Free Car Wash Inventory Management Analysis

I. Introduction
A. Overview of the Car Wash Facility
[Your Company Name] operates as a high-volume facility in downtown, offering a wide range of services including basic exterior washes, interior detailing, and specialty treatments like waxing and polishing. With a customer base of over 5000 monthly patrons, maintaining efficient inventory management is crucial to meet demand and ensure customer satisfaction.
B. Purpose and Scope of the Inventory Management Analysis
The primary goal of conducting this comprehensive analysis is to create more efficient inventory management processes in order to lower costs and optimize the levels of stock maintained. By thoroughly assessing the existing practices and pinpointing specific areas that require improvement, [Your Company Name] intends to significantly boost operational efficiency. This effort will focus on minimizing waste associated with inventory and enhancing the overall quality of service delivery. Through these targeted improvements, [Your Company Name] seeks to achieve a more streamlined and cost-effective approach to managing inventory.
II. Current Inventory Assessment
A. Inventory Categories
Category | Description |
|---|---|
Chemicals and Cleaning Supplies | Includes various car cleaning agents, waxes, and interior cleaning solutions. |
Spare Parts and Equipment | Essential items such as nozzles, hoses, and vacuum cleaners. |
Consumables | Towels, air fresheners, and disposable gloves for customer use. |
B. Inventory Levels and Turnover Rates
[Your Company Name] ensures a consistent and sufficient stock of essential items by conducting monthly audits and closely monitoring usage patterns. Specifically, chemicals and cleaning supplies are typically replaced approximately every 30 days due to their high turnover rate. Meanwhile, consumable items are restocked on a weekly basis, adjusting to meet the fluctuating demands of customers. On the other hand, the frequency at which spare parts are renewed is more variable and is primarily dependent upon the established maintenance schedules and the immediate requirements arising from repair activities.
C. Inventory Tracking Systems
The present state of inventory management relies on a blend of manually tracking stock and utilizing rudimentary spreadsheet software. Although this approach suffices for addressing fundamental requirements, it falls short in several key areas. Notably, these existing systems do not offer real-time updates, which means that information regarding inventory levels is not immediately refreshed and may therefore be outdated. Additionally, the current setup lacks the sophisticated reporting capabilities that would provide a comprehensive, detailed view of inventory data. As a result, this can lead to significant inefficiencies, particularly in the processes of procurement and general stock management.
III. Supplier Relations and Procurement
A. Supplier Evaluation
Our company, [Your Company Name], undertakes a comprehensive evaluation of our suppliers, focusing on several key criteria to ensure they meet our high standards. These criteria include, but are not limited to, the quality of the products they deliver, the reliability and punctuality of their delivery schedules, and their ability to respond promptly to urgent orders. Key suppliers in our network include local distributors for essential chemicals and manufacturers of specialized parts. We regularly review their performance to ensure they meet our standards and keep our supply chain efficient. This thorough evaluation maintains high standards in our supply chain management.
B. Procurement Processes
Efficient ordering procedures are crucial to ensuring the smooth and uninterrupted functioning of operations. To achieve this, orders are generally placed based on previously established reorder points, which are specific inventory levels that trigger replenishment, and forecasts of customer demand, which help predict future needs. These forecasts allow the company to maintain optimal inventory levels and avoid shortages or excesses that could disrupt operations. Negotiations with suppliers are crucial for securing favorable pricing and expedited delivery options, which help control costs, protect profit margins, and ensure timely arrival of essential inventory. This is vital during high demand or for crucial items, minimizing service disruptions and maintaining customer satisfaction.
IV. Inventory Optimization Strategies
A. Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory
Implementing Just-In-Time (JIT) principles for managing chemicals and consumables presents a viable strategy to significantly reduce storage costs and minimize waste. By employing a system that synchronizes inventory levels closely with customer demand patterns, [Your Company Name] is positioned to enhance both cash flow and overall operational efficiency. This approach meticulously tracks and analyzes customer demand to maintain optimal inventory levels, avoiding overstocking costs and ensuring timely supplies. However, accurate forecasting and maintaining appropriate buffer stock are crucial challenges. Balancing these requires careful planning and constant adjustment to sustain the benefits of JIT while mitigating its risks.
B. [Your Company Name] Analysis
[Your Company Name] employs a sophisticated classification system to categorize inventory items, taking into account both their value and their critical importance to the company's ongoing operations. This system is divided into three distinct classes: Class A, Class B, and Class C. Class A items, like high-value spare parts and specialized equipment, are vital to business operations and require strict inventory control. Class B items, including chemicals and cleaning supplies, are managed using Just-In-Time (JIT) practices to minimize costs and waste. Class C items, such as consumables, are controlled through automated reorder systems to maintain adequate stock levels. This classification ensures each inventory category is managed efficiently to support effective operations.
V. Quality Control and Maintenance
A. Quality Assurance Standards
Regular inspections are conducted to guarantee that all cleaning products and equipment comply with the safety and quality standards established by local regulatory bodies. In addition to these inspections, chemicals undergo rigorous batch testing to confirm their effectiveness and to ensure customer satisfaction, thereby maintaining a consistent level of service quality. Furthermore, Safety Data Sheets (SDS) are made readily accessible for every chemical that is kept in stock, providing detailed information on proper handling and disposal procedures to promote safe and responsible usage.
B. Equipment Maintenance
To ensure that our equipment remains in peak operating condition and avoids unexpected malfunctions, we have established a comprehensive maintenance schedule. This schedule mandates that thorough maintenance procedures be carried out on a quarterly basis. The primary aim of this routine is to prevent breakdowns and to ensure that our equipment continues to function efficiently. In addition to the quarterly maintenance, our operational equipment undergoes daily inspections. These frequent checks are designed to identify and address any minor issues as soon as they arise, thereby preventing them from escalating into major problems that could disrupt our operations.
Furthermore, we have implemented a system for emergency repair services. These services are readily available at all times to respond swiftly to any urgent issues that may occur. The prompt intervention by these emergency repair teams is crucial for minimizing service disruptions and for maintaining a high level of customer satisfaction. By being proactive in our maintenance efforts and prepared for emergencies, we strive to ensure continuous and reliable service to our customers.
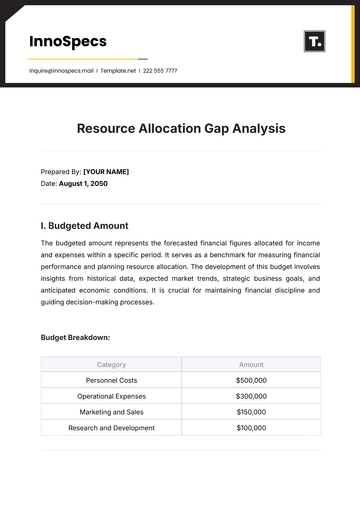
VI. Inventory Cost Analysis
A. Cost Breakdown
Category | Cost Breakdown |
|---|---|
Inventory Carrying Costs | Includes storage expenses, insurance premiums, and depreciation costs for equipment. |
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) | Analysis reveals cost per wash service, identifying opportunities for cost-effective product substitutions. |
B. Cost Reduction Strategies
The purpose of the annual supplier negotiations is to engage in detailed discussions with various suppliers to secure advantageous agreements that result in volume discounts and more favorable payment terms. These efforts are specifically designed to reduce the overall procurement costs associated with acquiring goods and services needed for operations. In parallel, waste reduction initiatives have been introduced, which focus on minimizing the generation of chemical waste. This goal is met by precise chemical use and recycling programs for consumables like towels and air fresheners, reducing waste and promoting sustainability.
VII. Inventory Security and Risk Management
A. Security Measures
Access to the areas where inventory is stored is tightly controlled to ensure security and prevent unauthorized entry. This is achieved through the use of CCTV (closed-circuit television) surveillance systems, which continuously monitor these areas, as well as access control systems that regulate and record who is allowed to enter the storage zones. To further bolster security measures, all staff members are provided with regular training focused on preventing theft and understanding the procedures for reporting any suspicious activities.
This training supports strong security measures and ensures that staff are knowledgeable about best practices. We also use advanced tracking systems to monitor inventory, utilizing barcode scanning for unique identification and RFID tags for detailed, real-time tracking of high-value items. This thorough inventory management approach reduces risks of shrinkage and loss by closely tracking the movement of goods.
B. Risk Mitigation Plans
Contingency plans encompass a range of strategies designed to ensure preparedness for unexpected events. Among these strategies is the maintenance of emergency stock levels for critical inventory items, which serves to mitigate the impact of supply chain disruptions. Additionally, these plans incorporate an updated disaster recovery manual that meticulously outlines the procedures to be followed in the event of inventory loss resulting from natural disasters or accidents. As part of the comprehensive approach to risk management, insurance policies related to inventory are rigorously reviewed and updated on a regular basis. This proactive measure ensures that the coverage remains adequate for various inventory-related incidents, thereby providing an essential safety net for the organization.
VIII. Technology and Systems Integration
A. Inventory Management Software
An extensive evaluation of various advanced inventory management software options—each equipped with real-time tracking and reporting capabilities—is currently in progress. In conjunction with this, detailed integration plans are being formulated to seamlessly incorporate the selected inventory management software with the existing point-of-sale (POS) and accounting systems. The goal of this integration is to streamline and enhance overall inventory operations. Additionally, comprehensive staff training sessions are scheduled to ensure that all users become thoroughly familiarized with the new software features and can optimize the system's usage to its fullest potential.
B. RFID and IoT Applications
A phase of preliminary testing is scheduled to take place, focusing on the implementation of Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) tags. The purpose of these tags is to facilitate automatic inventory tracking and to enable the real-time monitoring of stock levels. This initiative aims to significantly improve the accuracy of inventory records. Additionally, there are plans to integrate Internet of Things (IoT) sensors into the system. These sensors are intended to remotely monitor the levels of chemicals as well as the performance of various pieces of equipment. The adoption of these IoT sensors is expected to enhance operational efficiency by streamlining processes and minimizing the need for manual oversight.
IX. Future Recommendations
A. Long-term Inventory Management Strategies
The project involves the implementation of a centralized inventory control system that will be deployed across multiple locations. This system aims to standardize operations throughout the organization, thereby enhancing scalability and ensuring a consistent approach to inventory management. Alongside this, there will be an exploration of vendor-managed inventory (VMI) solutions in collaboration with key suppliers. The goal of this initiative is to optimize stock levels, ensuring that inventory is replenished efficiently, and to reduce the lead times required for procurement processes. By doing so, the company aims to maintain a more streamlined and responsive supply chain. Furthermore, the organization plans to implement ongoing improvement initiatives, fueled by routine audits and performance assessments, to systematically identify areas for enhancement, adopt best practices, and consistently boost the efficiency and effectiveness of its inventory management processes.
B. Technology Upgrades and Investments
Ensure that budget resources are diligently allocated towards the continuous advancement of software updates and technology upgrades. This strategy is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge in the market and ensuring operational efficiency. Furthermore, it is essential to conduct thorough research and systematically adopt emerging technologies, including but not limited to AI-driven predictive analytics. Such technologies can significantly enhance inventory forecasting capabilities and enable proactive decision-making processes.
C. Training and Development Needs
Organize and conduct regular training workshops specifically designed for staff members, focusing on the most advanced inventory management practices and the effective utilization of relevant software tools. Additionally, establish and offer comprehensive certification programs aimed at inventory handlers, with the goal of enhancing their skills in various critical areas such as handling, tracking, and optimizing inventory processes. Moreover, foster collaboration with industry experts to ensure continuous learning and the implementation of industry best practices, thereby keeping the team updated and proficient in the latest developments in inventory management.
X. Conclusion
A. Summary of Findings
The analysis highlights opportunities for improving inventory management efficiency, reducing costs, and enhancing customer service levels at [Your Company Name]. Recommendations focus on implementing robust inventory control measures, leveraging technology for better tracking and monitoring, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
B. Next Steps for Implementation
Developing a phased implementation plan based on prioritized recommendations to optimize inventory operations and achieve strategic objectives. Establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) and monitoring mechanisms to measure the success of implemented strategies and make necessary adjustments for sustainable growth.
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
Ensure streamlined inventory management with the Car Wash Inventory Management Analysis Template from Template.net. This editable and customizable tool integrates seamlessly into your operations, equipped with an AI Editor Tool for precision. Optimize stock levels, enhance supplier relations, and improve efficiency effortlessly with this comprehensive template, tailored to meet the unique needs of your car wash facility.