Grocery Store Waste Management Guideline Sample
I. Introduction
A. Purpose
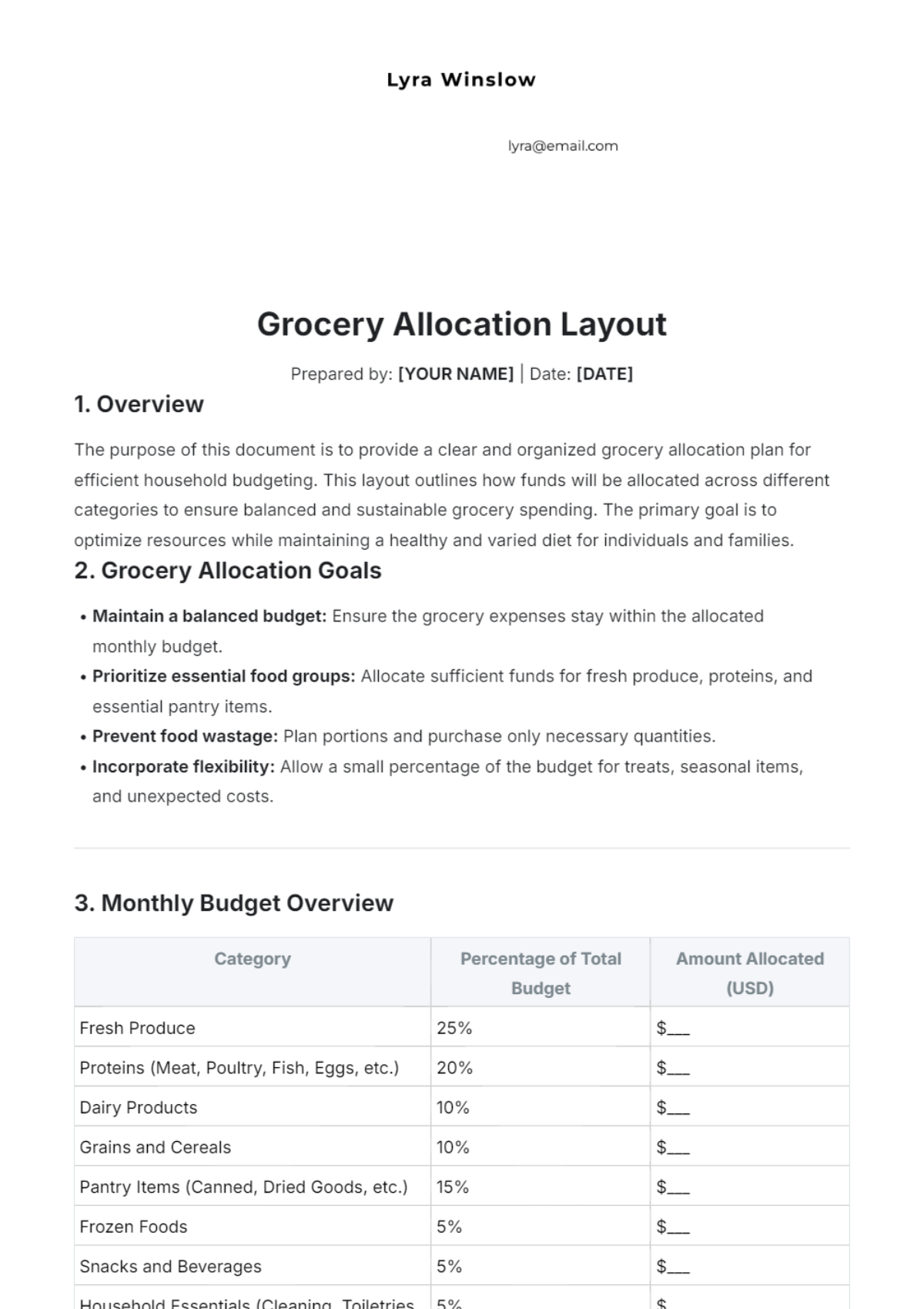
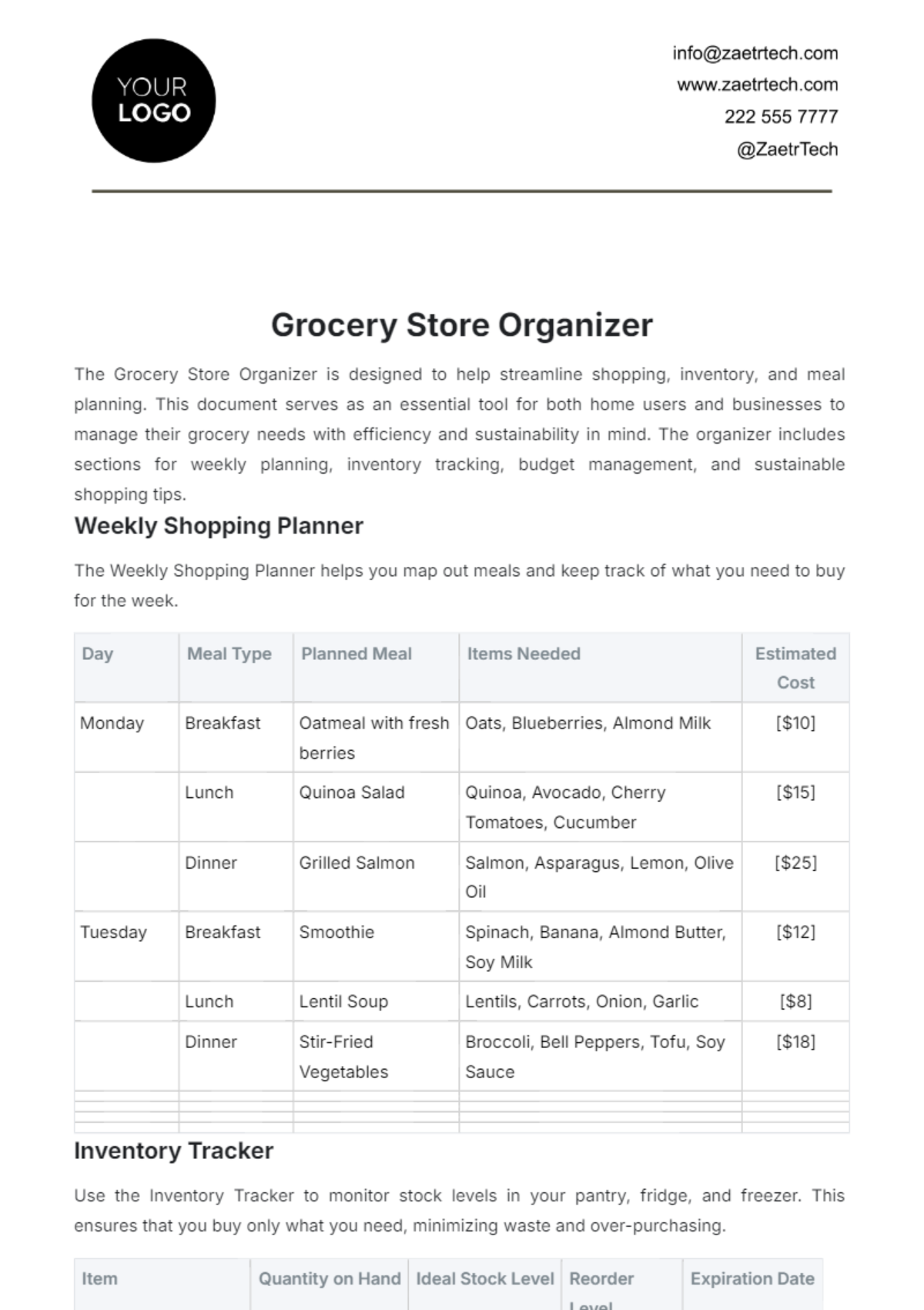
Establishing Guidelines: The purpose of this Grocery Store Waste Management Guideline is to establish clear procedures and practices for effective waste management at [Your Company Name]. This ensures that all staff are aware of their responsibilities and the processes involved in managing waste efficiently.
Environmental Responsibility: Adopting comprehensive waste management practices underscores our commitment to environmental sustainability. This guideline aims to reduce our environmental footprint by promoting recycling, reducing waste, and implementing responsible disposal methods.
Compliance: Ensuring compliance with local and national waste management regulations is crucial. This guideline provides a framework to meet legal requirements and promote safe and ethical waste disposal.
B. Scope
Applicability: This guideline applies to all departments and staff members at [Your Company Name]. It covers all types of waste generated within the store, including organic waste, recyclable materials, and hazardous waste.
Roles and Responsibilities: Each staff member has a role to play in waste management. This includes proper segregation, handling, and disposal of waste according to the procedures outlined in this document.
Continuous Improvement: The scope also includes a commitment to continuously improving our waste management practices. Regular reviews and updates to this guideline will ensure it remains effective and relevant.
C. Goals
Waste Reduction: One of the primary goals is to reduce the amount of waste generated. This involves implementing measures to minimize waste at the source, such as efficient inventory management and reducing packaging materials.
Recycling and Reuse: Another goal is to maximize the recycling and reuse of materials. This includes setting up proper recycling stations and encouraging the reuse of materials where possible.
Safe Disposal: Ensuring the safe and responsible disposal of non-recyclable and hazardous waste is also a key goal. This involves following best practices and regulations for handling and disposing of such materials.
II. Waste Segregation
Effective waste segregation is crucial for efficient waste management. The following table outlines the different types of waste and the appropriate segregation methods:
No. | Waste Type | Segregation Method |
|---|---|---|
1 | Organic Waste | Use designated bins for organic waste, separate from other types. |
2 | Recyclable Materials | Use clearly labeled recycling bins for paper, plastic, glass, and metal. |
3 | Hazardous Waste | Store hazardous waste in secure, labeled containers. |
4 | General Waste | Use bins for non-recyclable, non-hazardous waste. |
A. Organic Waste
Designated Bins: Organic waste should be disposed of in designated bins specifically for organic materials. This includes food scraps, spoiled produce, and other biodegradable items. Proper segregation helps in composting efforts and reduces contamination of other waste streams.
Separation Importance: Separating organic waste from other types of waste is crucial for effective composting. It prevents contamination and allows for the production of high-quality compost, which can be used to enrich soil or support community gardening projects.
B. Recyclable Materials
Clearly Labeled Bins: Recyclable materials should be placed in clearly labeled recycling bins. These bins should be strategically located throughout the store to encourage proper disposal. This includes bins for paper, plastic, glass, and metal.
Material Handling: Staff should be trained on the proper handling and disposal of recyclable materials. This ensures that recyclables are not contaminated with non-recyclable waste, which can compromise the recycling process.
C. Hazardous Waste
Secure Containers: Hazardous waste, such as cleaning chemicals and batteries, should be stored in secure, labeled containers. This prevents accidental exposure and ensures safe handling.
Proper Disposal: Hazardous waste must be disposed of according to local regulations. This often involves working with specialized waste disposal services to ensure safe and compliant disposal.
D. General Waste
Non-Recyclable Waste: General waste includes items that cannot be recycled or composted. These should be placed in designated bins for non-recyclable, non-hazardous waste. Proper disposal of general waste helps in maintaining a clean and safe store environment.
Regular Disposal: General waste bins should be emptied regularly to prevent overflow and maintain hygiene. Staff should be diligent in monitoring these bins and ensuring timely disposal.
III. Waste Reduction Strategies
The following table outlines key waste reduction strategies that can be implemented at [Your Company Name]:
No. | Strategy | Description |
|---|---|---|
1 | Inventory Management | Implement efficient inventory practices to reduce overstocking. |
2 | Packaging Reduction | Use minimal and eco-friendly packaging materials. |
3 | Donation Programs | Donate surplus food to local charities or food banks. |
4 | Staff Training | Educate staff on waste reduction techniques. |
A. Inventory Management
Efficient Practices: Implementing efficient inventory management practices helps in reducing overstocking and waste. This includes regular inventory checks, accurate demand forecasting, and timely restocking. By managing inventory effectively, we can minimize spoilage and reduce the amount of waste generated.
Technology Utilization: Utilizing technology, such as inventory management software, can enhance accuracy and efficiency. This helps in tracking stock levels, identifying slow-moving items, and making informed decisions to reduce waste.
B. Packaging Reduction
Eco-Friendly Materials: Using minimal and eco-friendly packaging materials helps in reducing waste. This includes opting for biodegradable, recyclable, or reusable packaging options. Reducing packaging waste not only benefits the environment but also aligns with customer preferences for sustainable products.
Supplier Collaboration: Collaborating with suppliers to reduce packaging waste is crucial. This can involve requesting bulk shipments with minimal packaging or working together to develop sustainable packaging solutions. Supplier collaboration can significantly impact our overall waste reduction efforts.
C. Donation Programs
Surplus Food Donation: Donating surplus food to local charities or food banks helps in reducing waste and supporting the community. This involves identifying surplus items that are safe for consumption and coordinating with local organizations for regular donations.
Partnerships: Establishing partnerships with local charities and food banks ensures a streamlined donation process. This helps in reducing food waste and making a positive impact on the community.
D. Staff Training
Waste Reduction Techniques: Educating staff on waste reduction techniques is essential. This includes training on efficient inventory management, proper handling of products, and identifying opportunities for waste reduction. Informed and engaged staff play a crucial role in minimizing waste.
Regular Workshops: Conducting regular workshops and training sessions helps in reinforcing waste reduction practices. This ensures that staff stay updated on best practices and continue to contribute to our waste reduction goals.
IV. Recycling Procedures
The following table outlines the recycling procedures for different types of recyclable materials at [Your Company Name]:
No. | Material Type | Recycling Procedure |
|---|---|---|
1 | Paper | Collect paper in designated bins and ensure it is free of contaminants. |
2 | Plastic | Rinse plastic containers and place them in recycling bins. |
3 | Glass | Separate glass by color and place in appropriate bins. |
4 | Metal | Rinse and place metal cans and containers in designated bins. |
A. Paper
Collection Bins: Collect paper in designated bins located throughout the store. Ensure that paper is free of contaminants such as food residue or plastic. Contaminated paper can hinder the recycling process and reduce the quality of recycled materials.
Regular Emptying: Regularly empty paper recycling bins to prevent overflow and ensure that collected paper is sent for recycling in a timely manner. This helps in maintaining cleanliness and efficiency in the recycling process.
B. Plastic
Rinsing Containers: Rinse plastic containers before placing them in recycling bins. This prevents contamination and ensures that plastics are clean and ready for recycling. Clean plastics are more likely to be accepted by recycling facilities and processed into new products.
Segregation: Segregate different types of plastics, if required, according to local recycling guidelines. This helps in enhancing the efficiency of the recycling process and ensuring that plastics are properly recycled.
C. Glass
Color Separation: Separate glass by color (e.g., clear, green, brown) and place them in appropriate bins. This helps in facilitating the recycling process, as different colors of glass are processed separately.
Handling Safety: Ensure safe handling of glass to prevent breakage and injury. Staff should be trained on proper handling techniques and provided with appropriate safety equipment.
D. Metal
Rinsing Cans: Rinse and clean metal cans and containers before placing them in designated recycling bins. This prevents contamination and ensures that metals are ready for recycling.
Segregation and Collection: Collect and segregate different types of metals, if required, according to local recycling guidelines. This helps in ensuring that metals are properly recycled and processed into new products.
V. Waste Disposal
The following table outlines the disposal procedures for different types of waste at [Your Company Name]:
No. | Waste Type | Disposal Procedure |
|---|---|---|
1 | Organic Waste | Compost organic waste or send to a composting facility. |
2 | Hazardous Waste | Dispose of hazardous waste through specialized waste disposal services. |
3 | General Waste | Collect general waste and dispose of it through regular waste collection services. |
4 | Electronic Waste | Recycle or dispose of electronic waste through certified e-waste disposal services. |
A. Organic Waste
Composting: Compost organic waste either on-site or send it to a composting facility. Composting helps in converting organic waste into valuable compost, which can be used to enrich soil. This reduces the amount of waste sent to landfills and supports sustainable practices.
Collection and Transport: Ensure proper collection and transport of organic waste to composting facilities. Use designated bins and follow local regulations for organic waste disposal.
B. Hazardous Waste
Specialized Services: Dispose of hazardous waste through specialized waste disposal services. This includes items such as cleaning chemicals, batteries, and other hazardous materials. Specialized services ensure safe and compliant disposal, preventing environmental contamination.
Storage and Handling: Store hazardous waste in secure, labeled containers until disposal. Staff should be trained on proper handling techniques and provided with appropriate safety equipment.
C. General Waste
Regular Collection: Collect general waste in designated bins and dispose of it through regular waste collection services. Ensure that bins are emptied regularly to maintain cleanliness and hygiene.
Minimizing Waste: Implement practices to minimize general waste, such as reducing packaging and encouraging the use of reusable items. This helps in reducing the overall volume of waste sent to landfills.
D. Electronic Waste
Certified Disposal Services: Recycle or dispose of electronic waste through certified e-waste disposal services. This includes items such as old computers, monitors, and other electronic devices. Certified services ensure that e-waste is properly handled and recycled, preventing environmental harm.
Data Security: Ensure that any data on electronic devices is securely erased before disposal. This protects sensitive information and ensures compliance with data protection regulations.
VI. Staff Training and Awareness
The following table outlines the key components of staff training and awareness programs for waste management at [Your Company Name]:
No. | Training Component | Description |
|---|---|---|
1 | Waste Segregation | Training on proper waste segregation techniques. |
2 | Recycling Procedures | Training on recycling procedures and best practices. |
3 | Hazardous Waste Handling | Training on safe handling and disposal of hazardous waste. |
4 | Waste Reduction Strategies | Training on strategies to reduce waste generation. |
A. Waste Segregation
Proper Techniques: Training on proper waste segregation techniques is essential for effective waste management. Staff should be educated on the different types of waste and how to segregate them correctly. This ensures that waste is properly sorted and reduces contamination.
Regular Refreshers: Conduct regular refresher courses to reinforce waste segregation practices. This helps in maintaining awareness and ensuring that staff continue to follow best practices.
B. Recycling Procedures
Best Practices: Training on recycling procedures and best practices helps in ensuring that recyclable materials are properly handled. This includes training on the use of recycling bins, cleaning recyclables, and understanding local recycling guidelines.
Incentives: Implement incentives to encourage staff participation in recycling programs. This can include recognition programs, rewards, or competitions to promote recycling efforts.
C. Hazardous Waste Handling
Safety Training: Training on the safe handling and disposal of hazardous waste is crucial. This includes proper storage, labeling, and disposal techniques, as well as the use of personal protective equipment. Safety training helps in preventing accidents and ensuring compliance with regulations.
Emergency Procedures: Educate staff on emergency procedures in case of hazardous waste spills or exposure. This includes immediate response actions, reporting procedures, and first aid measures.
D. Waste Reduction Strategies
Reducing Waste Generation: Training on strategies to reduce waste generation helps in minimizing waste at the source. This includes practices such as efficient inventory management, reducing packaging, and encouraging the use of reusable items.
Continuous Improvement: Encourage staff to identify and suggest new waste reduction strategies. This fosters a culture of continuous improvement and innovation in waste management practices.
VII. Waste Audit and Monitoring
The following table outlines the key components of the waste audit and monitoring process at [Your Company Name]:
No. | Audit Component | Description |
|---|---|---|
1 | Regular Audits | Conduct regular waste audits to assess waste management practices. |
2 | Data Collection | Collect data on the types and quantities of waste generated. |
3 | Performance Metrics | Establish performance metrics to evaluate waste management effectiveness. |
4 | Reporting and Review | Regularly report and review waste audit findings. |
A. Regular Audits
Audit Schedule: Conduct regular waste audits according to a predetermined schedule. Audits help in assessing the effectiveness of waste management practices and identifying areas for improvement. Regular audits ensure ongoing compliance and effectiveness.
Audit Teams: Form dedicated audit teams to conduct waste audits. These teams should include staff members from various departments to ensure comprehensive assessment and diverse perspectives.
B. Data Collection
Types and Quantities: Collect data on the types and quantities of waste generated. This includes detailed records of organic waste, recyclables, hazardous waste, and general waste. Accurate data collection is crucial for evaluating waste management practices and making informed decisions.
Tracking Systems: Implement tracking systems to record and monitor waste data. This can include digital tools or software to streamline data collection and analysis.
C. Performance Metrics
Evaluation Metrics: Establish performance metrics to evaluate the effectiveness of waste management practices. Metrics can include waste reduction targets, recycling rates, and compliance with segregation procedures. Regular evaluation helps in tracking progress and setting new goals.
Benchmarking: Compare performance metrics against industry benchmarks or best practices. This helps in identifying areas for improvement and setting realistic targets.
D. Reporting and Review
Audit Reports: Regularly report and review waste audit findings. Audit reports should include detailed analysis of data, identified issues, and recommendations for improvement. Reporting helps in maintaining transparency and accountability.
Action Plans: Develop action plans based on audit findings. This includes implementing recommended improvements and setting timelines for achieving targets. Regular review ensures that action plans are effective and progress is being made.
VIII. Collaboration with Suppliers
The following table outlines the key components of collaboration with suppliers for effective waste management at [Your Company Name]:
No. | Collaboration Component | Description |
|---|---|---|
1 | Sustainable Sourcing | Work with suppliers to source sustainable and eco-friendly products. |
2 | Packaging Reduction | Collaborate with suppliers to reduce packaging waste. |
3 | Return Programs | Establish return programs for reusable packaging and materials. |
4 | Supplier Audits | Conduct audits of supplier practices to ensure compliance with sustainability goals. |
A. Sustainable Sourcing
Eco-Friendly Products: Work with suppliers to source sustainable and eco-friendly products. This includes products made from recycled materials, biodegradable items, and sustainably sourced goods. Sustainable sourcing helps in reducing the environmental impact of our operations.
Supplier Criteria: Establish criteria for selecting suppliers based on their commitment to sustainability. This includes evaluating their environmental practices, certifications, and track record in sustainable sourcing.
B. Packaging Reduction
Minimal Packaging: Collaborate with suppliers to reduce packaging waste by opting for minimal packaging. This can involve bulk shipments, using recyclable materials, and reducing the use of plastic. Reducing packaging waste helps in minimizing the overall waste generated.
Innovative Solutions: Encourage suppliers to develop innovative packaging solutions that are environmentally friendly. This can include reusable packaging, compostable materials, and other sustainable options.
C. Return Programs
Reusable Packaging: Establish return programs for reusable packaging and materials. This includes working with suppliers to implement systems for returning and reusing packaging materials, such as pallets, crates, and containers. Return programs help in reducing waste and promoting a circular economy.
Incentives: Provide incentives for suppliers to participate in return programs. This can include cost-sharing arrangements, recognition programs, or other benefits to encourage supplier collaboration.
D. Supplier Audits
Audit Practices: Conduct audits of supplier practices to ensure compliance with our sustainability goals. Supplier audits help in verifying their commitment to sustainable practices and identifying areas for improvement.
Regular Reviews: Regularly review supplier practices and performance. This includes evaluating their waste management practices, environmental impact, and alignment with our sustainability goals. Regular reviews ensure ongoing collaboration and continuous improvement.
IX. Monitoring and Continuous Improvement
A. Performance Tracking
Regular Monitoring: Continuously track waste management performance using established metrics. This includes monitoring waste reduction targets, recycling rates, and compliance with segregation procedures. Regular monitoring helps in identifying trends and areas for improvement.
Data Analysis: Analyze waste management data to identify patterns and areas for improvement. Data analysis provides insights into the effectiveness of current practices and informs decision-making for future improvements.
B. Feedback Mechanisms
Staff Input: Implement feedback mechanisms to gather input from staff on waste management practices. This includes surveys, suggestion boxes, and regular meetings to discuss waste management issues. Staff input is valuable for identifying practical improvements and ensuring engagement.
Customer Feedback: Gather feedback from customers on waste management initiatives. This can include feedback on packaging, recycling facilities, and overall sustainability efforts. Customer feedback helps in aligning practices with customer expectations and enhancing the overall customer experience.
C. Continuous Training
Ongoing Development: Provide ongoing training and development for staff on waste management practices. This includes regular refresher courses, workshops, and access to resources on best practices. Continuous training ensures that staff are knowledgeable and up-to-date with current practices.
New Initiatives: Educate staff on new waste management initiatives and technologies. This includes training on new recycling programs, waste reduction strategies, and other innovative practices. Keeping staff informed about new initiatives helps in maintaining engagement and effectiveness.
D. Improvement Programs
Innovation and Research: Develop programs to encourage innovation and research in waste management practices. This includes exploring new technologies, methods, and strategies for reducing waste and improving sustainability. Innovation and research drive continuous improvement and progress.
Regular Reviews: Conduct regular reviews of waste management practices and performance. This includes evaluating the effectiveness of current practices, identifying areas for improvement, and setting new goals. Regular reviews ensure ongoing improvement and adaptation to changing circumstances.
Continuous monitoring and improvement are essential for maintaining effective waste management practices. By regularly evaluating performance, gathering feedback, and implementing new initiatives, we can ensure that our waste management efforts remain effective and aligned with our sustainability goals.