Professional Grocery Store Inventory SOP
I. Introduction
A. Purpose
Objective of the SOP
[Your Company Name]'s Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) outlines the systematic approach for managing inventory in our grocery store, aiming to streamline operations, enhance accuracy, and ensure efficient stock management. The SOP provides clear guidelines to minimize stockouts, reduce inventory shrinkage, and optimize stock levels to meet customer demand effectively. Implementing this SOP will lead to improved operational efficiency and higher customer satisfaction.
Benefits of Implementing the SOP
By adhering to this SOP, the store will experience more consistent inventory control, fewer discrepancies between physical and recorded stock, and improved vendor relationships. The structured processes will reduce the likelihood of overstocking and stockouts, thereby decreasing waste and increasing profitability. Additionally, staff will have clear procedures to follow, reducing training time and errors.
B. Scope
Applicability to Staff and Departments
This SOP applies to all employees involved in inventory management, including those responsible for ordering, receiving, stocking, and auditing inventory. It is relevant to store managers, inventory clerks, and any staff handling inventory-related tasks. The procedures outlined are designed to be followed by all relevant departments to ensure cohesive inventory management.
Types of Inventory Covered
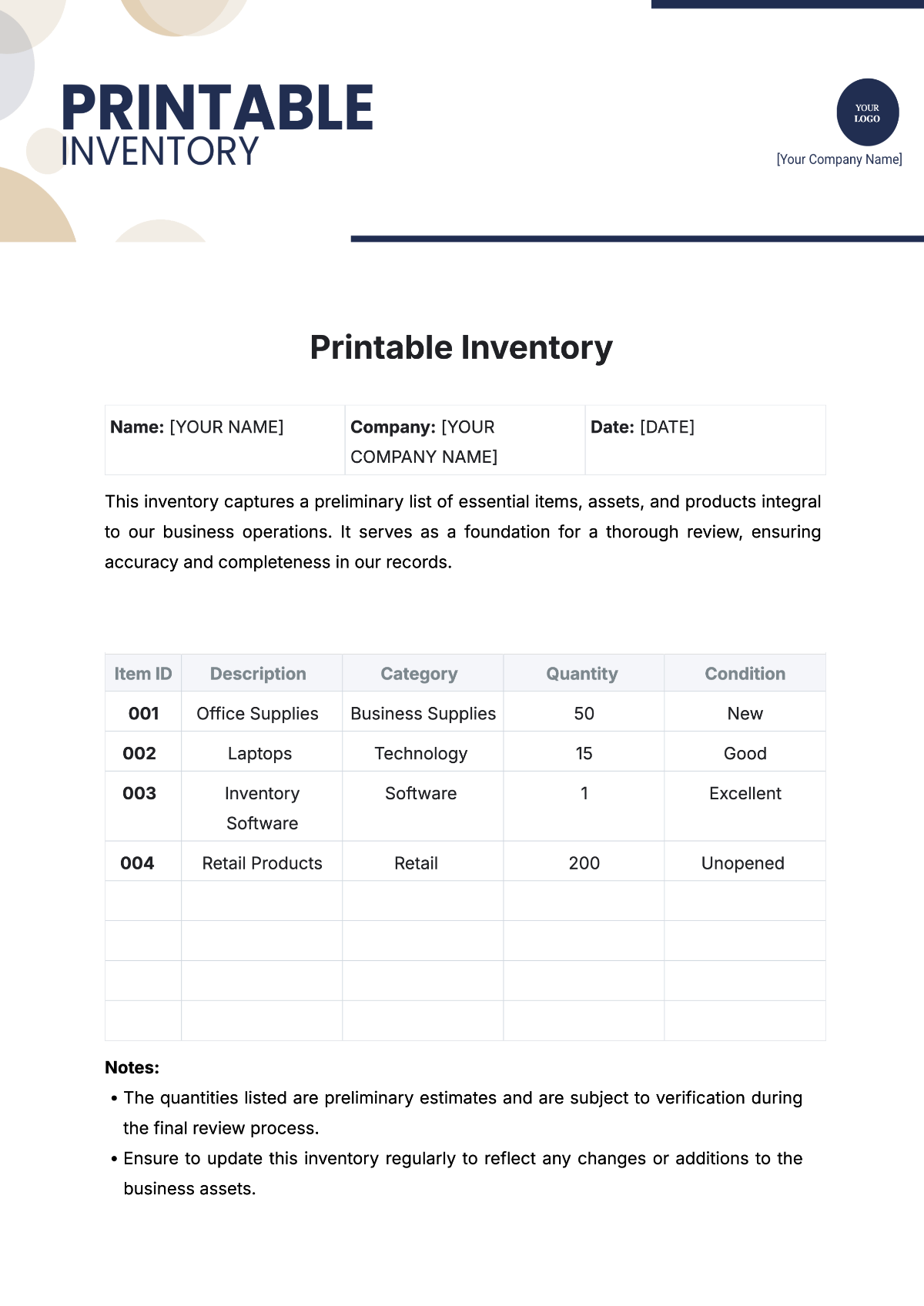
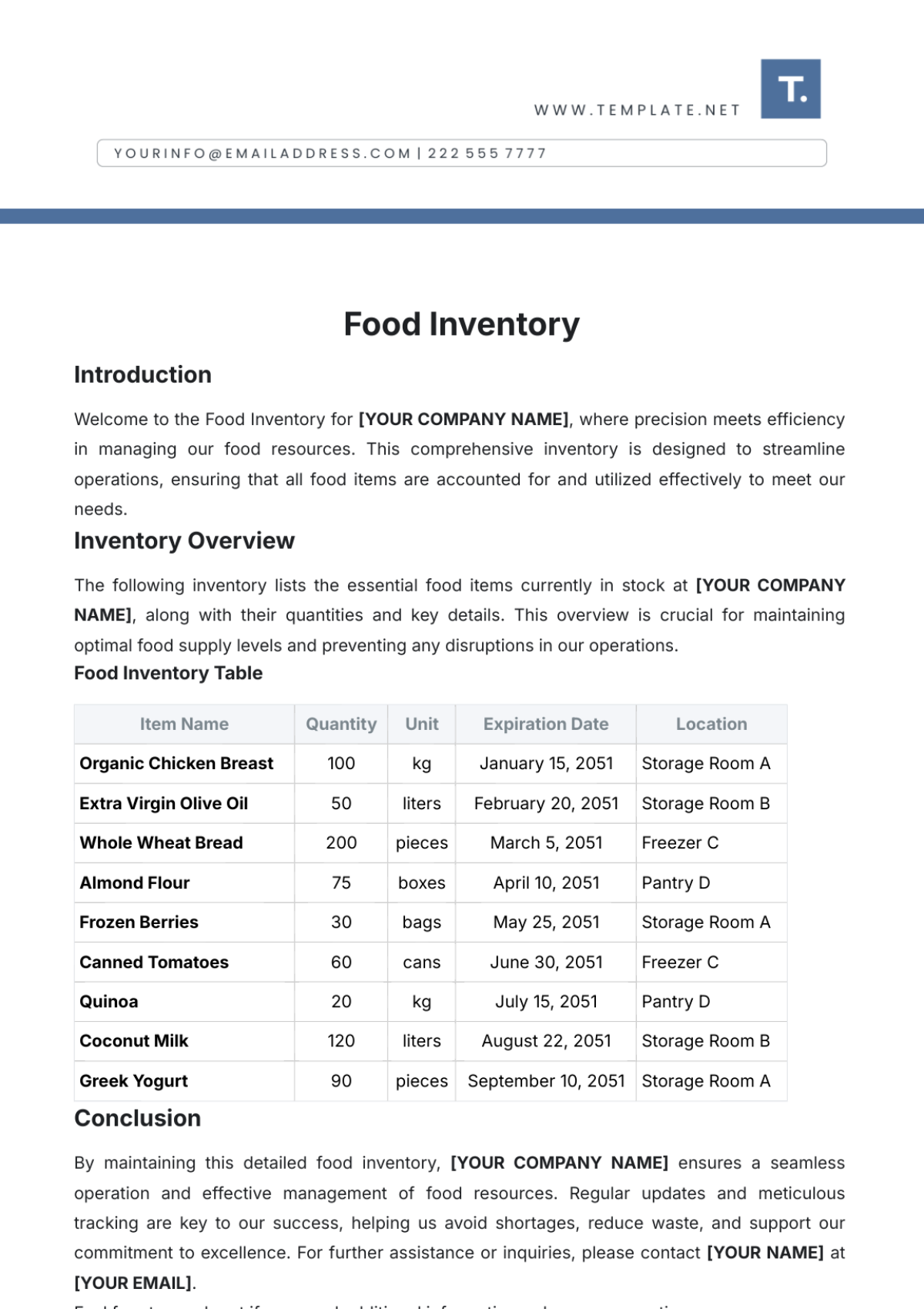
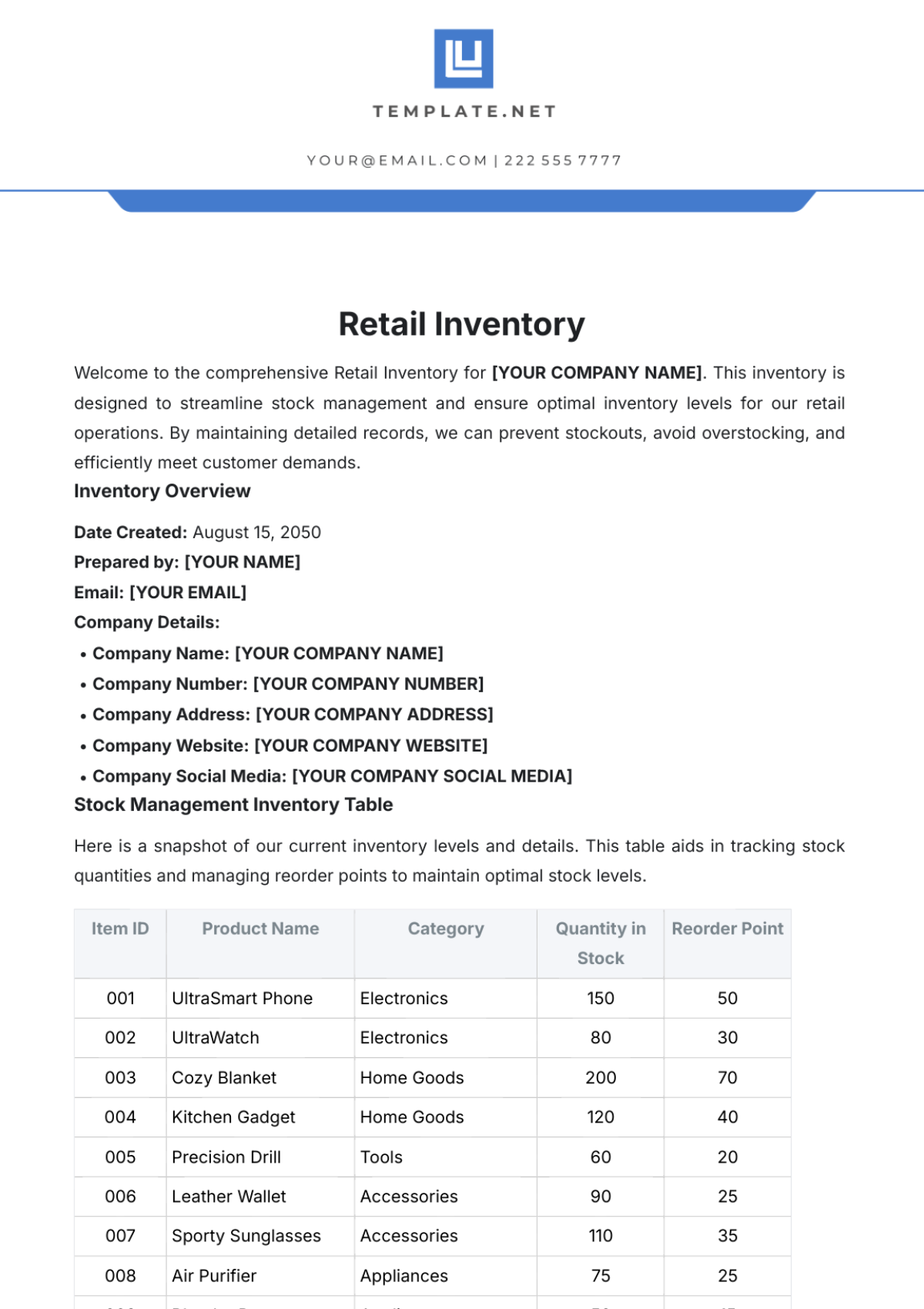
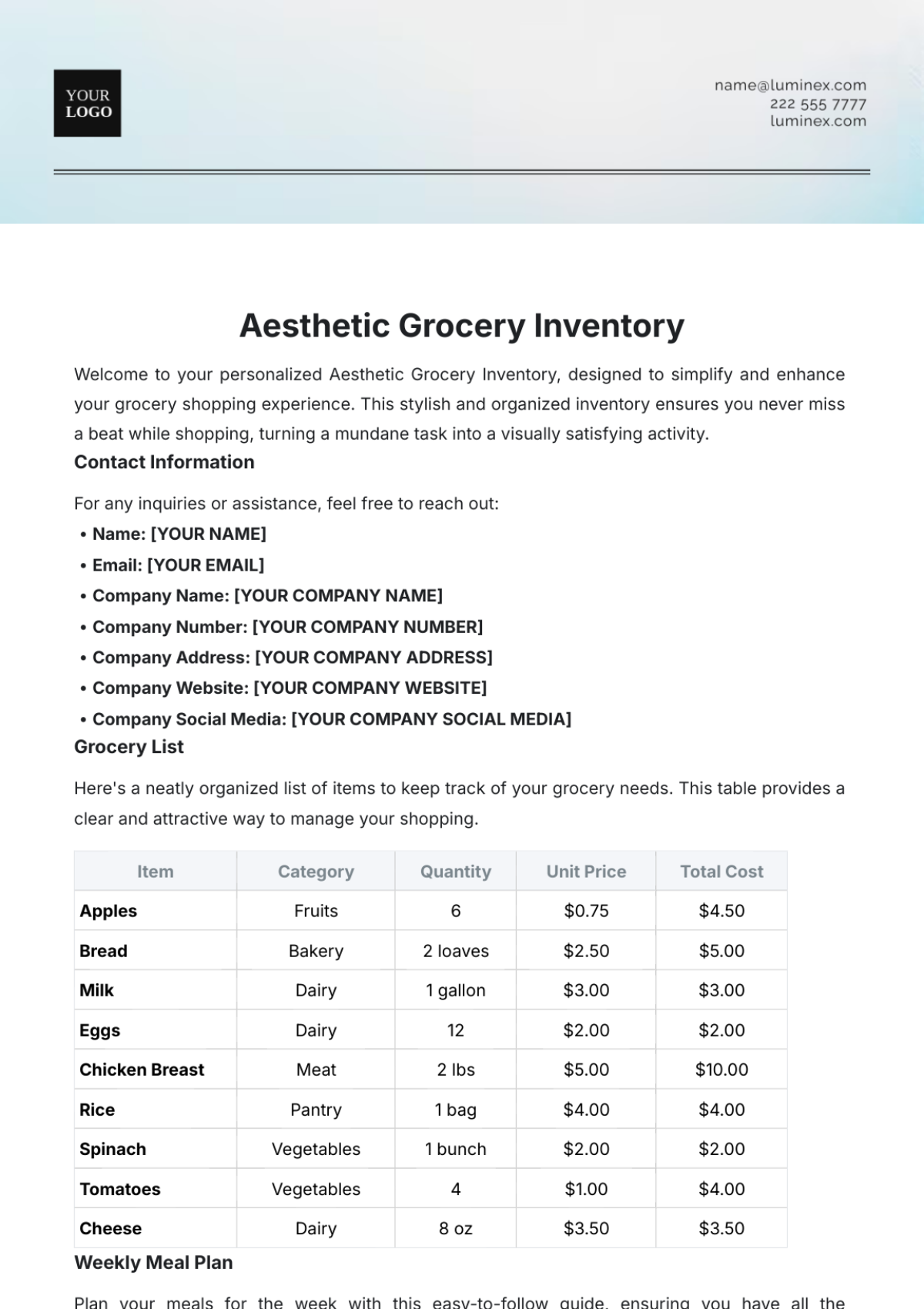
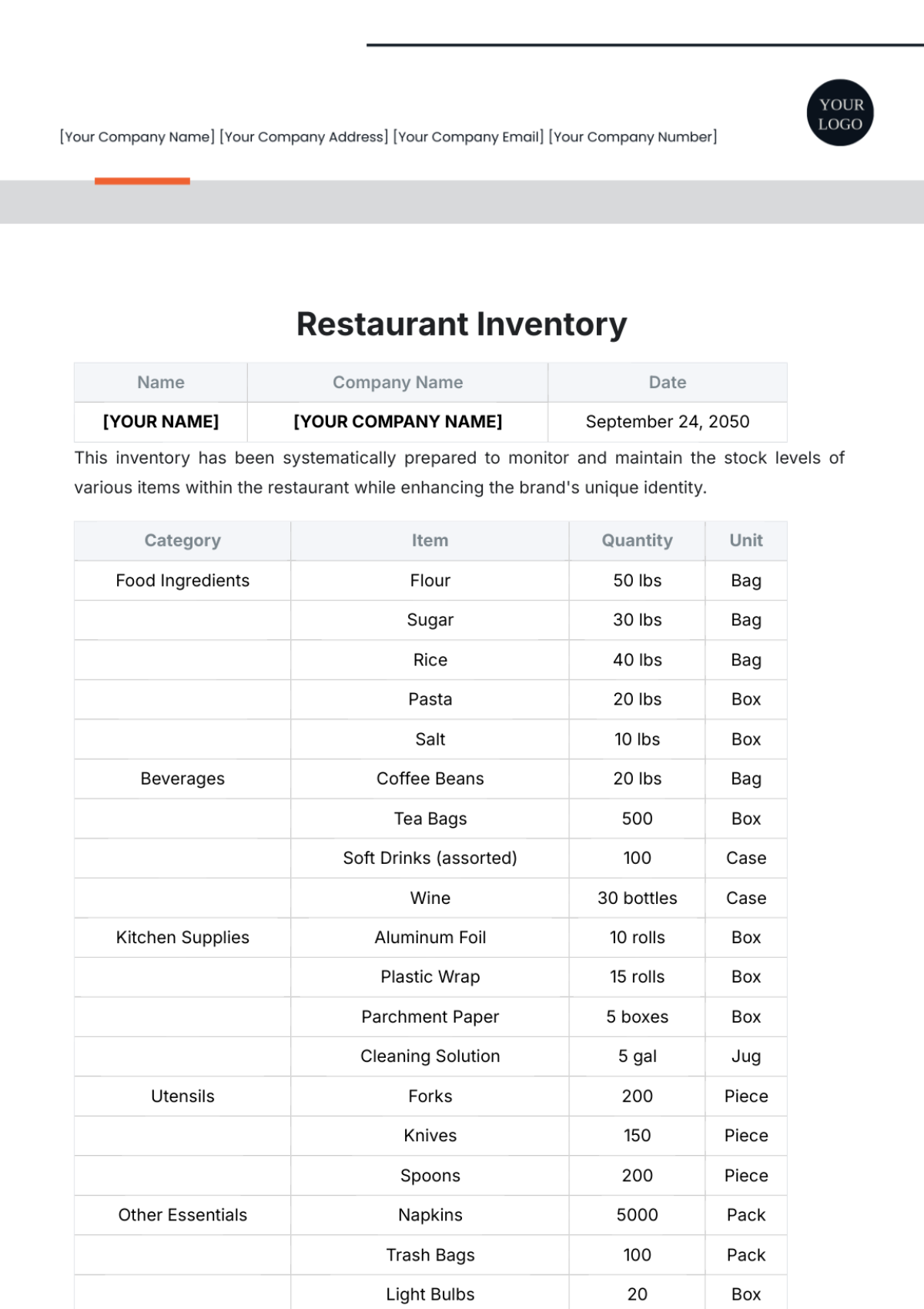
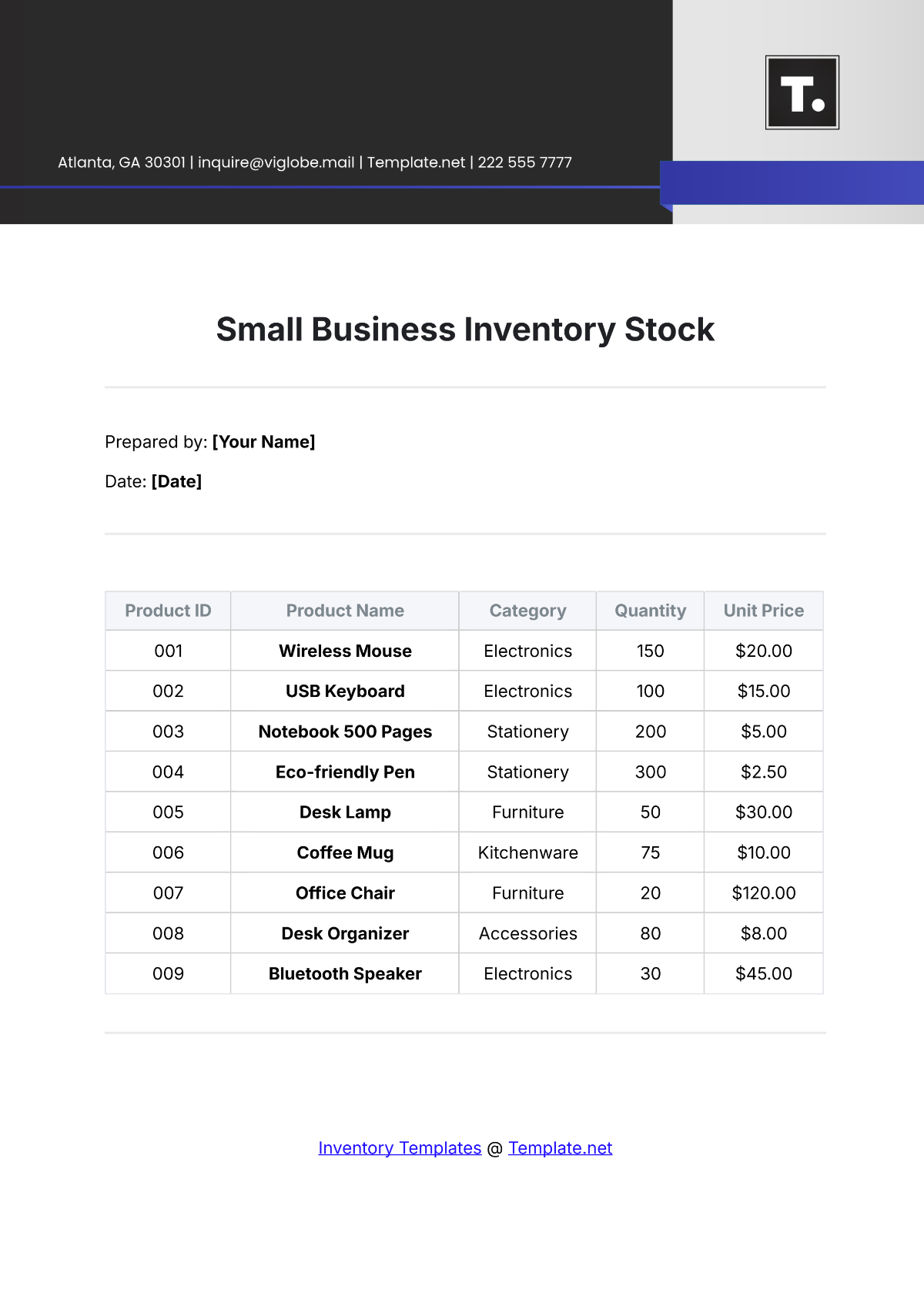
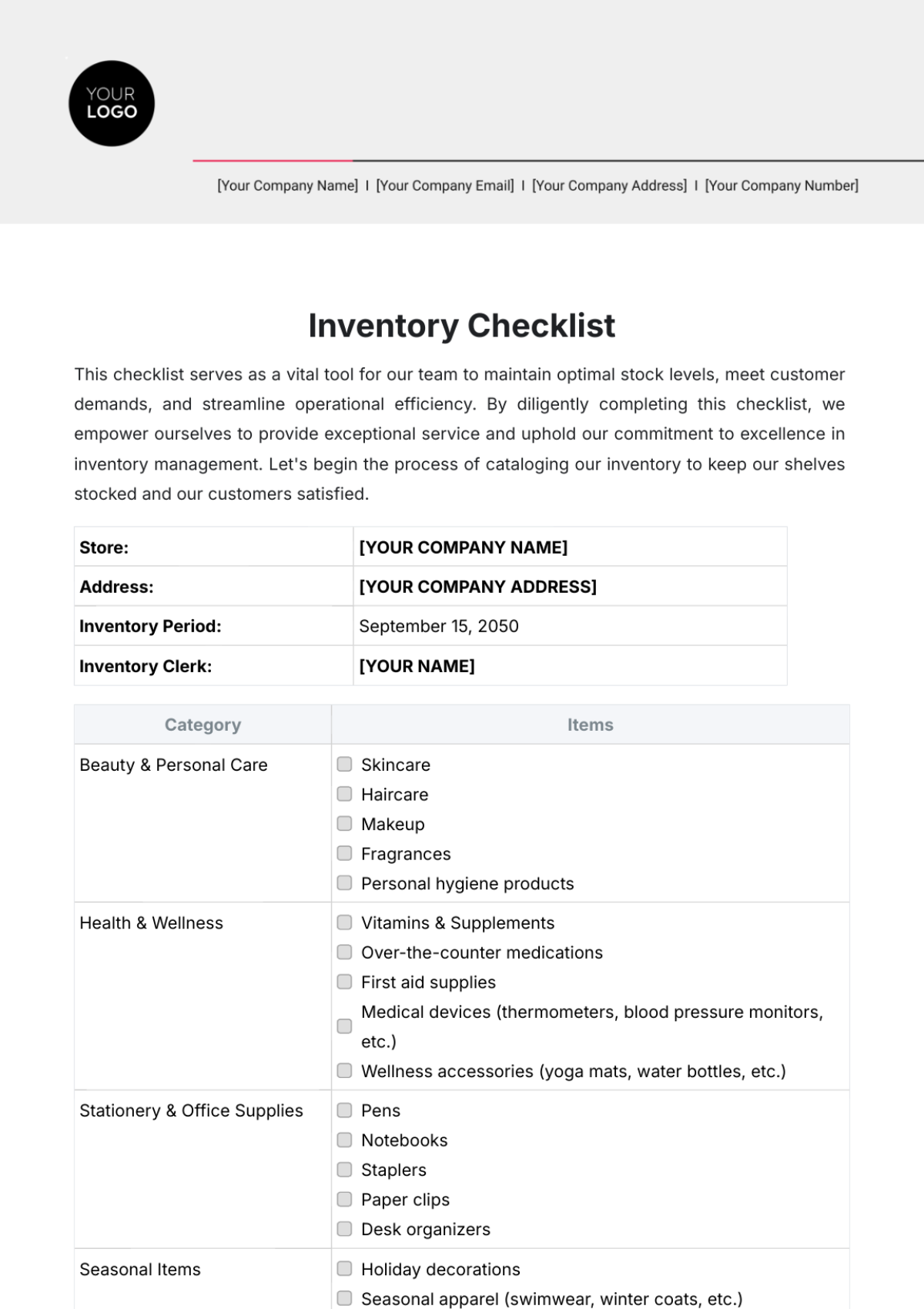
The SOP covers all inventory types within the store, including perishable goods like fresh produce and dairy, non-perishable items such as canned goods and dry foods, and seasonal or promotional products. It includes guidelines for both high-turnover and slow-moving items, addressing the specific needs of each category. This comprehensive approach ensures that all inventory is managed effectively.
C. Definitions
Key Terms and Concepts
Stock Keeping Unit (SKU): A unique identifier assigned to each product to track inventory and manage stock levels. Each SKU represents a distinct product variation, such as size or flavor.
Reorder Point: The predetermined inventory level at which a new order should be placed to prevent stockouts. This point is calculated based on sales trends, lead times, and safety stock.
FIFO (First-In, First-Out): An inventory management principle where the oldest stock is sold first to ensure product freshness and reduce the risk of inventory obsolescence.
Abbreviations and Acronyms
SOP: Standard Operating Procedure, a document that outlines the processes and procedures for inventory management.
FIFO: First-In, First-Out, a method for managing inventory to ensure that older products are used before newer ones.
SKU: Stock Keeping Unit, a unique code used to identify and track products in inventory systems.
II. Inventory Management Procedures
A. Ordering Inventory
Reorder Points and Thresholds
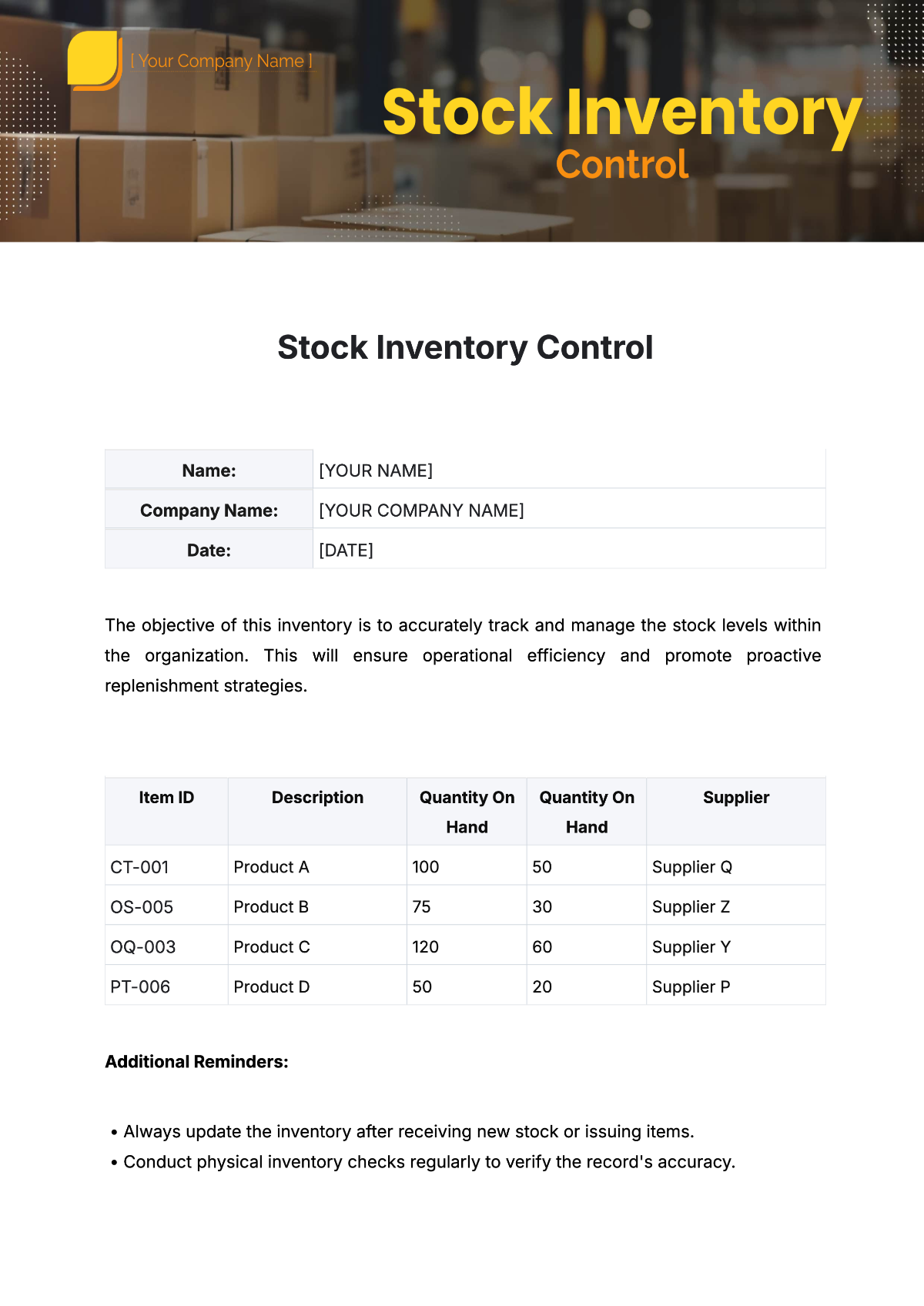
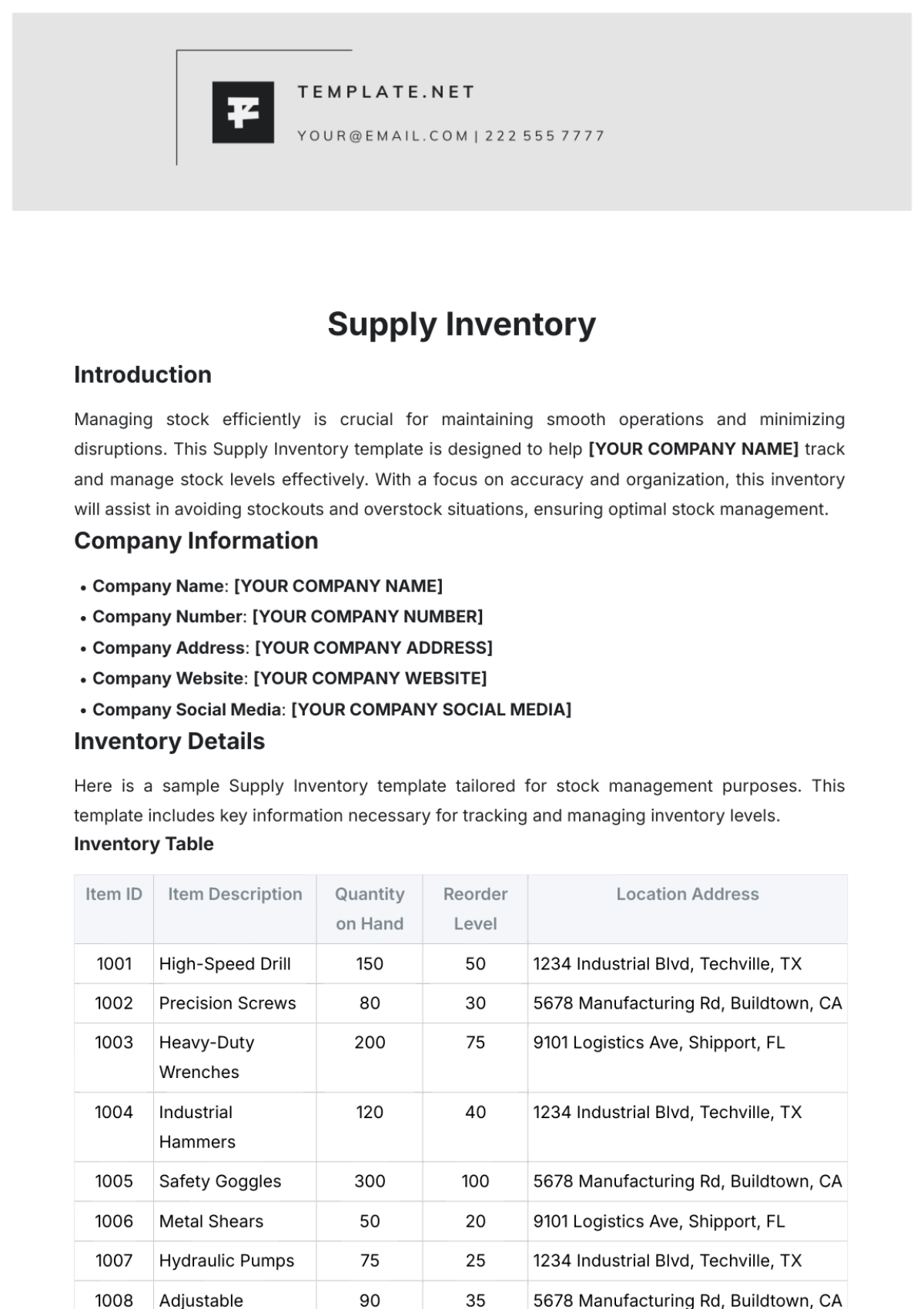
Criteria for Determining Reorder Points: Reorder points are established based on historical sales data, lead times from suppliers, and desired safety stock levels. Consideration is given to product demand variability and seasonal fluctuations. The goal is to ensure inventory is replenished before it reaches critically low levels.
Calculating Safety Stock Levels: Safety stock levels are determined using statistical analysis of past sales data and lead time variability. A safety stock formula that accounts for average demand and supply chain delays helps prevent stockouts. Regular review and adjustment of safety stock levels are necessary to respond to changing conditions.
Order Placement
Vendor Selection Process: Select vendors based on their reliability, cost-effectiveness, and product quality. Maintain a preferred vendor list and periodically evaluate vendor performance through feedback and performance metrics. Ensure that vendors can meet delivery schedules and maintain product standards.
Order Forms and Documentation: Use standardized order forms to capture necessary details such as product SKU, quantity, and delivery instructions. Ensure that all orders are documented with accurate and complete information to facilitate order fulfillment and future audits. Maintain copies of all order forms for record-keeping.
Approval Process for Orders: All orders must be reviewed and approved by the inventory manager to ensure alignment with budget constraints and inventory needs. Approval should be based on current stock levels, sales forecasts, and financial considerations. Unauthorized or incorrect orders must be rectified before submission to suppliers.
B. Receiving Inventory
Inspection Procedures
Checking for Damage and Accuracy: Upon receipt, inspect all goods for visible damage and verify quantities against purchase orders. Any discrepancies or damages should be recorded immediately and reported to the supplier for resolution. Ensure that all received items meet quality standards and match the ordered specifications.
Verification Against Purchase Orders: Cross-check received items with the corresponding purchase orders to confirm accuracy. Ensure that product descriptions, quantities, and specifications align with the order details. Update inventory records to reflect accurate stock levels upon verification.
Documentation
Receiving Logs: Maintain detailed receiving logs that include information on the received items, delivery dates, and supplier details. Logs should be updated promptly to reflect the most current inventory status. These records are crucial for tracking inventory flow and resolving any issues.
Supplier Delivery Notes: File all supplier delivery notes along with purchase orders and receiving logs. Delivery notes provide a record of what was shipped and received, supporting accurate inventory management and facilitating audits. Ensure that delivery notes are signed and dated upon receipt.
Handling Discrepancies
Reporting Procedures for Issues: Report any discrepancies, such as missing items or damaged goods, to the supplier immediately. Document the issues in the receiving log and communicate them to the inventory manager for further action. Follow up with the supplier to address and resolve the discrepancies.
Steps for Resolving Discrepancies: Work with suppliers to resolve discrepancies by verifying order details and arranging for replacement or credit if necessary. Adjust inventory records to reflect the resolution of issues. Ensure that corrective actions are documented and reviewed to prevent recurrence.
C. Stocking Inventory
Product Placement
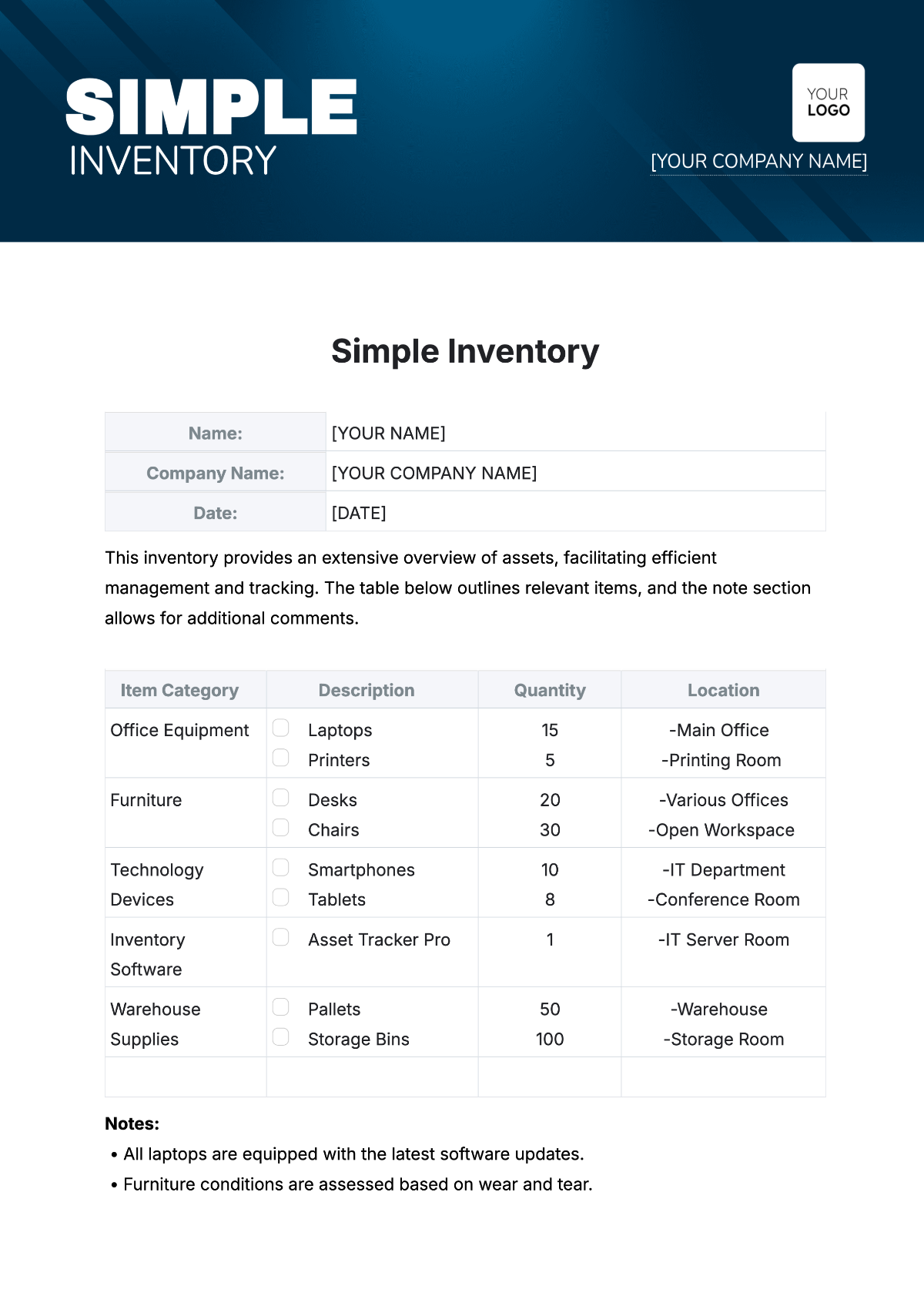
Shelf Organization and Layout: Arrange products on shelves according to the store’s layout plan and customer preferences. Ensure that high-demand items are placed in accessible locations and that products are organized logically by category. Regularly review and adjust shelf placement to optimize sales and customer experience.
FIFO (First-In, First-Out) Principles: Implement FIFO by positioning older inventory in front and newer stock in the back to ensure that older products are sold first. This practice helps reduce waste and ensures that customers receive fresh products. Regularly rotate stock to maintain FIFO compliance.
Labeling and Tagging
Price Tags and Barcodes: Ensure all products are labeled with accurate price tags and barcodes. Verify that price tags are correctly aligned with the product and that barcodes are scannable for efficient checkout. Update labels promptly to reflect any price changes or promotions.
Expiry Date Management: Clearly mark expiry dates on all perishable products and regularly check inventory for approaching expiry dates. Implement a system to remove expired items from shelves to maintain product freshness and comply with health regulations. Conduct periodic reviews to ensure effective expiry date management.
D. Monitoring and Adjustments
Inventory Tracking
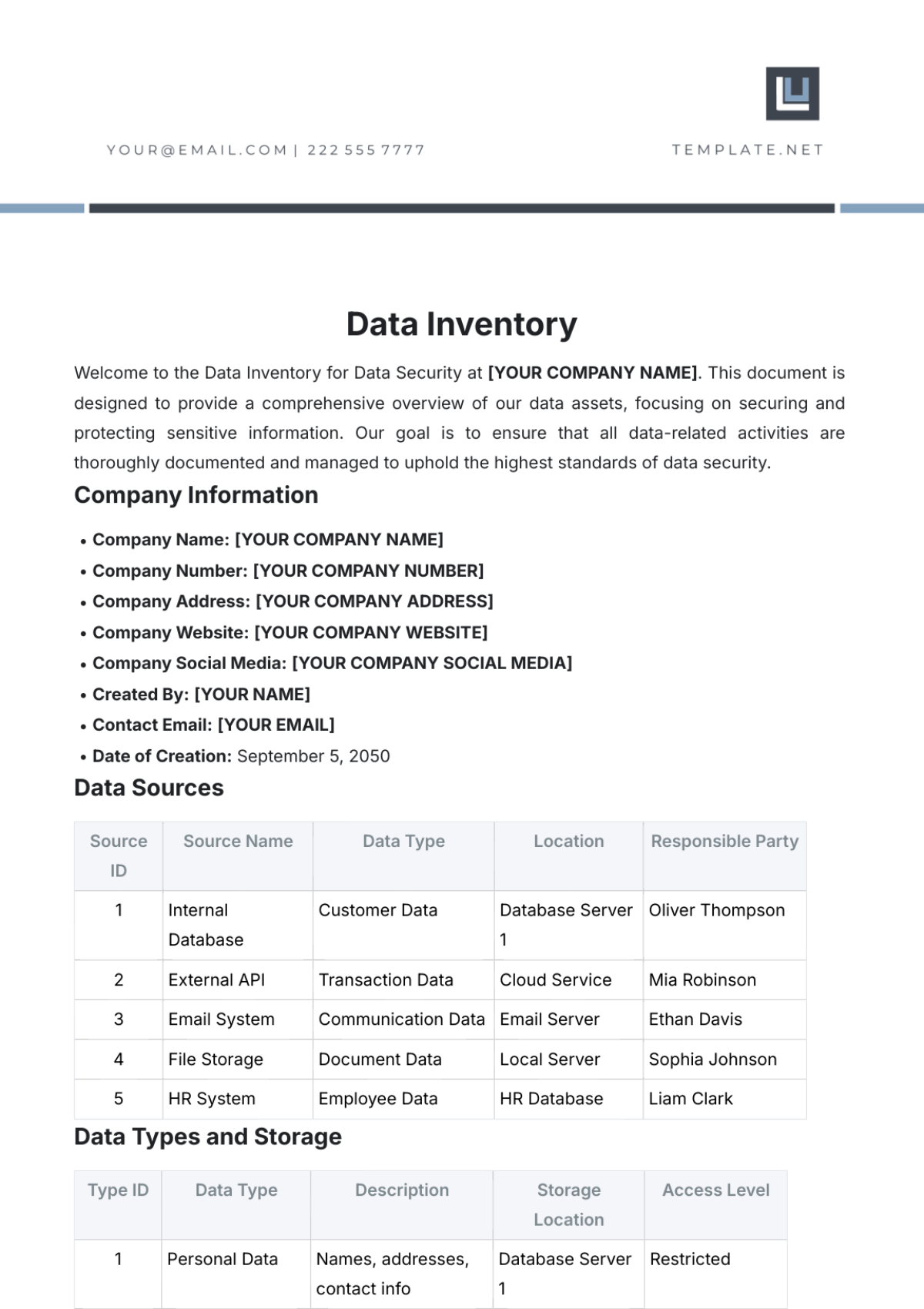
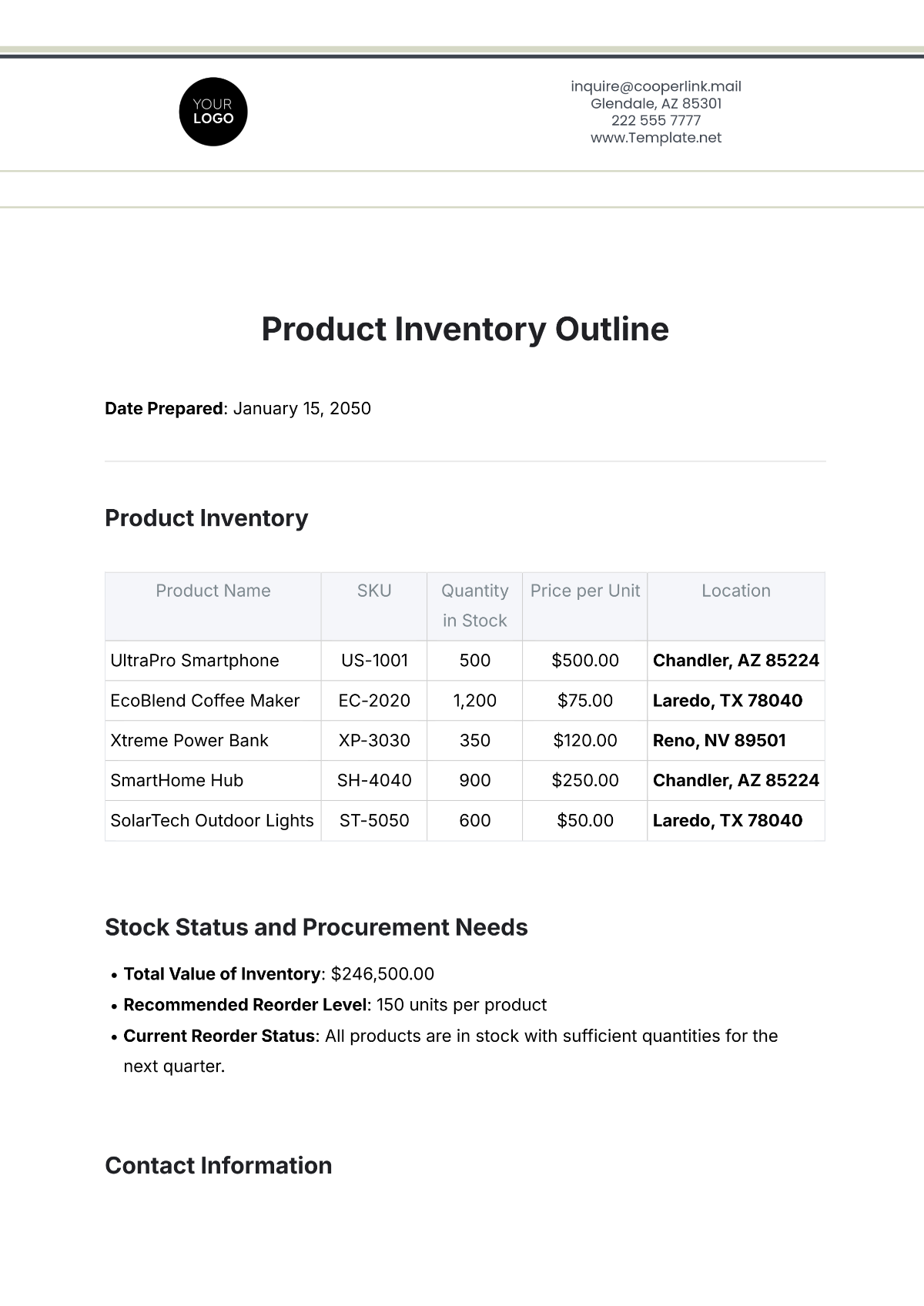
Methods for Tracking Stock Levels: Utilize inventory management software to track stock levels in real-time and manage inventory efficiently. Regularly update stock levels based on sales data, receipts, and adjustments. Ensure that all transactions are recorded accurately to maintain up-to-date inventory records.
Inventory Management Software Usage: Train staff on the use of inventory management software to ensure accurate data entry and reporting. Regularly check software functionality and perform system maintenance to prevent errors. Utilize software features to generate reports and analyze inventory trends.
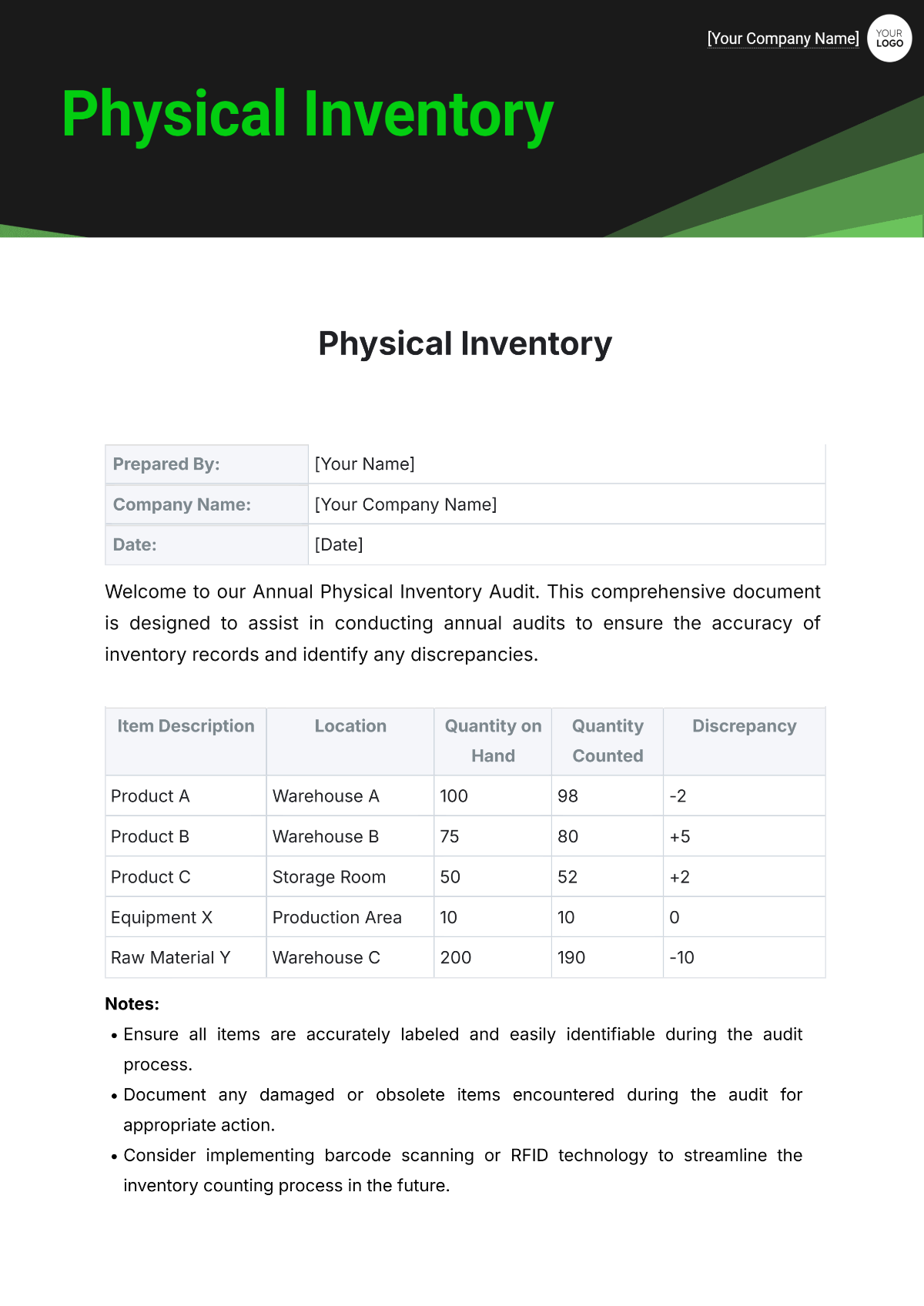
Cycle Counts and Audits
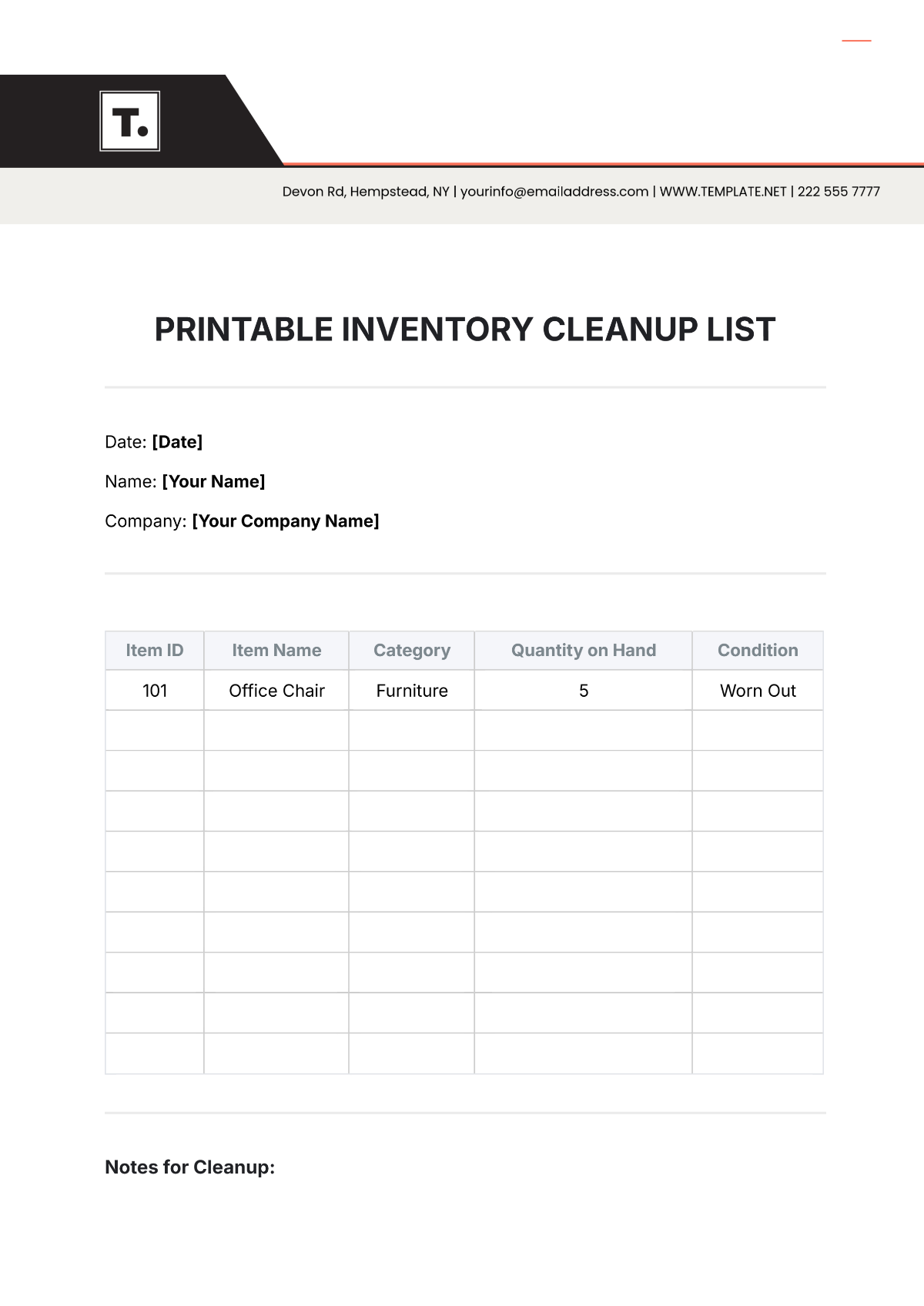
Schedule for Regular Counts: Conduct cycle counts on a scheduled basis, such as weekly or monthly, to verify inventory accuracy. Rotate the areas counted to ensure all inventory is reviewed periodically. Document cycle count results and address any discrepancies identified.
Procedures for Conducting Audits: Follow established procedures for conducting full inventory audits, including verifying physical stock against recorded amounts. Involve multiple staff members in the audit process to ensure accuracy and objectivity. Review audit findings and implement corrective actions as needed.
Adjustments
Handling Stock Discrepancies: Investigate and resolve discrepancies identified during cycle counts or audits by reviewing records and conducting physical checks. Adjust inventory records to reflect accurate stock levels and document the reasons for adjustments. Implement measures to prevent future discrepancies.
Updating Inventory Records: Regularly update inventory records to ensure they reflect actual stock levels. Record all adjustments, including reasons for changes, to maintain accurate and transparent records. Review inventory records periodically to identify and address any trends or issues.
III. Roles and Responsibilities
A. Inventory Manager
Oversight of Inventory Processes
The Inventory Manager is responsible for overseeing all aspects of inventory management, including ordering, receiving, stocking, and auditing. They ensure compliance with SOPs and handle any escalated issues related to inventory. The Inventory Manager also reviews inventory reports and provides recommendations for improvements.
Reporting and Analysis
Prepare and analyze regular inventory reports, including stock levels, turnover rates, and discrepancies. Use these reports to identify trends, forecast future inventory needs, and make data-driven decisions. Share insights with other departments to support overall store operations.
B. Store Staff
Responsibilities in Ordering and Stocking
Assist with ordering and stocking inventory according to SOP guidelines and store policies. Ensure that products are placed correctly on shelves, labeled accurately, and organized efficiently. Report any issues or concerns related to inventory to the Inventory Manager.
Adherence to SOPs
Follow all SOP procedures related to inventory management, including handling and storing products, performing cycle counts, and documenting discrepancies. Participate in training and refresher courses to stay updated on SOP changes and best practices. Maintain a high level of accuracy and attention to detail in all inventory-related tasks.
C. Suppliers
Delivery and Documentation
Ensure timely and accurate delivery of inventory items as per the agreed schedule. Provide all necessary documentation, including delivery notes and invoices, to support the receiving process. Address any issues with deliveries, such as discrepancies or damages, promptly and professionally.
Quality Assurance
Maintain product quality standards and adhere to contractual agreements regarding product specifications. Collaborate with the Inventory Manager to resolve any quality issues or concerns. Provide support and information as needed to facilitate smooth inventory management.
IV. Inventory Controls
A. Stock Replenishment
Automatic Reordering Systems
Implement automatic reordering systems that trigger orders based on predefined stock levels and sales data. Use inventory management software to set reorder points and thresholds for different product categories. Monitor and adjust reorder parameters as needed to respond to changes in demand or supply chain conditions.
Manual Reordering Procedures
When necessary, manually review inventory levels and place orders based on current stock and forecasted needs. Follow established procedures for manual ordering to ensure consistency and accuracy. Communicate with suppliers to confirm order details and expected delivery dates.
B. Loss Prevention
Security Measures
Implement security measures such as surveillance cameras and alarm systems to deter theft and unauthorized access. Regularly review security footage and conduct spot checks to ensure the effectiveness of security protocols. Train staff on recognizing and reporting suspicious behavior.
Shrinkage Control
Monitor and analyze inventory shrinkage, including theft, damage, and administrative errors. Implement corrective actions to address identified causes of shrinkage, such as improving handling procedures or enhancing security measures. Regularly review and adjust loss prevention strategies based on shrinkage data.
C. Documentation and Record Keeping
Maintaining Accurate Records
Ensure that all inventory transactions, including receipts, adjustments, and transfers, are accurately recorded in the inventory management system. Keep detailed records of all inventory-related activities for auditing and compliance purposes. Regularly review records to ensure accuracy and completeness.
Retention Policies
Follow established policies for retaining inventory records, including purchase orders, receiving logs, and audit reports. Store records securely and in accordance with legal and regulatory requirements. Implement procedures for the timely disposal of outdated or unnecessary records.
V. Training and Compliance
A. Training Programs
Initial Training
Provide comprehensive training to new employees on inventory management procedures, including ordering, receiving, stocking, and reporting. Ensure that all staff are familiar with the SOP and understand their roles and responsibilities. Use a combination of classroom training, hands-on practice, and written materials.
Ongoing Training
Offer regular refresher courses and updates on inventory management practices to keep staff informed of any changes or improvements. Address any knowledge gaps or areas for improvement identified during performance reviews or audits. Encourage staff to seek additional training opportunities as needed.
B. Compliance Monitoring
Regular Audits and Reviews
Conduct regular audits and reviews of inventory management practices to ensure compliance with SOPs. Assess adherence to procedures and identify any areas requiring improvement or corrective action. Document audit findings and follow up on any issues identified.
Corrective Actions
Implement corrective actions for any non-compliance or procedural issues identified during audits or performance reviews. Develop action plans to address root causes and prevent recurrence. Monitor the effectiveness of corrective actions and make adjustments as needed.
C. Continuous Improvement
Feedback Mechanism
Establish a feedback mechanism for staff to report any issues, suggestions, or concerns related to inventory management. Use feedback to identify opportunities for improvement and enhance SOP procedures. Regularly review and incorporate feedback into the SOP as appropriate.
Review and Update Procedures
Periodically review and update the SOP to ensure it remains relevant and effective. Incorporate changes based on feedback, audit results, and industry best practices. Communicate any updates to all relevant staff and provide training on new procedures.
VI. Health and Safety
A. Compliance with Health Regulations
Food Safety Standards
Adhere to all relevant food safety regulations, including temperature controls, hygiene practices, and proper handling procedures. Ensure that all staff are trained in food safety protocols and that these protocols are consistently followed. Regularly review and update procedures to comply with the latest health and safety standards.
Sanitation Procedures
Implement rigorous sanitation procedures to maintain a clean and safe environment for inventory storage and handling. Regularly clean and sanitize storage areas, equipment, and utensils to prevent contamination. Document sanitation practices and conduct routine inspections to ensure compliance.
Hazardous Materials Handling
Properly handle and store hazardous materials, such as cleaning agents and chemicals, according to safety guidelines. Ensure that all staff are trained in the safe handling and disposal of hazardous materials. Maintain clear labeling and documentation for all hazardous materials used in the store.
B. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Types of PPE Required
Provide appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) to staff based on their roles and tasks, including gloves, aprons, and safety glasses. Ensure that PPE is used consistently during inventory handling and stocking activities. Regularly inspect PPE for wear and replace it as needed.
PPE Usage Guidelines
Establish guidelines for the proper use and maintenance of PPE, including donning and doffing procedures. Train staff on the correct use of PPE and the importance of wearing it during inventory-related tasks. Enforce PPE usage policies to ensure compliance and safety.
PPE Training and Compliance
Conduct regular training sessions on PPE usage and safety protocols to ensure that all staff understand and adhere to guidelines. Monitor compliance with PPE requirements and address any issues promptly. Update training materials and procedures as necessary to reflect changes in regulations or best practices.
C. Emergency Procedures
Emergency Contact Information
Maintain and display a list of emergency contact numbers, including local emergency services, store management, and relevant health and safety personnel. Ensure that all staff know how to access and use this information in case of an emergency. Review and update contact information regularly.
Incident Reporting Procedures
Establish clear procedures for reporting and documenting any incidents or accidents related to inventory management. Ensure that staff are trained on how to report incidents promptly and accurately. Review incident reports to identify causes and implement corrective actions as needed.
First Aid and Response
Equip the store with first aid kits and ensure that they are easily accessible. Train staff in basic first aid and emergency response procedures to handle injuries or health issues that may arise. Conduct regular drills to practice emergency response and ensure staff readiness.
VII. Performance Metrics and Reporting
A. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Inventory Turnover Ratio
Track the inventory turnover ratio to assess the efficiency of inventory management and the frequency at which inventory is sold and replaced. Analyze turnover rates to identify slow-moving items and adjust inventory strategies accordingly. Set targets for turnover ratios based on industry benchmarks and store performance.
Stock Accuracy
Measure the accuracy of inventory records by comparing physical counts with recorded stock levels. Monitor discrepancies and take corrective actions to improve stock accuracy. Aim for high levels of accuracy to ensure reliable inventory data and minimize stock-related issues.
Shrinkage Rate
Calculate the shrinkage rate to determine the percentage of inventory lost due to theft, damage, or administrative errors. Implement strategies to reduce shrinkage and monitor the effectiveness of these measures. Regularly review shrinkage data and adjust inventory control practices as needed.
B. Reporting Procedures
Regular Inventory Reports
Generate and review regular inventory reports, including daily, weekly, and monthly summaries of stock levels, sales, and adjustments. Use these reports to assess inventory performance and make informed decisions. Share reports with relevant stakeholders, including store management and finance teams.
Exception Reporting
Identify and report any exceptions or irregularities, such as significant discrepancies or unusual patterns in inventory data. Investigate the causes of these exceptions and take appropriate actions to address them. Document findings and recommendations for process improvements.
Performance Review Meetings
Conduct regular performance review meetings with inventory staff to discuss report findings, address issues, and set performance goals. Use these meetings to provide feedback, recognize achievements, and plan for continuous improvement. Ensure that meeting outcomes are documented and acted upon.
VIII. Review and Revision
A. SOP Review Schedule
Periodic Reviews
Schedule regular reviews of the SOP to ensure it remains relevant and effective. Conduct reviews annually or more frequently if there are significant changes in inventory practices or regulations. Involve key stakeholders in the review process to gather input and ensure comprehensive updates.
Review Process
Follow a structured process for reviewing and updating the SOP, including assessing current procedures, identifying areas for improvement, and incorporating feedback. Document any changes made to the SOP and communicate updates to all relevant staff. Ensure that revised procedures are implemented consistently across the store.
Approval of Revisions
Obtain approval for SOP revisions from store management or designated approvers before implementing changes. Ensure that all stakeholders are informed of the approved revisions and that updated SOP documents are distributed accordingly. Maintain a version history of the SOP to track changes over time.
B. Continuous Improvement
Feedback Collection
Continuously collect feedback from staff, management, and other stakeholders regarding the SOP and inventory management practices. Use feedback to identify opportunities for improvement and address any issues or concerns. Encourage staff to provide suggestions for enhancing inventory processes.
Process Enhancements
Implement process enhancements based on feedback, performance metrics, and industry best practices. Regularly review inventory management processes to identify and adopt new technologies or methodologies that can improve efficiency and accuracy. Monitor the impact of enhancements and make adjustments as needed.
Training on Updates
Provide training and support to staff on any updates or changes to the SOP. Ensure that all employees are familiar with new procedures and understand their impact on inventory management. Offer refresher courses and resources to help staff adapt to changes and maintain compliance.