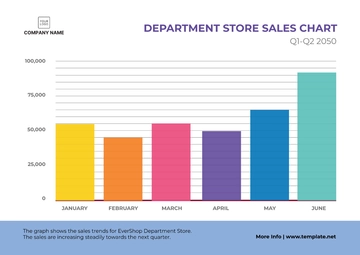
Free Printable Grocery Store Merchandising SOP

1. Introduction
1.1 Purpose
The purpose of this Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) is to provide comprehensive guidelines for effective merchandising at [Your Company Name] grocery stores. This SOP is designed to ensure consistency in product presentation, enhance the visual appeal of the store, and optimize product placement to increase sales. By adhering to these guidelines, the store aims to create an engaging shopping environment that attracts and retains customers. The ultimate goal is to drive profitability and enhance customer satisfaction through strategic merchandising practices.
1.2 Scope
This SOP applies to all employees involved in merchandising at [Your Company Name] grocery stores. It encompasses store managers, assistant managers, department managers, and store associates. The procedures outlined in this document cover the entire merchandising process, from initial planning and execution to monitoring performance and making necessary adjustments. It is crucial for all personnel to understand and follow these procedures to ensure uniformity across all store locations and achieve the desired merchandising outcomes.
1.3 Definitions
Merchandising: The strategic activities involved in promoting and selling products through their presentation and organization in retail environments. Effective merchandising aims to maximize sales and enhance the shopping experience by optimizing product visibility and accessibility.
Planogram: A detailed diagram or model that illustrates the optimal placement of retail products on shelves. It serves as a visual guide for store staff to ensure products are displayed according to pre-determined strategies and marketing objectives.
Endcap: A prominent display located at the end of an aisle, used to showcase promotional items, seasonal products, or high-margin goods. Endcaps are strategically positioned to attract customer attention and drive impulse purchases.
2. Roles and Responsibilities
2.1 Store Manager
The store manager plays a pivotal role in overseeing and ensuring compliance with the SOP. Their responsibilities include:
Overall Compliance: Ensuring that all merchandising practices adhere to the guidelines set forth in this SOP. The store manager is responsible for maintaining the consistency and quality of merchandising across the store.
Coordination: Collaborating with department managers to implement and execute merchandising strategies effectively. This involves regular communication to align departmental goals with overall store objectives.
Planogram Review: Reviewing and approving planograms to ensure they meet the store's merchandising goals. This includes evaluating the effectiveness of product placement and making necessary adjustments.
Sales Monitoring: Monitoring sales performance and analyzing trends to identify areas for improvement. The store manager uses sales data to refine merchandising strategies and address any issues that may arise.
2.2 Assistant Manager
The assistant manager supports the store manager in executing merchandising plans and maintaining store operations. Their duties include:
Implementation Support: Assisting in the execution of merchandising plans as outlined by the store manager. This involves overseeing the setup of displays, ensuring adherence to planograms, and managing store associates during merchandising activities.
Supervision: Supervising store associates to ensure that merchandising tasks are completed accurately and efficiently. The assistant manager provides guidance and support to staff as needed.
Cleanliness and Organization: Ensuring that display areas are clean, well-organized, and visually appealing. The assistant manager is responsible for maintaining store standards and addressing any issues related to store presentation.
2.3 Department Manager
Department managers are responsible for specific areas within the store and play a crucial role in merchandising:
Plan Development: Developing and implementing merchandising plans tailored to their respective departments. This includes creating displays, setting product placement strategies, and coordinating with vendors.
Vendor Coordination: Working with vendors to obtain promotional materials and arrange product placements. Department managers negotiate terms for product displays and ensure timely delivery of materials.
Staff Training: Training department staff on effective merchandising techniques and best practices. This involves providing guidance on product placement, display creation, and customer service.
2.4 Store Associates
Store associates are responsible for executing merchandising plans and maintaining store presentation. Their responsibilities include:
Execution: Following the planogram and merchandising instructions provided by managers. Store associates set up displays, arrange products on shelves, and ensure adherence to visual merchandising guidelines.
Maintenance: Keeping display areas clean and organized throughout the day. Store associates are responsible for tidying up shelves, removing damaged products, and replenishing stock as needed.
Reporting: Reporting any issues or discrepancies related to merchandising to department managers. This includes notifying managers of stock shortages, display problems, or other concerns that may affect store presentation.
3. Merchandising Planning
3.1 Sales Data Analysis
Effective merchandising begins with a thorough analysis of sales data to inform decision-making:
Historical Data Analysis: Reviewing past sales data to identify trends, customer preferences, and seasonal variations. This analysis helps in understanding which products are popular and which ones may need more promotional support.
Forecasting: Using sales data to forecast future demand and plan product placement strategies accordingly. Accurate forecasting enables the store to anticipate customer needs and adjust inventory levels.
High-Margin Products: Identifying high-margin products that should receive prominent placement to maximize profitability. High-margin items often benefit from increased visibility and strategic positioning.
3.2 Planogram Development
Planograms are essential tools for ensuring effective product placement and merchandising:
Development: Creating detailed planograms that outline the optimal placement of products on shelves. Planograms should reflect sales data analysis and merchandising goals to ensure that products are positioned for maximum impact.
Clarity and Detail: Ensuring that planograms are clear, detailed, and easy to follow. This includes providing precise instructions for product placement, shelf labeling, and display arrangements.
Regular Updates: Reviewing and updating planograms regularly to adapt to changes in inventory, sales trends, and promotional activities. Keeping planograms current ensures that merchandising strategies remain effective and relevant.
3.3 Vendor Coordination
Effective coordination with vendors is crucial for successful merchandising:
Communication: Establishing clear communication channels with vendors to obtain promotional materials, product displays, and other resources. Effective communication helps to ensure that vendors understand the store's merchandising needs and requirements.
Negotiation: Negotiating with vendors for better product placement, promotional support, and favorable terms. Strong vendor relationships can lead to mutually beneficial arrangements and enhanced merchandising opportunities.
Timely Delivery: Ensuring that promotional materials and products are delivered on time and in good condition. Timely delivery is essential for maintaining store presentation and executing promotional activities.
4. Merchandising Execution
4.1 Product Placement
Proper product placement is key to effective merchandising:
Planogram Adherence: Following the planogram for product placement to ensure consistency and alignment with merchandising strategies. Adhering to the planogram helps to maintain the store's visual standards and maximize sales.
Eye-Level Placement: Positioning high-margin and high-demand products at eye level to attract customer attention and encourage purchases. Eye-level placement is a proven technique for increasing product visibility and driving sales.
Endcap Utilization: Using endcaps for promotional items, seasonal products, and high-margin goods. Endcaps are strategically located to capture customer attention and drive impulse purchases.
4.2 Display Creation
Creating visually appealing displays is essential for attracting customers:
Visual Appeal: Designing displays that are visually appealing and engaging. This includes using color schemes, signage, and product arrangement techniques to create a compelling shopping experience.
Display Techniques: Implementing various display techniques, such as color blocking, cross-merchandising, and vertical merchandising. These techniques help to highlight products, create focal points, and enhance overall store presentation.
Lighting and Cleanliness: Ensuring that displays are well-lit and clean. Proper lighting enhances the visual appeal of products, while cleanliness ensures that displays are attractive and free from clutter.
4.3 Stock Management
Effective stock management is crucial for maintaining store operations:
Inventory Checks: Regularly checking inventory levels to ensure that shelves are adequately stocked. This includes monitoring product availability, identifying low stock levels, and replenishing items as needed.
Product Rotation: Using the FIFO (First In, First Out) method to rotate products and ensure that older stock is sold before newer stock. Proper product rotation helps to reduce waste and ensure that customers receive fresh products.
Removal of Damaged Products: Promptly removing damaged or expired products from shelves to maintain store presentation and ensure product quality. Regular inspections help to identify and address any issues with product integrity.
4.4 Pricing and Signage
Accurate pricing and effective signage contribute to successful merchandising:
Price Tags: Ensuring that all products have clear and accurate price tags. Price tags should be easy to read and reflect the correct pricing information.
Promotional Signage: Using signage to highlight promotions, special offers, and new products. Promotional signage helps to draw attention to deals and encourage customers to take advantage of discounts.
Branding: Keeping signage clean, professional, and aligned with the store's branding. Consistent branding helps to reinforce the store's image and create a cohesive shopping experience.
5. Monitoring and Adjustment
5.1 Sales Monitoring
Ongoing sales monitoring is essential for evaluating merchandising effectiveness:
Regular Review: Monitoring sales data regularly to assess the impact of merchandising strategies. Analyzing sales performance helps to identify successful tactics and areas for improvement.
Performance Analysis: Evaluating the performance of individual products and displays to determine their effectiveness. This includes tracking sales trends, customer feedback, and the impact of promotional activities.
Adjustment: Making necessary adjustments to merchandising plans based on sales data and performance analysis. Adjustments may include repositioning products, updating displays, or changing promotional strategies.
5.2 Customer Feedback
Customer feedback provides valuable insights into merchandising practices:
Feedback Collection: Collecting feedback from customers on store layout, product placement, and overall shopping experience. Feedback can be gathered through surveys, comment cards, or direct interactions with customers.
Informed Adjustments: Using customer feedback to make informed adjustments to merchandising plans. Addressing customer preferences and concerns helps to improve store presentation and enhance customer satisfaction.
Engagement: Engaging with customers to understand their needs and preferences. Building strong customer relationships helps to tailor merchandising strategies to meet their expectations.
5.3 Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement is key to maintaining effective merchandising practices:
Regular Reviews: Conducting regular reviews of merchandising strategies and planograms to ensure they remain effective and relevant. This includes assessing the impact of changes and identifying opportunities for enhancement.
Best Practices: Implementing best practices and innovative merchandising techniques to stay competitive. Staying informed about industry trends and emerging technologies helps to improve store presentation and customer engagement.
Staff Training: Providing ongoing training for staff on merchandising trends and techniques. Regular training ensures that employees are equipped with the knowledge and skills needed to execute effective merchandising strategies.
6. Health and Safety
6.1 Safety Guidelines
Adhering to safety guidelines is essential for ensuring a safe shopping environment:
Compliance: Ensuring that all displays and product placements comply with health and safety regulations. This includes following guidelines related to product placement, shelf stability, and customer safety.
Shelf Stability: Avoiding the placement of heavy items on high shelves to prevent accidents and ensure customer safety. Properly securing displays helps to prevent potential hazards.
Aisle Clearance: Keeping aisles and walkways clear of obstructions to allow safe and easy access for customers. Regularly inspecting aisles and addressing any potential hazards helps to maintain a safe shopping environment.
6.2 Emergency Procedures
Training staff on emergency procedures is crucial for handling unexpected situations:
Emergency Training: Providing training on emergency procedures related to merchandising activities. This includes instructions for responding to incidents such as fires, accidents, or medical emergencies.
Emergency Equipment: Ensuring that staff know the location of fire exits, first aid kits, and other emergency equipment. Regularly reviewing emergency procedures helps to ensure staff preparedness.
Reporting: Reporting any safety hazards or incidents to the store manager immediately. Prompt reporting allows for timely resolution and helps to maintain a safe store environment.
7. Training and Development
7.1 Initial Training
Comprehensive initial training is essential for new employees:
Overview: Providing an overview of merchandising principles and practices to new hires. This includes introducing them to the store's merchandising goals, strategies, and expectations.
Hands-On Training: Offering hands-on training with experienced staff members to demonstrate merchandising techniques and procedures. Practical experience helps new hires to understand and apply merchandising concepts effectively.
Understanding Importance: Ensuring that new hires understand the importance of merchandising in driving sales and enhancing the customer experience. Emphasizing the impact of effective merchandising on store success helps to motivate and engage employees.
7.2 Ongoing Training
Ongoing training supports staff development and keeps them informed about industry trends:
Regular Sessions: Offering regular training sessions on new merchandising trends, techniques, and technologies. Staying current with industry developments helps staff to implement effective merchandising strategies.
Workshops and Conferences: Encouraging staff to attend workshops, industry conferences, and other professional development opportunities. These events provide valuable insights and networking opportunities.
Online Resources: Providing access to online training resources and materials for continuous learning. Online resources offer flexibility and convenience for staff to enhance their skills.
8. Documentation and Record Keeping
8.1 Planogram Records
Maintaining accurate planogram records is essential for consistency:
Documentation: Keeping detailed records of all planograms, including versions and updates. This documentation serves as a reference for staff and ensures that planograms are implemented correctly.
Accessibility: Ensuring that planograms are easily accessible to all relevant staff members. Providing access to planograms helps to ensure that merchandising practices are followed consistently.
Audit Review: Reviewing planogram records during merchandising audits to verify compliance and identify areas for improvement. Regular audits help to maintain planogram accuracy and effectiveness.
8.2 Sales Data Reports
Sales data reports provide valuable insights into merchandising performance:
Record Keeping: Keeping detailed records of sales data and merchandising performance metrics. This includes tracking sales by product category, department, and promotional activity.
Performance Analysis: Using sales data reports to analyze the impact of merchandising strategies on sales. Performance analysis helps to identify successful tactics and areas for improvement.
Staff Sharing: Sharing relevant data with staff to inform future merchandising plans and decision-making. Providing staff with performance insights helps to align their efforts with store objectives.
9. Compliance and Auditing
9.1 Internal Audits
Regular internal audits help to ensure compliance with the SOP:
Audit Frequency: Conducting internal audits at regular intervals to assess compliance with merchandising guidelines and procedures. Regular audits help to identify and address any issues or discrepancies.
Findings and Improvement: Using audit findings to improve merchandising practices and address any identified issues. Implementing corrective actions helps to maintain high standards and enhance store performance.
Documentation: Documenting audit results and actions taken to address any issues. Maintaining records of audit findings helps to track progress and ensure accountability.
9.2 External Audits
Preparing for external audits is essential for maintaining industry standards:
Preparation: Ensuring that all merchandising activities comply with industry standards, regulations, and best practices. Preparing for external audits involves reviewing and updating merchandising practices as needed.
Documentation: Providing auditors with access to necessary documentation and records, including planograms, sales data reports, and training materials. Proper documentation facilitates a smooth audit process.
Recommendations: Implementing recommendations from external audits to enhance merchandising practices and address any areas for improvement. External audits provide valuable feedback for continuous improvement.
10. Approval and Revision History
11.1 Approval
Approved by: [Your Name]
Title: [Your Title]

Date:
11.2 Revision History
Revision | Date | Description of Changes | Author |
|---|---|---|---|
1.0 | 01/01/2050 | Initial release of the SOP | [Your Name] |
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
Standardize merchandising with the Printable Grocery Store Merchandising SOP Template on Template.net. It’s customizable and editable, designed for detailed procedures. Utilize our Ai Editor Tool to create Standard Operating Procedures covering product placement, display standards, and visual merchandising, enhancing store presentation and customer engagement.