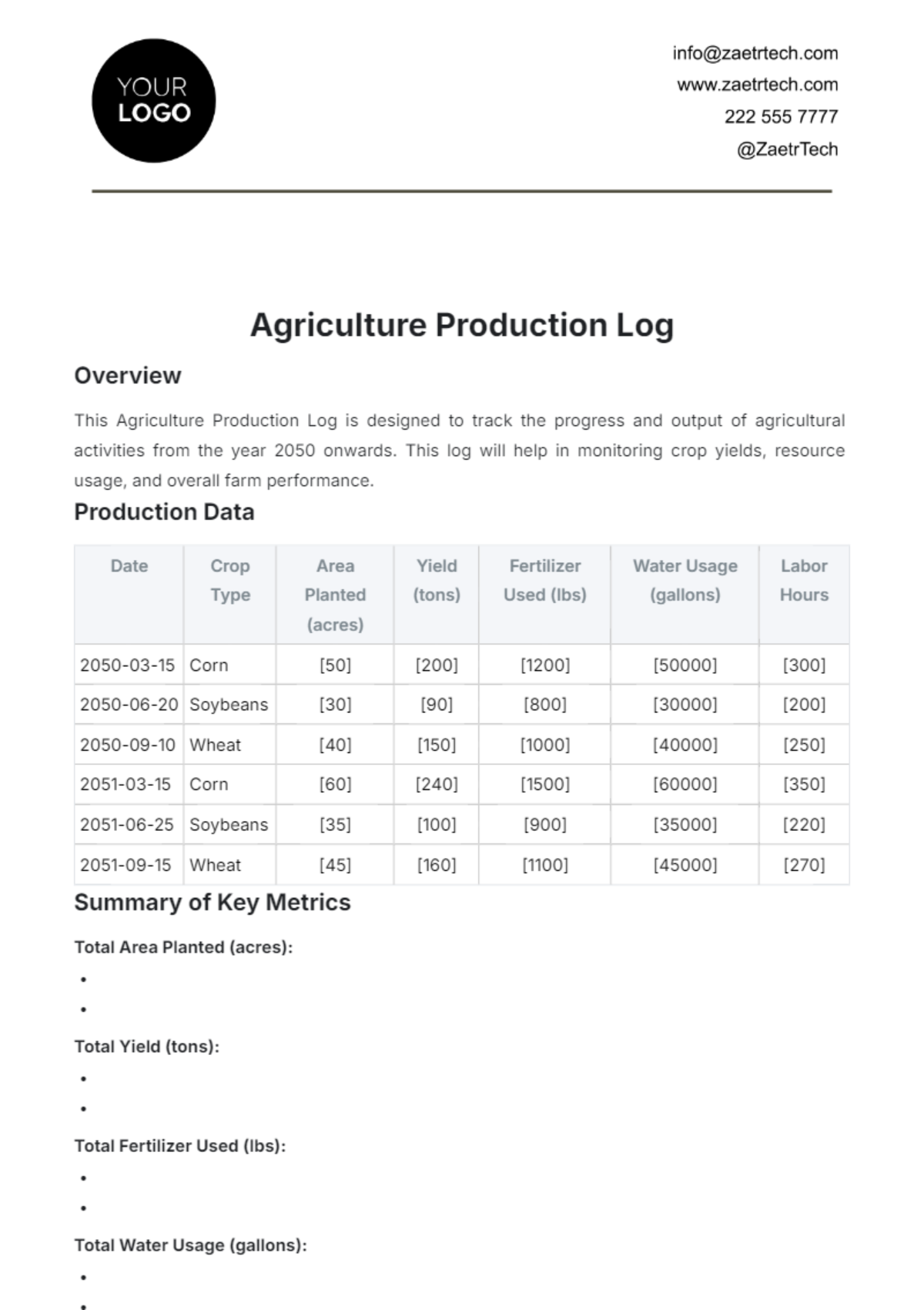
Agriculture Tools Maintenance Protocol
I. Introduction
The purpose of this Agriculture Tools Maintenance Protocol is to ensure the longevity and efficient operation of [Your Company Name] agricultural tools and equipment. Regular maintenance helps prevent breakdowns, ensures safety, and optimizes performance, contributing to the overall productivity of our agricultural activities. This protocol outlines the procedures for daily, weekly, monthly, and seasonal maintenance, inventory management, safety practices, and training programs.
II. Inventory Management
To maintain an organized and efficient workflow, we have implemented a systematic check-in and check-out procedure for our tools and equipment. Each tool must be signed out at the beginning of its use and signed back in at the end of the day. This process ensures accountability and allows us to keep track of our assets effectively.
Hand tools (shovels, rakes, hoes)
Power tools (chainsaws, trimmers, blowers)
Planting equipment (seeders, planters)
Harvesting equipment (scythes, sickles)
Maintenance equipment (wrenches, screwdrivers)
Safety equipment (gloves, goggles, helmets)
Inventory tracking will be conducted using a digital log that records each tool's status and usage. This log will be updated daily to reflect the current condition and location of every piece of equipment. Regular audits will be performed to ensure accuracy and identify any discrepancies promptly.
III. Daily Maintenance Procedures
Daily maintenance is essential to ensure that all tools and equipment are in good working condition and ready for use. This includes basic cleaning, inspection, lubrication, and proper storage at the end of each day.
Tool/Equipment | Maintenance Procedure |
|---|---|
Hand tools | Inspecting for damage |
Power tools | Checking fuel/oil levels |
Planting equipment | Inspecting moving parts |
Harvesting tools | Sharpening blades |
Maintenance tools | Inspecting for wear |
Safety equipment | Inspecting for damage |
Cleaning Tools After Use: Remove soil, debris, and any residues from the tools using appropriate cleaning materials.
Inspecting for Damage or Wear: Check for any signs of damage, wear, or malfunction. Report any issues immediately.
Lubricating Moving Parts: Apply lubricants to moving parts to ensure smooth operation and prevent rust.
Proper Storage Practices: Store tools in designated areas to prevent damage and facilitate easy access.
IV. Weekly Maintenance Procedures
Weekly maintenance involves a more thorough inspection and servicing of tools and equipment to identify and address any emerging issues before they become significant problems. This includes detailed inspections, sharpening, tightening, and replenishing consumables.
Tool/Equipment | Maintenance Procedure |
|---|---|
Hand tools | Sharpening blades |
Power tools | Tightening screws |
Planting equipment | Calibrating parts |
Harvesting tools | Sharpening edges |
Maintenance tools | Replenishing supplies |
Safety equipment | Replacing damaged parts |
Detailed Inspection for Wear and Tear: Examine each tool thoroughly to identify any signs of wear, tear, or potential issues.
Sharpening Blades and Cutting Edges: Use appropriate sharpening tools to maintain the efficiency and effectiveness of cutting tools.
Checking and Tightening Bolts and Screws: Ensure that all fasteners are secure and in good condition to prevent accidents.
Replenishing Consumables: Replace oil, fuel, and other consumables to ensure that tools are ready for use.
V. Monthly Maintenance Procedures
Monthly maintenance includes comprehensive inspection, testing, and replacement of worn-out parts to ensure the optimal functioning of all tools and equipment.
Tool/Equipment | Maintenance Procedure |
|---|---|
Hand tools | Replacing parts |
Power tools | Testing |
Planting equipment | Calibration |
Harvesting tools | Blade replacement |
Maintenance tools | Replenishing stocks |
Safety equipment | Testing |
Comprehensive Inspection and Testing: Conduct a thorough examination and functionality test for each tool.
Calibrating Equipment for Accuracy: Ensure that all tools requiring precision are properly calibrated.
Replacing Worn-Out Parts: Replace any parts showing signs of significant wear to prevent failures.
Ensuring Safety Features are Functional: Verify that all safety features are operational and effective.
VI. Seasonal Maintenance Procedures
Seasonal maintenance prepares tools for storage during the off-season and ensures they are ready for use in the upcoming season. This involves winterizing equipment, conducting major repairs, and thorough preparation.
Tool/Equipment | Maintenance Procedure |
|---|---|
Hand tools | Rust prevention |
Power tools | Winterizing, major repairs |
Planting equipment | Calibration |
Harvesting tools | Major repairs |
Maintenance tools | Replenishing stocks |
Safety equipment | Inspection |
Preparing Tools for Storage (Off-Season): Clean and store tools in a dry, secure location to prevent damage.
Winterizing Equipment: Drain fluids, apply protective coatings, and store power tools appropriately.
Conducting Major Repairs and Overhauls: Perform any necessary major repairs to ensure tools are in top condition.
Preparing Tools for the Upcoming Season: Inspect and prepare tools to be ready for immediate use when the season starts.
VII. Safety Procedures
A. PPE Requirements
All personnel must wear appropriate Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) when handling tools and equipment. This includes gloves, goggles, helmets, and any other necessary protective gear to prevent injuries and ensure safety.
B. In Case of Accidents
In the event of an accident, immediate action is required to ensure the safety of all personnel. Follow these emergency procedures:
Assess the situation and ensure personal safety.
Administer first aid if necessary.
Call emergency services if required.
Report the accident to a supervisor.
Document the incident and any injuries sustained.
Conduct a thorough investigation to prevent future occurrences.
C. Hazardous Materials
Proper disposal of hazardous materials is crucial for maintaining a safe working environment. Follow the guidelines below for disposing of different categories of hazardous materials:
Oils and Lubricants: Collect in designated containers, dispose of through authorized recycling centers
Fuel: Store in approved containers, dispose of through hazardous waste disposal services
Cleaning Chemicals: Follow manufacturer instructions, dispose of through hazardous waste facilities
VIII. Training and Education
Regular training and education programs are essential to ensure that all personnel are knowledgeable about maintenance procedures and safety practices. These programs will be conducted regularly to keep everyone informed and up-to-date.
Program | Frequency | Duration |
|---|---|---|
Basic Tool Maintenance | Quarterly | 2 hours |
Advanced Equipment Handling | Bi-annually | 4 hours |
Safety and PPE Training | Annually | 3 hours |
Emergency Response Training | Annually | 2 hours |
IX. Responsibility
Clear roles and responsibilities are essential for the effective implementation of the maintenance protocol. The table below outlines the specific responsibilities for each role within our organization:
Role | Responsibilities |
|---|---|
Manager | Oversee maintenance procedures, conduct inspections |
Tool Custodian | Manage inventory, track tool usage, ensure proper storage |
Technician | Perform maintenance tasks, report issues, conduct repairs |
Safety Officer | Ensure safety protocols are followed, conduct safety training |
X. Evaluation and Improvement
We will regularly evaluate our maintenance practices to ensure they are effective and up-to-date. This evaluation will be conducted semi-annually, and feedback from staff will be collected to identify areas for improvement. Continuous improvement strategies will be implemented to enhance our maintenance protocol and ensure the highest standards of efficiency and safety.