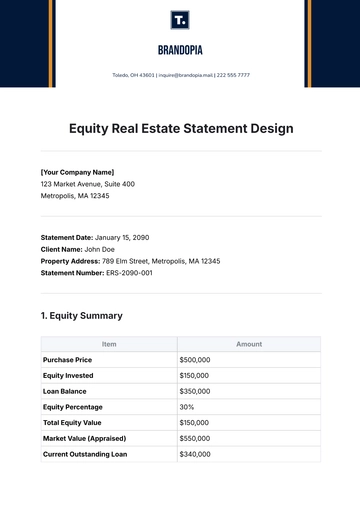
Free Blank Church Crisis Management Statement

I. Introduction
A. Purpose of the Statement
(This section defines the objectives of the Church Crisis Management Statement, establishing its role in guiding the church's response to various crises. It aims to ensure preparedness and effective management of emergencies to safeguard the well-being of the church community.)
B. Scope and Applicability
(Outlines the types of crises covered by the statement, including natural disasters, health emergencies, and security incidents. It also specifies who the plan applies to, including church staff, volunteers, and members.)
C. Overview of the Crisis Management Approach
(Provides a brief summary of the crisis management strategy, including the principles of response and recovery. It sets the framework for how the church will handle crises in a structured and organized manner.)
II. Crisis Management Team
A. Team Structure
(Describes the composition of the crisis management team, including leadership roles and specific responsibilities. It ensures that all members understand their duties and the hierarchy of decision-making.)
B. Chain of Command
(Establishes the order of authority and communication within the crisis management team. This section ensures clarity on who makes decisions and how information flows during a crisis.)
C. Selection Criteria for Team Members
(Details the qualifications and skills required for team members, including expertise in emergency management, communication, and legal matters. This ensures that the team is well-equipped to handle crises effectively.)
III. Crisis Identification and Classification
A. Definition of Crisis
(Provides a clear definition of what constitutes a crisis within the church context. This helps in distinguishing between routine issues and situations requiring immediate and structured response.)
B. Types of Crises Covered
(Lists and describes various types of crises, including natural disasters (e.g., hurricanes), safety incidents (e.g., violence), health emergencies (e.g., pandemics), financial issues, and legal matters. It ensures that the plan addresses a broad range of potential emergencies.)
IV. Communication Plan
A. Internal Communication Procedures
(Outlines methods for notifying church staff and members during a crisis, including communication channels and protocols. This ensures that everyone within the organization is informed and can act according to the plan.)
B. External Communication Procedures
(Describes how the church will communicate with external parties, including the media, local authorities, and the community. It includes protocols for issuing public statements and managing media relations.)
C. Liaison with Authorities
(Details the procedures for coordinating with local emergency services and government agencies. This ensures effective collaboration and support during a crisis.)
V. Response Procedures
A. Immediate Actions
(Specifies the initial steps to be taken in response to a crisis, such as implementing safety measures, conducting evacuations, and contacting emergency services. It focuses on immediate response to protect lives and property.)
B. Ongoing Actions
(Outlines the continued response efforts, including coordination with emergency services, resource management, and regular updates to stakeholders. This ensures that the response remains effective throughout the crisis.)
C. Recovery Procedures
(Describes the steps for assessing damage, providing support, and restoring normal operations after the immediate crisis has been managed. It emphasizes the importance of recovery and rebuilding efforts.)
VI. Resource Management
A. Financial Resources
(Details how financial resources will be allocated during a crisis, including emergency funds and budget adjustments. This ensures that the church can manage the financial aspects of crisis response and recovery.)
B. Personnel Resources
(Outlines how staffing and volunteer needs will be addressed during a crisis, including recruitment and assignment of roles. It ensures that adequate personnel are available to handle the situation.)
C. Material Resources
(Specifies the management of physical resources such as emergency supplies and equipment. This ensures that necessary materials are readily available and effectively utilized.)
VII. Training and Drills
A. Training Programs for Staff and Volunteers
(Describes the training programs designed to prepare staff and volunteers for crisis situations. It includes regular sessions to ensure everyone is knowledgeable about their roles and responsibilities.)
B. Crisis Drills and Simulations
(Outlines the schedule and types of drills and simulations to test the effectiveness of the crisis management plan. This helps identify areas for improvement and ensures preparedness.)
C. Evaluation and Feedback
(Details the process for evaluating the effectiveness of training and drills, including collecting feedback from participants. This ensures continuous improvement of the crisis management plan.)
VIII. Documentation and Reporting
A. Crisis Documentation Procedures
(Specifies how incidents will be documented, including the creation of logs and reports. This ensures that all aspects of the crisis response are recorded for future reference.)
B. Post-Crisis Review
(Outlines the process for reviewing the crisis response after the event, including analyzing what worked well and identifying areas for improvement. This helps in refining the crisis management plan.)
C. Plan Updates
(Details how and when the crisis management plan will be updated based on lessons learned and changing circumstances. This ensures that the plan remains current and effective.)
IX. Plan Review and Maintenance
A. Regular Review Schedule
(Establishes a timeline for regularly reviewing the crisis management plan to ensure its relevance and effectiveness. This includes setting dates for periodic reviews.)
B. Update Procedures
(Outlines the process for making updates to the plan, including who is responsible and how changes will be communicated. This ensures that updates are managed systematically.)
C. Responsibility for Maintenance
(Specifies who is responsible for maintaining and revising the crisis management plan. This ensures that there is accountability for keeping the plan up-to-date.)
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
The Blank Church Crisis Management Statement Template from Template.net is an essential tool for any church looking to prepare for emergencies. Fully editable and customizable, this template allows you to tailor the crisis management plan to your specific needs. Enhanced with an AI Editor Tool, it ensures a professional and comprehensive approach to crisis preparedness.