. Introduction
A comprehensive school analysis is vital for understanding the various factors that influence the educational environment and outcomes. This guide aims to provide a systematic approach for conducting a thorough analysis of a school’s performance, facilities, resources, and overall environment. By identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT), educational leaders can make informed decisions to enhance the quality of education provided.
II. Objectives of the School Analysis
Setting clear objectives is crucial for the effectiveness of the school analysis. These objectives help in guiding the analysis process and ensuring that all relevant aspects are considered. Each objective focuses on a critical area of the school’s operations and performance, providing a comprehensive view of strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities for improvement.
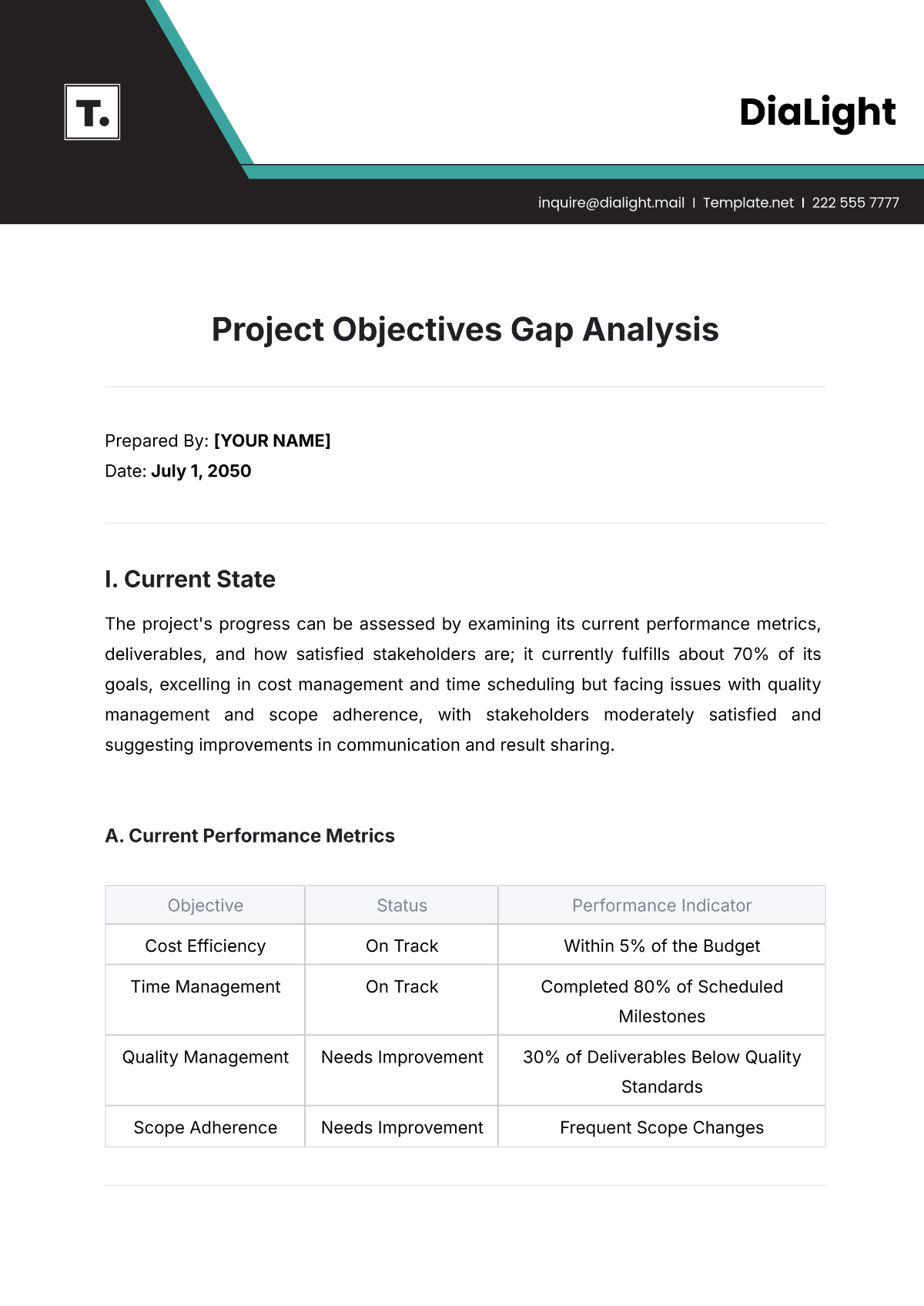
A. Identify Strengths and Weaknesses
Objective: To determine the areas where the school excels and areas that need improvement.
Identifying strengths and weaknesses is fundamental for understanding the current state of the school. This objective ensures a balanced view, highlighting both successes and areas that require attention.
Key Components:
Academic Performance: Evaluate student achievement and curriculum effectiveness.
Standardized Test Scores: Review scores from state and national assessments to gauge overall academic achievement and identify trends.
Grade Point Averages (GPAs): Analyze GPAs across different grades to understand academic performance over time.
Subject-Specific Performance: Examine performance in key subjects such as Math, Science, English, and Social Studies to identify strengths and weaknesses in specific areas.
Graduation Rates: Assess the percentage of students who graduate on time and identify any factors contributing to delays or dropouts.
College and Career Readiness: Evaluate how well the school prepares students for post-secondary education and careers, including participation in Advanced Placement (AP) courses and vocational programs.
Teaching Quality: Assess teacher qualifications, training, and instructional methods.
Teacher Certification and Licensure: Ensure that teachers hold the necessary certifications and licenses required for their positions.
Professional Development: Review the availability and effectiveness of professional development programs. Determine if teachers have access to ongoing training that enhances their instructional skills and knowledge.
Teaching Methods: Observe classroom practices to evaluate the use of innovative and effective teaching methods. Assess the implementation of differentiated instruction to meet diverse student needs.
Teacher Evaluation: Analyze results from teacher evaluations and student feedback to identify areas of strength and areas needing improvement.
Student Support Services: Review the availability and quality of counseling, tutoring, and extracurricular activities.
Counseling Services: Evaluate the availability and effectiveness of counseling services, including academic advising, college and career counseling, and mental health support.
Tutoring Programs: Assess the accessibility and impact of tutoring programs designed to support students who need additional academic assistance.
Extracurricular Activities: Examine the range and quality of extracurricular activities offered, including sports, arts, clubs, and organizations. Determine participation rates and the impact on student development.
Special Education Services: Review the support provided to students with disabilities, including Individualized Education Programs (IEPs) and the availability of specialized staff.
B. Evaluate Resources and Facilities
Objective: To assess the adequacy and condition of the school’s physical and educational resources.
Evaluating resources and facilities is essential for ensuring that the school environment supports effective teaching and learning. This objective focuses on both the physical infrastructure and the resources available to students and teachers.
Key Components:
Infrastructure: Examine the condition and suitability of buildings, classrooms, and common areas.
Building Condition: Inspect the overall condition of school buildings, including structural integrity, safety features, and maintenance needs.
Classroom Environment: Assess the adequacy of classroom spaces, including size, layout, lighting, and ventilation. Determine if classrooms are conducive to learning and adequately equipped with necessary furniture and tools.
Common Areas: Evaluate the condition and usability of common areas such as libraries, gyms, cafeterias, and outdoor spaces. Ensure these areas are well-maintained and meet the needs of students and staff.
Learning Materials: Evaluate the availability and quality of textbooks, technology, and other instructional materials.
Textbooks and Resources: Review the availability, condition, and relevance of textbooks and other printed materials. Ensure that materials are up-to-date and aligned with the curriculum.
Technology Integration: Assess the availability and use of technology, including computers, tablets, smartboards, and software. Determine if students and teachers have adequate access to technology and if it is effectively integrated into teaching and learning.
Library Resources: Evaluate the resources available in the school library, including books, periodicals, and digital media. Ensure that the library supports research and learning across all subject areas.
Financial Resources: Analyze the school’s budget and funding sources.
Budget Analysis: Review the school’s budget to understand how funds are allocated across various departments and programs. Identify any areas of financial strain or underfunding.
Funding Sources: Examine the diversity and stability of funding sources, including government funding, grants, donations, and fundraising efforts.
Financial Management: Assess the effectiveness of financial management practices, including budgeting, accounting, and financial planning. Determine if resources are used efficiently and strategically to support school goals.
C. Understand Stakeholder Perspectives
Objective: To gather insights from students, parents, teachers, and the community to inform decision-making.
Understanding the perspectives of various stakeholders is crucial for making informed and inclusive decisions. This objective focuses on collecting and analyzing feedback from the school community to identify strengths, concerns, and areas for improvement.
Key Components:
Surveys and Interviews: Conduct surveys and interviews to collect feedback from all stakeholders.
Student Surveys: Design and distribute surveys to gather students' perspectives on their educational experiences, including academic challenges, support services, and school climate.
Parent Surveys: Collect feedback from parents on their satisfaction with the school, communication with teachers and administration, and their child’s academic and social development.
Teacher Surveys: Gather teachers' insights on curriculum effectiveness, professional development needs, and overall job satisfaction.
Interviews: Conduct one-on-one interviews with selected stakeholders to gain deeper insights into specific issues and experiences.
Focus Groups: Organize focus groups to discuss specific issues in-depth.
Student Focus Groups: Facilitate discussions with groups of students to explore their views on teaching methods, school culture, and extracurricular activities.
Parent Focus Groups: Engage parents in conversations about their expectations, concerns, and suggestions for school improvement.
Teacher Focus Groups: Hold focus groups with teachers to discuss instructional practices, professional development, and support services. Identify common challenges and potential solutions.
Community Engagement: Evaluate the school’s relationship with the local community and identify areas for improvement.
Community Partnerships: Assess the school’s partnerships with local businesses, non-profit organizations, and community groups. Determine the impact of these partnerships on student learning and community involvement.
Community Programs: Review the effectiveness of community outreach and engagement programs, such as open houses, volunteer opportunities, and community service projects.
Feedback Mechanisms: Establish mechanisms for ongoing feedback from the community, including suggestion boxes, online portals, and regular community meetings.
Setting clear objectives for the school analysis ensures a comprehensive and focused approach to evaluating the school’s performance and environment. By identifying strengths and weaknesses, evaluating resources and facilities, and understanding stakeholder perspectives, [Your Company Name] can develop strategic action plans to address identified issues and improve overall school performance. These objectives guide the analysis process, ensuring that all relevant aspects are considered and that the findings are actionable and aligned with the school’s goals.
III. Methodology
The methodology outlines the steps and tools used to conduct the school analysis. A systematic approach ensures comprehensive and accurate findings.
A. Data Collection
Objective: To gather quantitative and qualitative data from various sources.
Key Components:
Academic Records: Collect data on student performance, graduation rates, and standardized test scores.
Surveys: Design and distribute surveys to students, parents, and staff.
Observations: Conduct classroom observations to assess teaching methods and student engagement.
B. Data Analysis
Objective: To interpret the collected data and identify trends and patterns.
Key Components:
Statistical Analysis: Use statistical methods to analyze quantitative data.
Thematic Analysis: Identify themes and patterns in qualitative data from surveys and interviews.
Comparative Analysis: Compare the school’s performance with regional and national benchmarks.
C. Reporting
Objective: To present the findings in a clear and actionable format.
Key Components:
Executive Summary: Provide a concise overview of the key findings and recommendations.
Detailed Report: Include comprehensive data analysis, charts, and graphs to support the findings.
Action Plan: Develop a strategic plan with specific actions to address identified issues.
IV. Academic Performance Analysis
Analyzing academic performance is critical for understanding student achievement and curriculum effectiveness. This section outlines the key areas to focus on.
A. Student Achievement
Objective: To evaluate students' academic performance across various subjects.
Key Components:
Standardized Test Scores: Analyze performance on state and national standardized tests.
Grade Point Averages: Review GPA trends over the past few years.
Graduation Rates: Examine the percentage of students graduating on time.
B. Curriculum Effectiveness
Objective: To assess the relevance and rigor of the curriculum.
Key Components:
Curriculum Alignment: Ensure that the curriculum aligns with state standards and educational goals.
Course Offerings: Evaluate the variety and availability of courses, including advanced placement (AP) and elective courses.
Instructional Methods: Assess the effectiveness of teaching strategies and instructional methods.
C. Student Progress and Growth
Objective: To track individual student progress and growth over time.
Key Components:
Growth Metrics: Use growth metrics to assess individual student improvement.
Interventions: Evaluate the effectiveness of academic interventions and support programs.
Personalized Learning: Analyze the implementation and impact of personalized learning plans.
V. Teaching Quality Analysis
The quality of teaching is a significant factor in student success. This section focuses on evaluating teacher qualifications, training, and instructional practices.
A. Teacher Qualifications
Objective: To assess the qualifications and expertise of the teaching staff.
Key Components:
Certification and Licensure: Ensure that all teachers hold appropriate certifications and licenses.
Educational Background: Review teachers’ educational backgrounds and degrees.
Professional Experience: Evaluate the years of teaching experience and areas of specialization.
B. Professional Development
Objective: To assess the effectiveness of ongoing professional development for teachers.
Key Components:
Training Programs: Review the availability and quality of professional development programs.
Teacher Collaboration: Assess opportunities for teacher collaboration and peer learning.
Impact on Teaching: Evaluate how professional development impacts instructional practices and student outcomes.
C. Instructional Practices
Objective: To evaluate the effectiveness of instructional methods used by teachers.
Key Components:
Classroom Management: Observe classroom management techniques and student engagement.
Differentiated Instruction: Assess the use of differentiated instruction to meet diverse student needs.
Use of Technology: Evaluate the integration of technology into teaching and learning.
VI. Resources and Facilities Analysis
The availability and condition of resources and facilities significantly impact the learning environment. This section focuses on evaluating these critical components.
A. Infrastructure
Objective: To assess the adequacy and condition of the school’s physical infrastructure.
Key Components:
Building Condition: Inspect the condition of school buildings, including safety and maintenance.
Classroom Environment: Evaluate the adequacy of classroom spaces, furniture, and equipment.
Common Areas: Assess the condition and usability of common areas such as libraries, gyms, and cafeterias.
B. Learning Materials
Objective: To evaluate the availability and quality of learning materials.
Key Components:
Textbooks and Resources: Ensure that textbooks and learning resources are up-to-date and relevant.
Technology Access: Assess the availability and use of technology, including computers, tablets, and smartboards.
Library Resources: Evaluate the adequacy of library resources, including books, journals, and digital media.
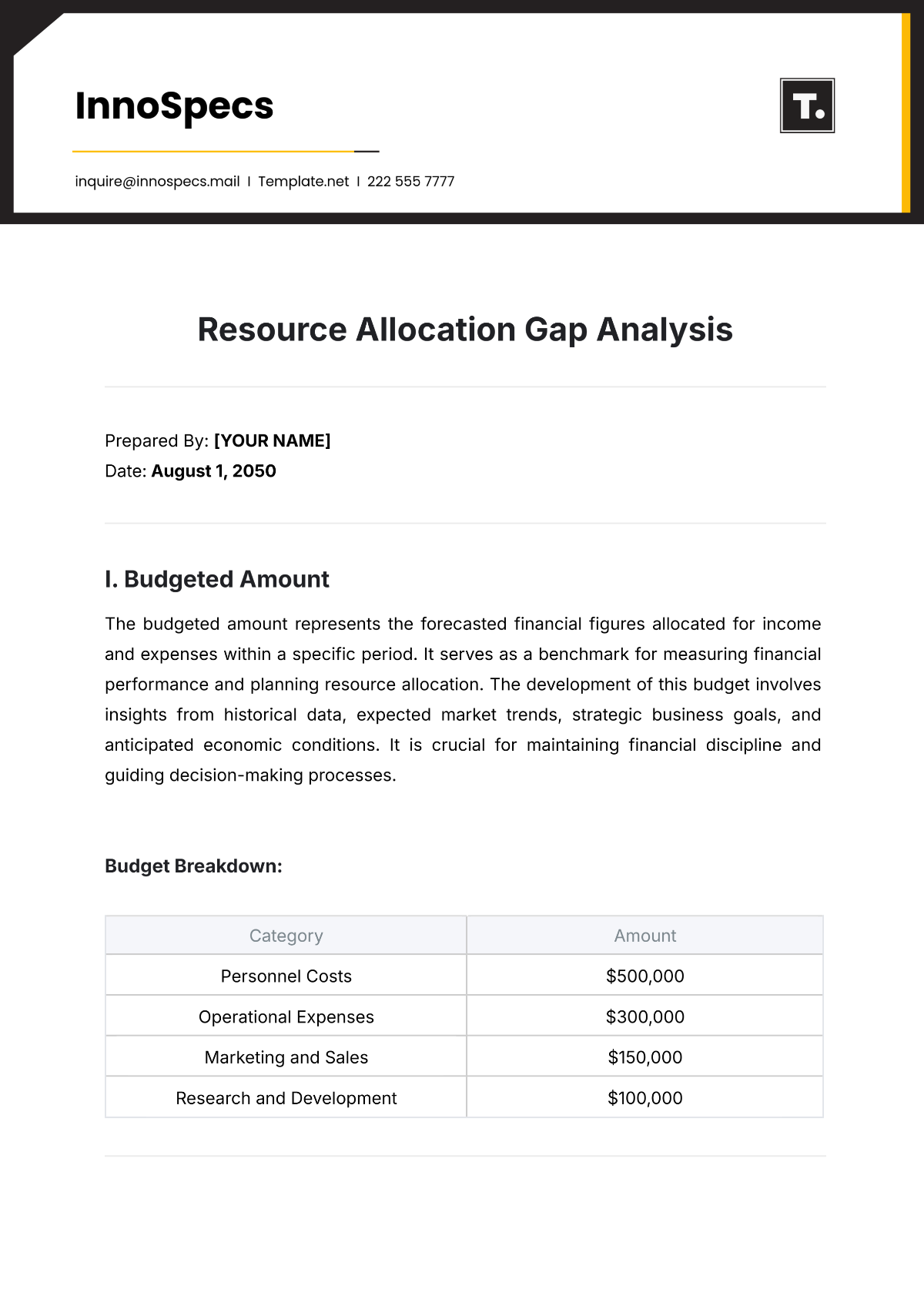
C. Financial Resources
Objective: To analyze the school’s financial health and resource allocation.
Key Components:
Budget Analysis: Review the school’s budget and funding sources.
Resource Allocation: Evaluate how financial resources are allocated across various programs and departments.
Financial Planning: Assess the effectiveness of financial planning and management practices.
VII. Stakeholder Perspectives
Gathering input from stakeholders provides valuable insights into the school’s strengths and areas for improvement. This section outlines methods for collecting and analyzing stakeholder feedback.
A. Surveys and Interviews
Objective: To gather comprehensive feedback from students, parents, and staff.
Key Components:
Survey Design: Develop surveys to collect feedback on various aspects of the school environment.
Conduct Interviews: Hold interviews with key stakeholders to gather in-depth insights.
Data Analysis: Analyze survey and interview data to identify trends and patterns.
B. Focus Groups
Objective: To facilitate in-depth discussions on specific issues.
Key Components:
Group Composition: Form focus groups with diverse representation from the school community.
Discussion Topics: Develop a structured agenda to guide focus group discussions.
Reporting: Summarize key findings from focus group discussions and incorporate them into the overall analysis.
C. Community Engagement
Objective: To evaluate the school’s relationship with the local community.
Key Components:
Partnerships: Assess the school’s partnerships with local businesses, organizations, and community groups.
Community Programs: Evaluate the effectiveness of community outreach and engagement programs.
Feedback Mechanisms: Establish mechanisms for ongoing feedback from the community.
VIII. Action Plan Development
Developing a strategic action plan is essential for addressing the findings of the school analysis. This section outlines the steps for creating an actionable plan.
A. Prioritizing Issues
Objective: To identify and prioritize the most critical issues to address.
Key Components:
Impact Assessment: Assess the potential impact of addressing each identified issue.
Resource Availability: Consider the availability of resources to address each issue.
Stakeholder Input: Incorporate feedback from stakeholders to prioritize issues.
B. Developing Strategies
Objective: To develop effective strategies to address prioritized issues.
Key Components:
Action Steps: Define specific action steps for each strategy.
Responsible Parties: Assign responsibility for implementing each action step.
Timelines: Establish clear timelines for implementation.
C. Monitoring and Evaluation
Objective: To ensure the successful implementation and ongoing evaluation of the action plan.
Key Components:
Progress Monitoring: Develop a system for monitoring the progress of action plan implementation.
Evaluation Metrics: Define metrics for evaluating the effectiveness of implemented strategies.
Continuous Improvement: Establish a process for continuous improvement based on evaluation findings.
IX. Conclusion
Conducting a comprehensive school analysis is critical for identifying areas of improvement and enhancing the educational environment. By systematically evaluating academic performance, teaching quality, resources, facilities, and stakeholder perspectives, [Your Company Name] can develop strategic action plans to address identified issues and improve overall school performance.
For any questions or further information, please contact [Your Name] at [Your Email] or [Your Company Number].