Agriculture Employee SWOT Analysis
Introduction
Conducting a SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats) of our agricultural workforce is essential to understand the internal and external factors that influence our operations. This comprehensive analysis will help us identify areas of strength to build upon, weaknesses to address, opportunities to exploit, and threats to mitigate. The findings will inform our strategic planning and workforce development initiatives at [Your Company Name].
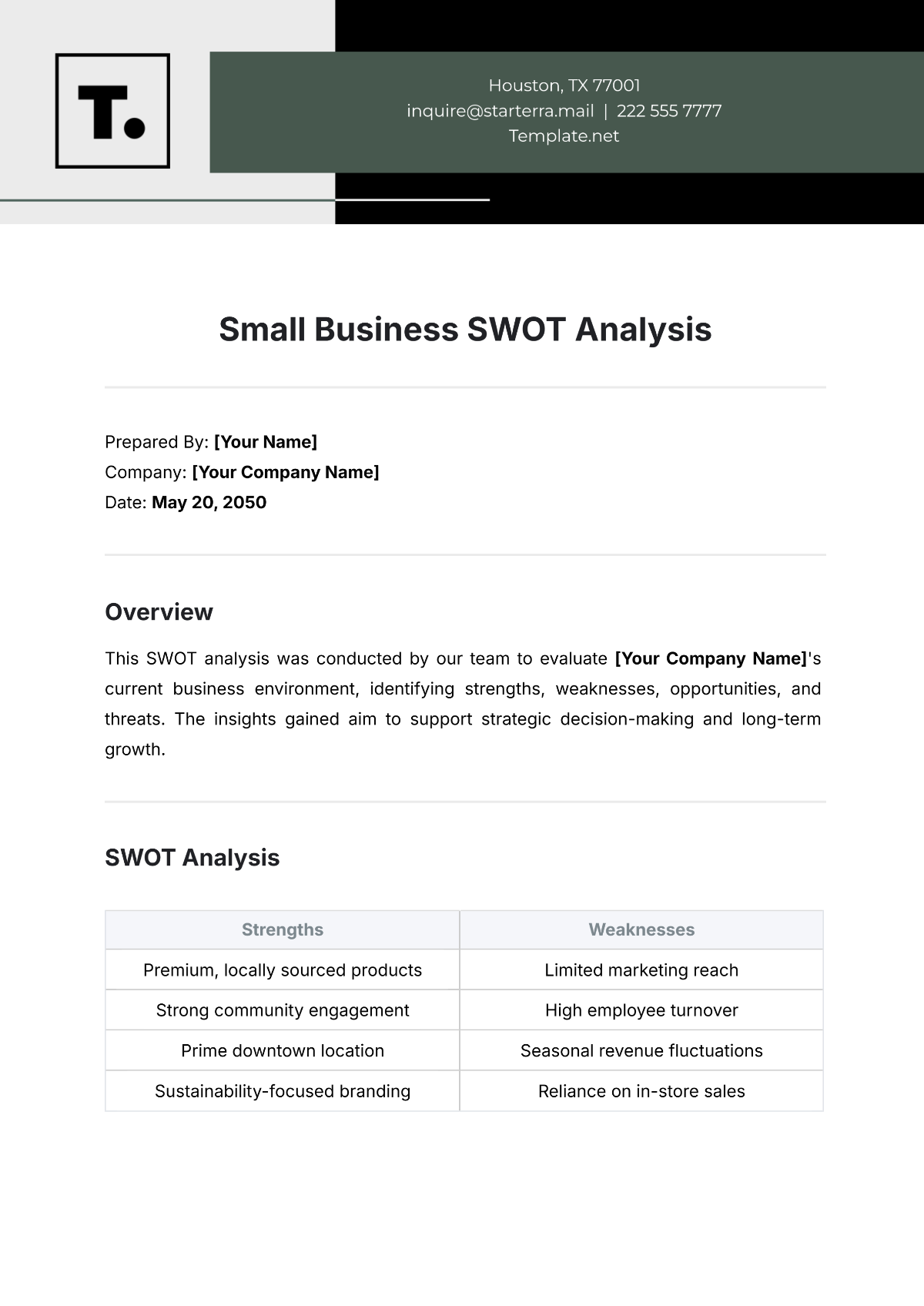
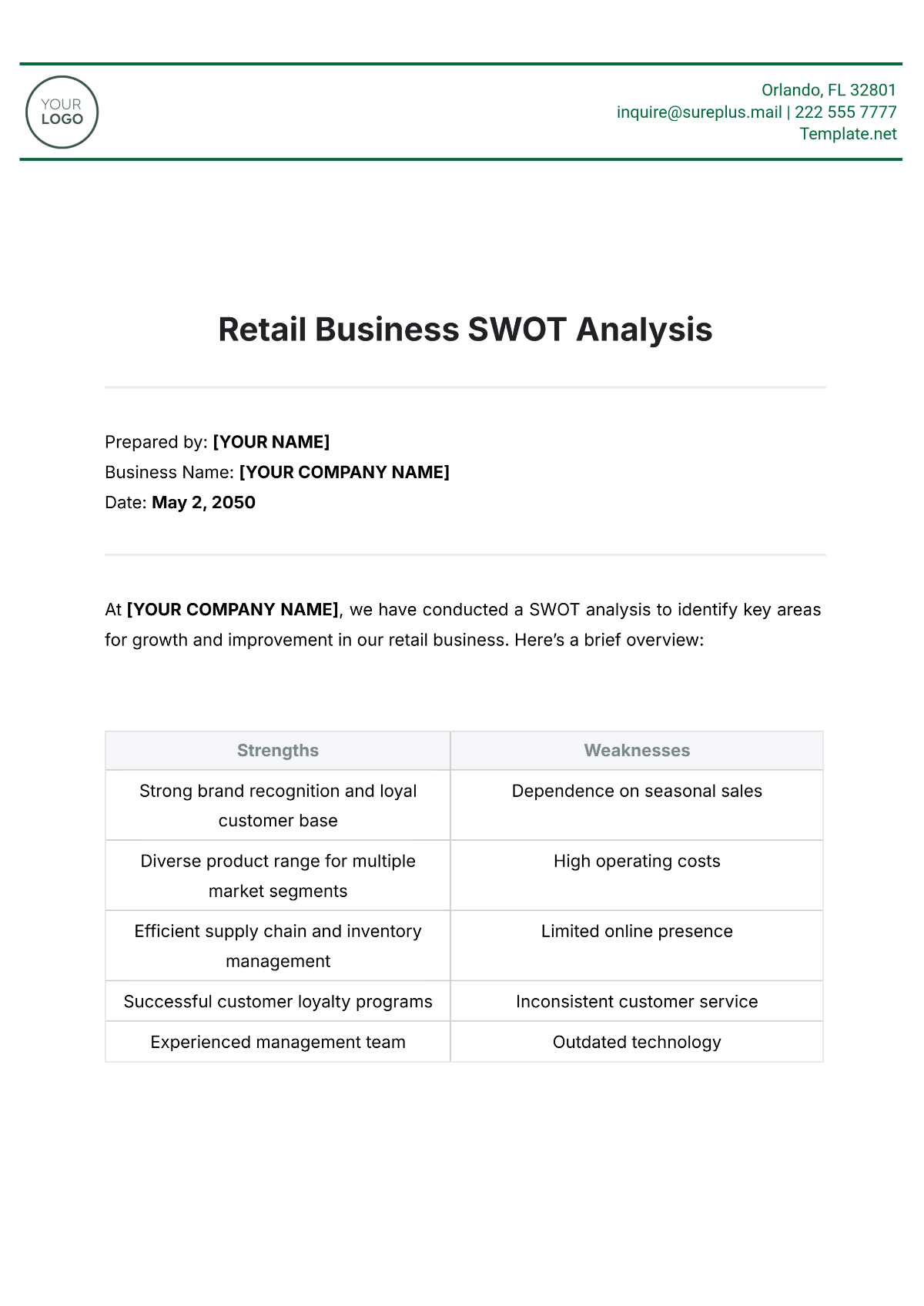
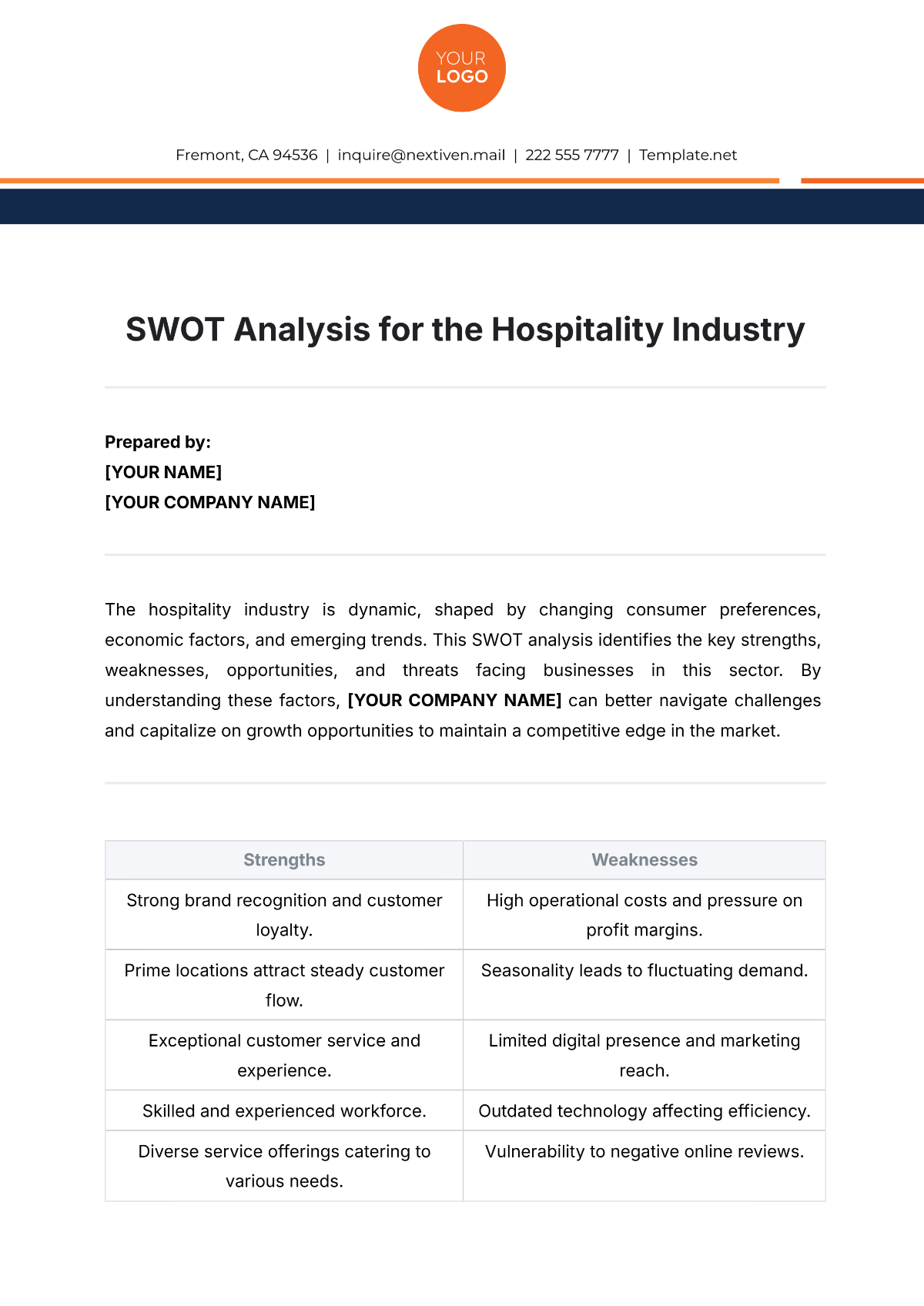
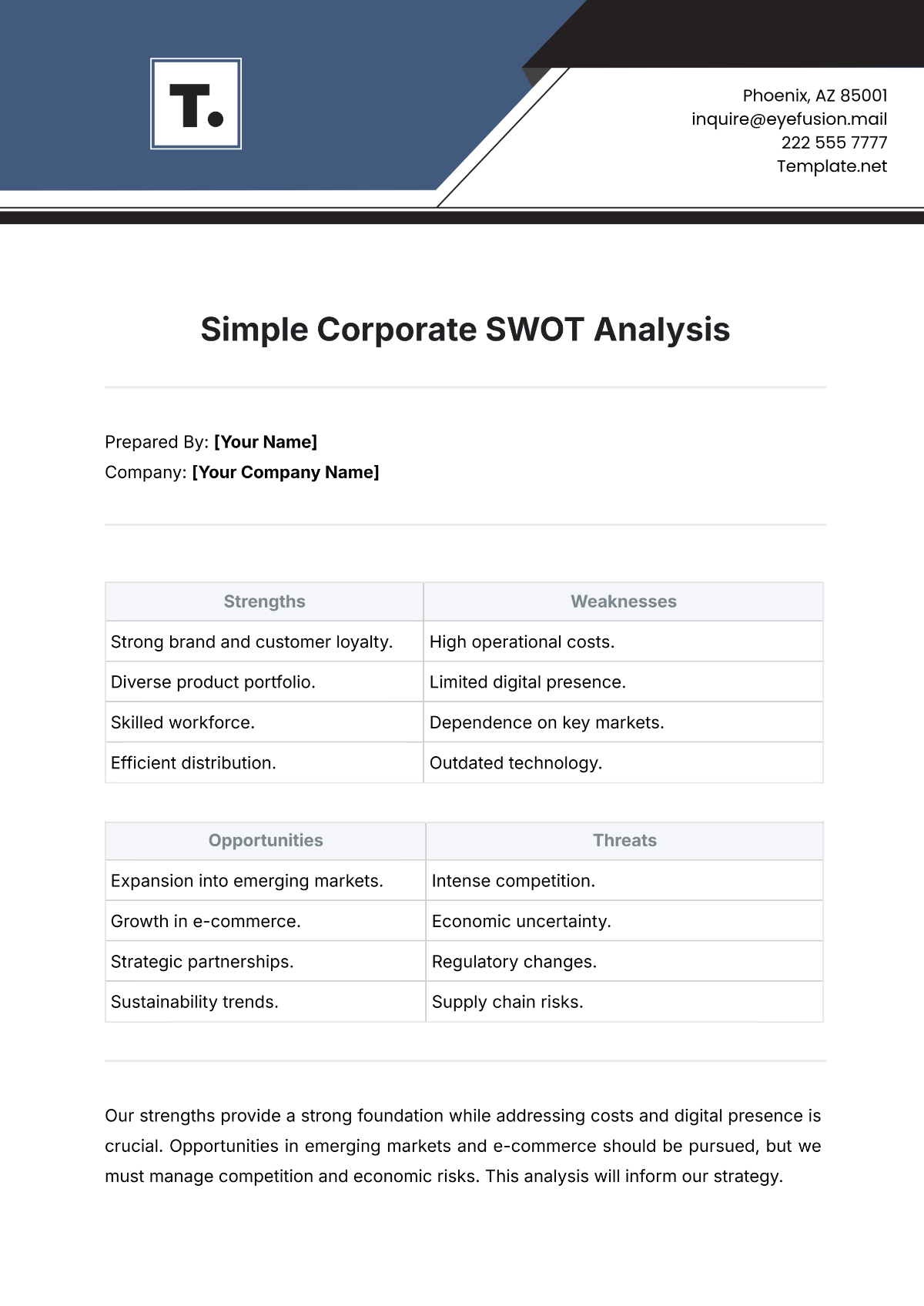
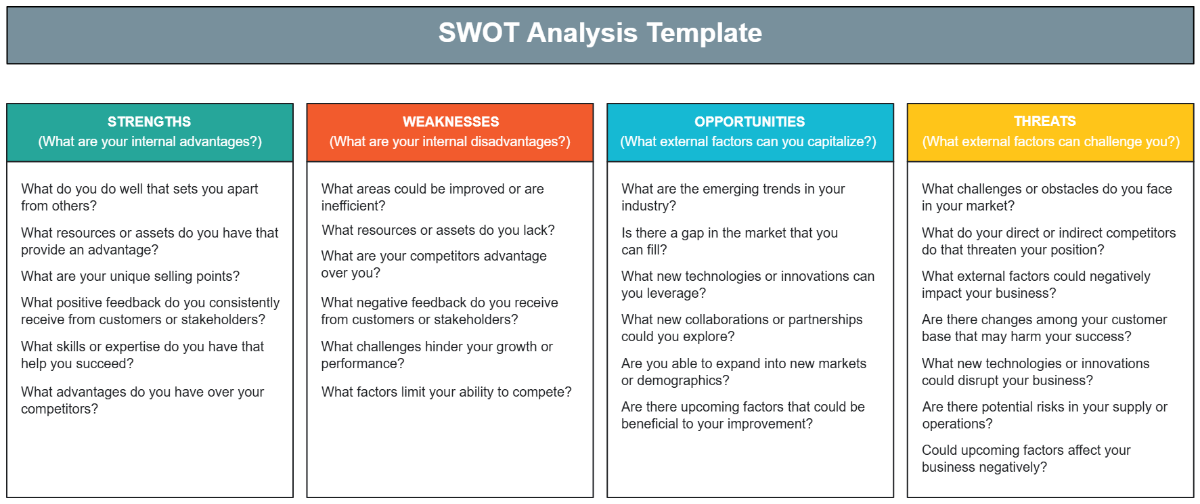
1. Strengths
Identifying the strengths of our agricultural workforce helps us understand what we do well and provides a foundation for building competitive advantages. This section outlines the key strengths of our employees and workforce practices.
Key Strengths
1.1 Skilled Workforce
Our employees possess a high level of expertise and technical skills, particularly in advanced farming techniques and equipment operation. This skillset allows us to maintain high productivity and efficiency.
1.2 Strong Work Ethic
Our workforce is dedicated and hardworking, often going above and beyond to meet production targets and ensure the quality of our agricultural products. This strong work ethic is a significant asset to our operations.
1.3 Comprehensive Training Programs
We have developed robust training programs that ensure our employees are well-prepared for their roles. These programs cover technical skills, safety protocols, and continuous professional development.
1.4 High Employee Retention
Our company enjoys a high employee retention rate, which reflects job satisfaction and loyalty among our workforce. This stability allows us to maintain continuity and reduce the costs associated with turnover.
1.5 Commitment to Safety
Safety is a top priority at [Your Company Name], and our workforce is highly compliant with safety protocols. This commitment to safety minimizes workplace accidents and enhances overall productivity.
Table: Key Strengths
Strength | Details |
|---|---|
Skilled Workforce | High level of expertise in advanced farming techniques and equipment operation. |
Strong Work Ethic | Dedicated and hardworking employees who meet production targets and ensure product quality. |
Comprehensive Training Programs | Robust training programs covering technical skills, safety protocols, and continuous professional development. |
High Employee Retention | High retention rate reflecting job satisfaction and loyalty, reducing turnover costs. |
Commitment to Safety | Strong adherence to safety protocols, minimizing workplace accidents and enhancing productivity. |
2. Weaknesses
Identifying weaknesses in our workforce allows us to address areas that may hinder our performance and growth. This section outlines the key weaknesses that need to be addressed to enhance our workforce's effectiveness.
Key Weaknesses
2.1 Skill Gaps in Emerging Technologies
While our workforce is skilled in traditional agricultural practices, there are gaps in knowledge and expertise related to emerging technologies such as precision agriculture and data analytics.
2.2 Limited Diversity
Our workforce lacks diversity in terms of gender, ethnicity, and age. This homogeneity can limit creativity, innovation, and the ability to relate to diverse customer bases.
2.3 Inconsistent Performance Management
Our current performance management system lacks consistency and may not adequately identify and address underperformance. This can lead to missed opportunities for improvement and development.
2.4 Communication Barriers
There are communication barriers between different departments and levels of the organization. These barriers can lead to misunderstandings, inefficiencies, and a lack of cohesive strategy implementation.
2.5 Resistance to Change
Some employees show resistance to adopting new practices and technologies, which can hinder our ability to innovate and stay competitive in a rapidly evolving industry.
Table: Key Weaknesses
Weakness | Details |
|---|---|
Skill Gaps in Emerging Technologies | Gaps in knowledge and expertise related to precision agriculture, data analytics, and other emerging technologies. |
Limited Diversity | Lack of diversity in gender, ethnicity, and age, which can limit creativity, innovation, and customer relatability. |
Inconsistent Performance Management | Inadequate system for identifying and addressing underperformance, leading to missed opportunities for improvement. |
Communication Barriers | Barriers between departments and organizational levels causing misunderstandings and inefficiencies. |
Resistance to Change | Resistance to adopting new practices and technologies, hindering innovation and competitiveness. |
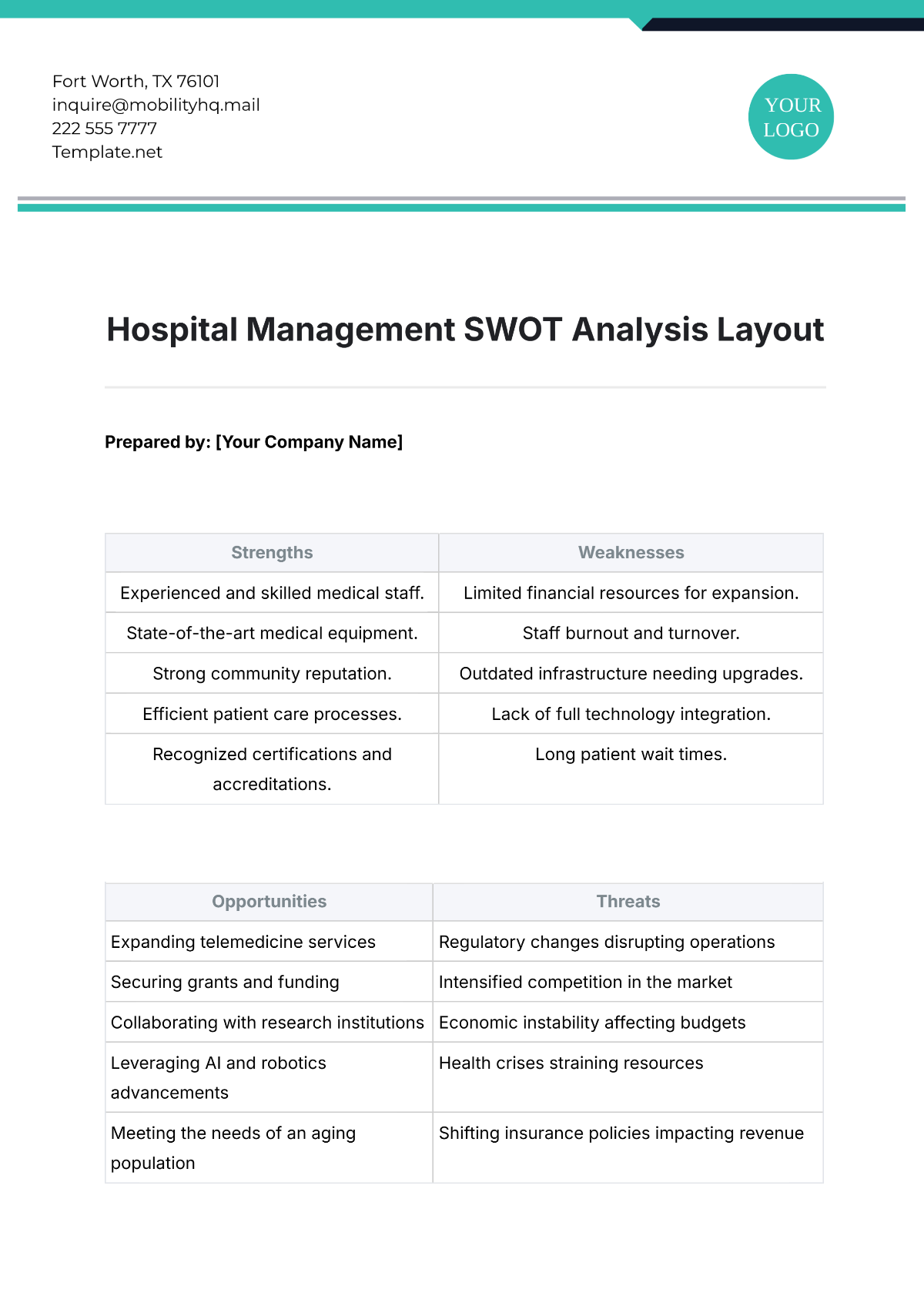
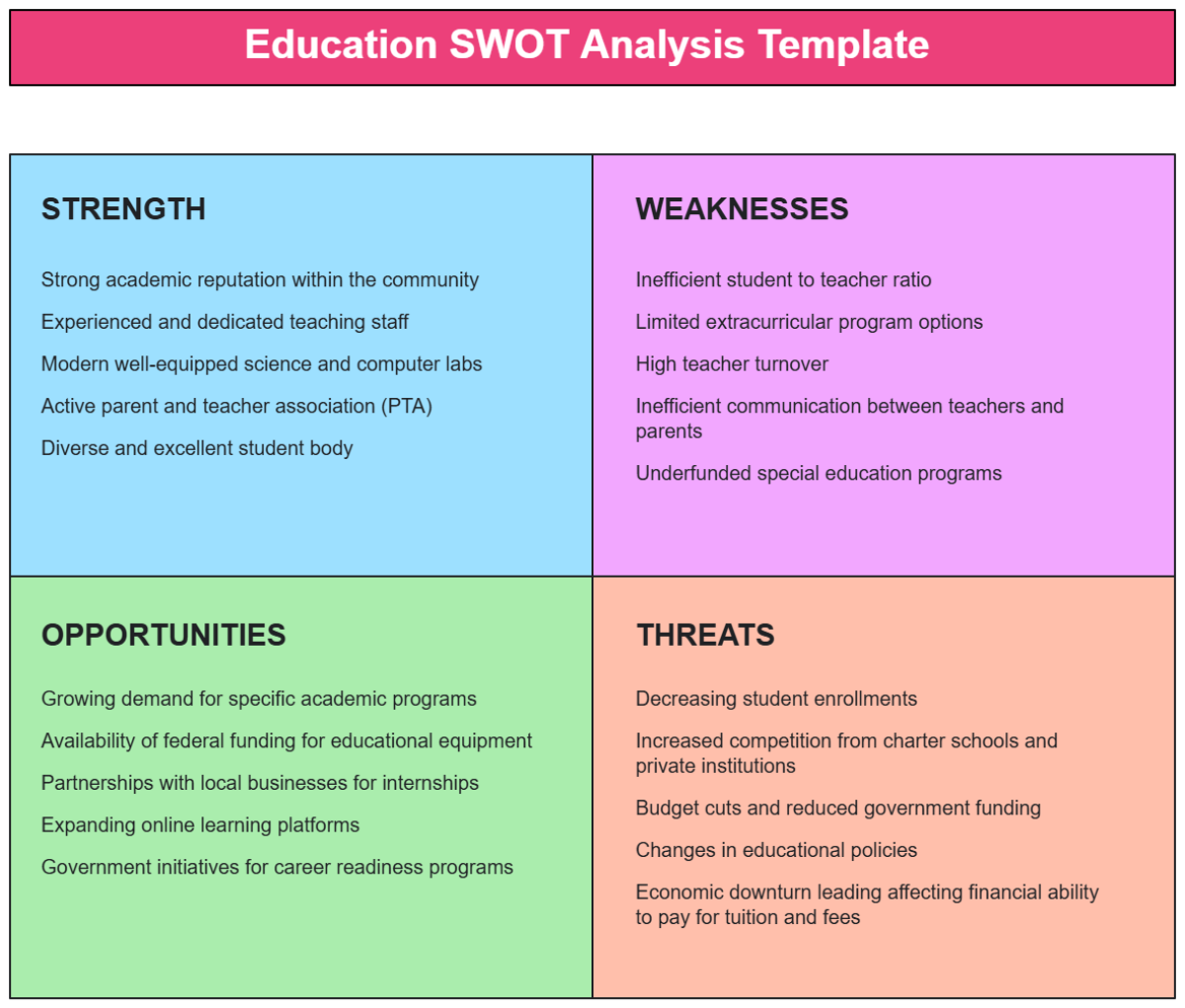
3. Opportunities
Identifying opportunities allows us to leverage external factors to our advantage and enhance our workforce capabilities. This section outlines the key opportunities available to our agricultural workforce.
Key Opportunities
3.1 Adoption of Advanced Technologies
The adoption of advanced technologies such as precision agriculture, automation, and artificial intelligence presents opportunities to improve productivity, efficiency, and sustainability in our operations.
3.2 Expansion into New Markets
Expanding into new markets, both domestically and internationally, can increase demand for our products and services, leading to growth in workforce requirements and the development of new skills.
3.3 Partnerships with Educational Institutions
Collaborating with universities and technical schools can provide access to a pipeline of skilled graduates and opportunities for joint research and development projects.
3.4 Enhanced Training Programs
Developing enhanced training programs, particularly in emerging technologies and sustainable practices, can bridge skill gaps and prepare our workforce for future challenges.
3.5 Government Incentives and Grants
There are various government incentives and grants available for agricultural businesses that invest in sustainability, innovation, and workforce development. These financial aids can support our growth and development initiatives.
Table: Key Opportunities
Opportunity | Details |
|---|---|
Adoption of Advanced Technologies | Improving productivity, efficiency, and sustainability through the use of precision agriculture, automation, and artificial intelligence. |
Expansion into New Markets | Increasing demand for products and services by expanding into new domestic and international markets. |
Partnerships with Educational Institutions | Accessing a pipeline of skilled graduates and opportunities for joint research and development projects through collaborations. |
Enhanced Training Programs | Bridging skill gaps and preparing the workforce for future challenges through enhanced training programs in emerging technologies and sustainable practices. |
Government Incentives and Grants | Leveraging financial support for sustainability, innovation, and workforce development initiatives through government programs. |
4. Threats
Identifying threats helps us anticipate and mitigate potential challenges that could negatively impact our workforce and operations. This section outlines the key threats facing our agricultural workforce.
Key Threats
4.1 Labor Shortages
The agricultural industry faces a general shortage of labor, which can impact our ability to meet production targets and maintain operational efficiency.
4.2 Economic Instability
Economic instability, such as fluctuations in commodity prices and trade policies, can affect our profitability and ability to invest in workforce development.
4.3 Regulatory Changes
Changes in agricultural and labor regulations can impose new compliance requirements and increase operational costs, potentially impacting workforce management.
4.4 Technological Displacement
The rapid advancement of technology can lead to job displacement, requiring significant reskilling and adaptation among our workforce.
4.5 Climate Change
Climate change poses a significant threat to agricultural productivity and sustainability, potentially leading to reduced crop yields and increased operational challenges.
Table: Key Threats
Threat | Details |
|---|---|
Labor Shortages | General shortage of labor in the agricultural industry impacting production targets and operational efficiency. |
Economic Instability | Fluctuations in commodity prices and trade policies affecting profitability and investment in workforce development. |
Regulatory Changes | New compliance requirements and increased operational costs due to changes in agricultural and labor regulations. |
Technological Displacement | Job displacement caused by rapid technological advancements, necessitating significant reskilling and adaptation. |
Climate Change | Reduced crop yields and increased operational challenges due to the impacts of climate change on agricultural productivity. |
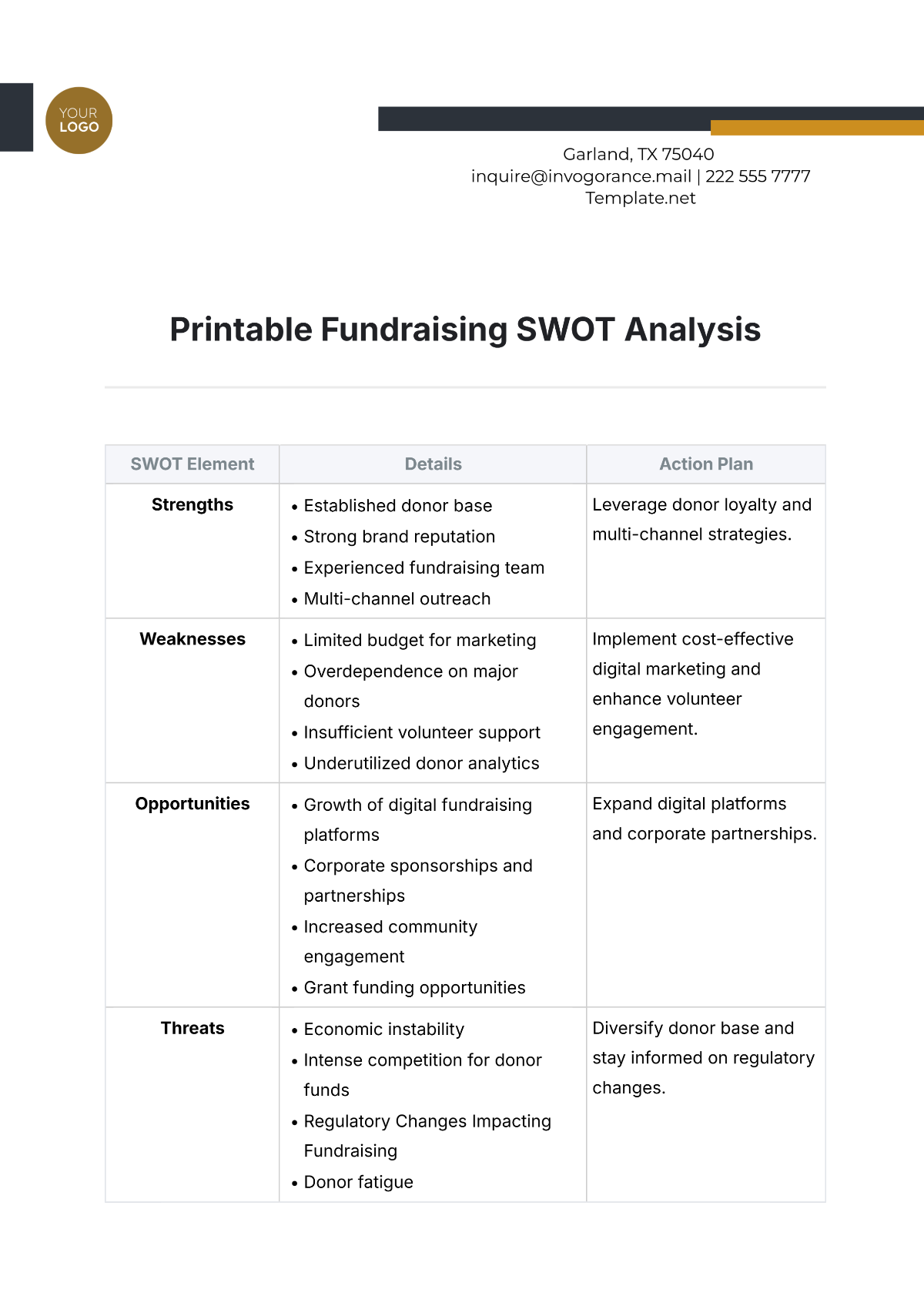
5. Strategic Recommendations
Based on the SWOT analysis, this chapter provides strategic recommendations for leveraging strengths, addressing weaknesses, capitalizing on opportunities, and mitigating threats. These recommendations aim to enhance our workforce capabilities and support the long-term success of [Your Company Name].
Recommendations for Strengths
1. Leverage Skilled Workforce
Strategy: Promote the expertise of our skilled workforce in marketing materials to attract new clients and partners. Implement mentorship programs to transfer knowledge and skills to less experienced employees.
2. Enhance Training Programs
Strategy: Continuously update and expand our training programs to cover emerging technologies and best practices. Offer incentives for employees to pursue additional certifications and training opportunities.
Recommendations for Weaknesses
1. Address Skill Gaps
Strategy: Develop specialized training programs focused on emerging technologies such as precision agriculture and data analytics. Partner with educational institutions to provide employees with access to relevant courses and certifications.
2. Improve Diversity
Strategy: Implement targeted recruitment strategies to attract a diverse pool of candidates. Foster an inclusive work environment through diversity training and the establishment of employee resource groups.
3. Strengthen Performance Management
Strategy: Standardize the performance management process across the organization. Use objective metrics and regular feedback to identify areas for improvement and recognize high performers.
4. Enhance Communication
Strategy: Establish clear communication channels and protocols between departments. Implement regular cross-departmental meetings and collaboration platforms to facilitate information sharing and coordination.
5. Encourage Adoption of New Practices
Strategy: Foster a culture of innovation by recognizing and rewarding employees who embrace new technologies and practices. Provide training and support to ease the transition to new methods and tools.
Recommendations for Opportunities
1. Adopt Advanced Technologies
Strategy: Invest in the latest agricultural technologies to enhance productivity and sustainability. Provide training for employees on how to use and maintain these technologies effectively.
2. Expand into New Markets
Strategy: Conduct market research to identify potential new markets for expansion. Develop targeted marketing strategies and allocate resources to support entry into these markets.
3. Form Partnerships with Educational Institutions
Strategy: Establish formal partnerships with universities and technical schools to create a pipeline of skilled graduates. Collaborate on research and development projects to drive innovation.
4. Enhance Training Programs
Strategy: Continuously improve and expand training programs to address skill gaps and prepare employees for future challenges. Offer a mix of in-person and online training options to accommodate different learning preferences.
5. Leverage Government Incentives
Strategy: Identify and apply for government grants and incentives that support workforce development, sustainability, and innovation. Allocate resources to manage the application process and ensure compliance with grant requirements.
Recommendations for Threats
1. Mitigate Labor Shortages
Strategy: Implement recruitment and retention strategies to attract and retain skilled workers. Explore automation and mechanization to reduce reliance on manual labor.
2. Prepare for Economic Instability
Strategy: Diversify revenue streams to reduce dependence on any single market or commodity. Develop contingency plans to manage economic fluctuations and ensure financial stability.
3. Stay Ahead of Regulatory Changes
Strategy: Monitor regulatory developments and engage with industry associations to stay informed about potential changes. Develop compliance plans and allocate resources to ensure adherence to new regulations.
4. Address Technological Displacement
Strategy: Provide reskilling and upskilling opportunities to employees whose jobs may be affected by technological advancements. Promote a culture of continuous learning and adaptation.
5. Adapt to Climate Change
Strategy: Implement sustainable farming practices to mitigate the impacts of climate change. Invest in research and development to identify resilient crop varieties and innovative farming techniques.
Conclusion
The comprehensive SWOT analysis of [Your Company Name]'s agricultural workforce has provided valuable insights into our strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. By leveraging our strengths, addressing weaknesses, capitalizing on opportunities, and mitigating threats, we can enhance our workforce capabilities and support the long-term success and sustainability of our agricultural operations. Implementing the strategic recommendations outlined in this report will ensure that we remain competitive, innovative, and resilient in the face of future challenges.