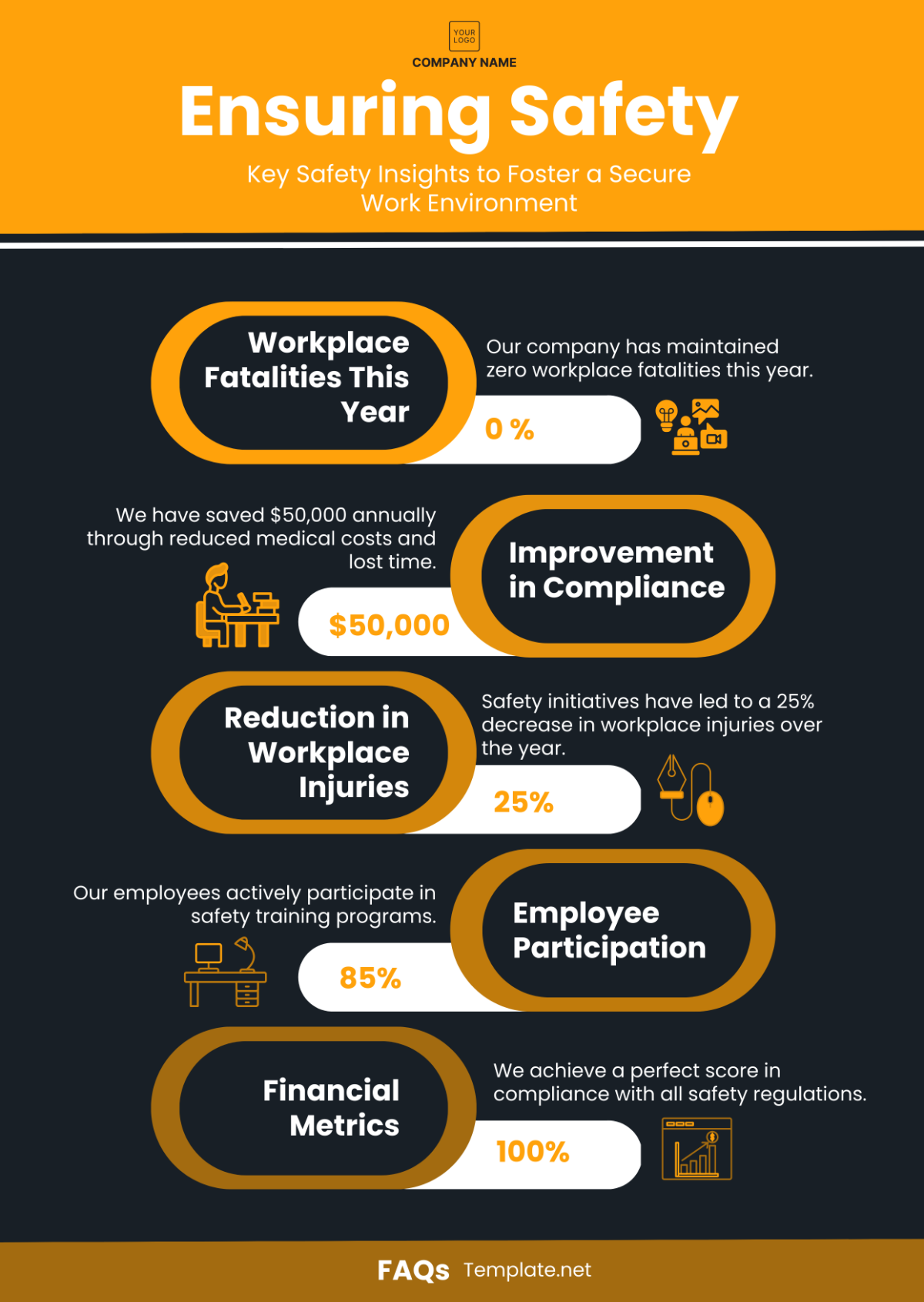
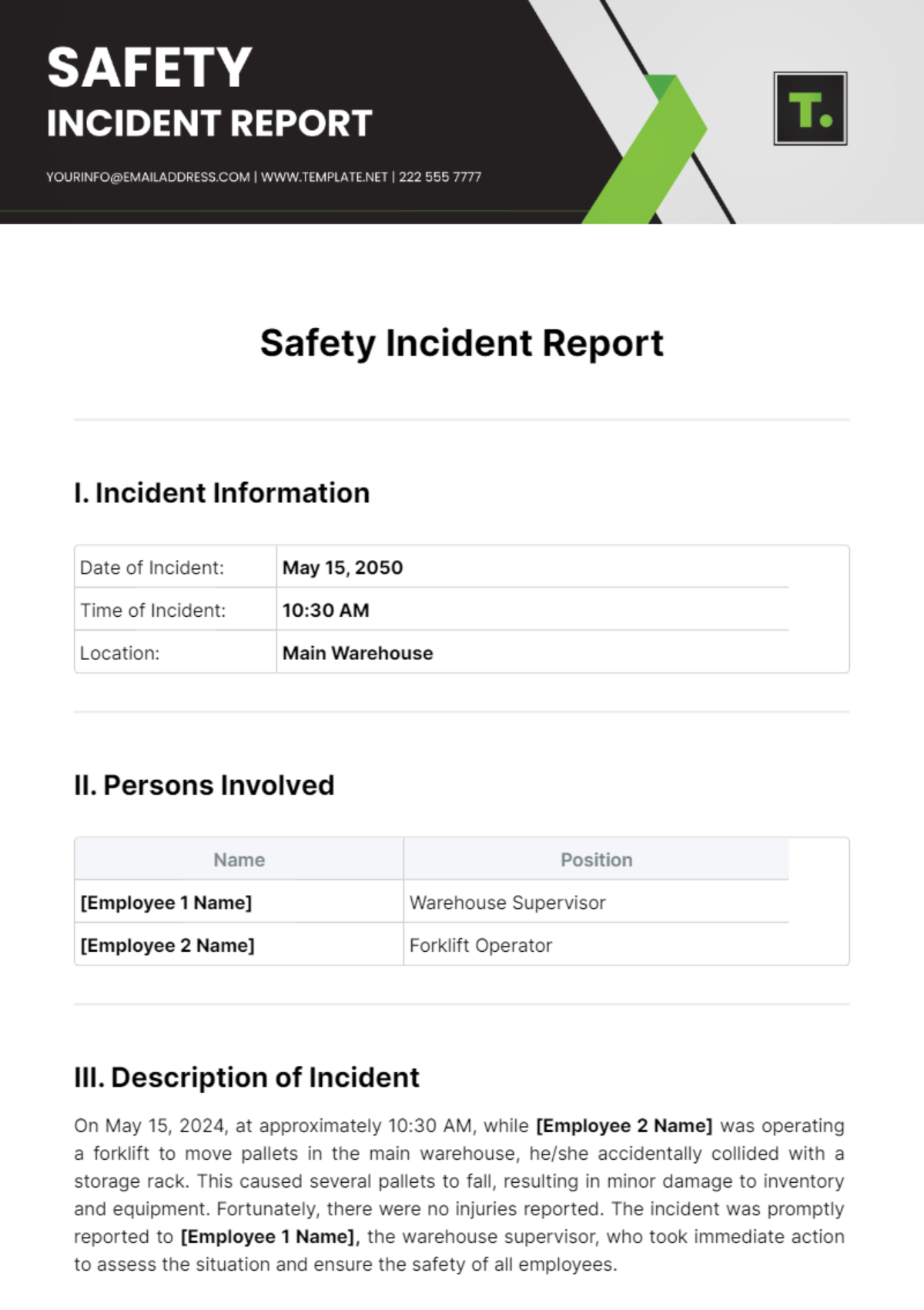
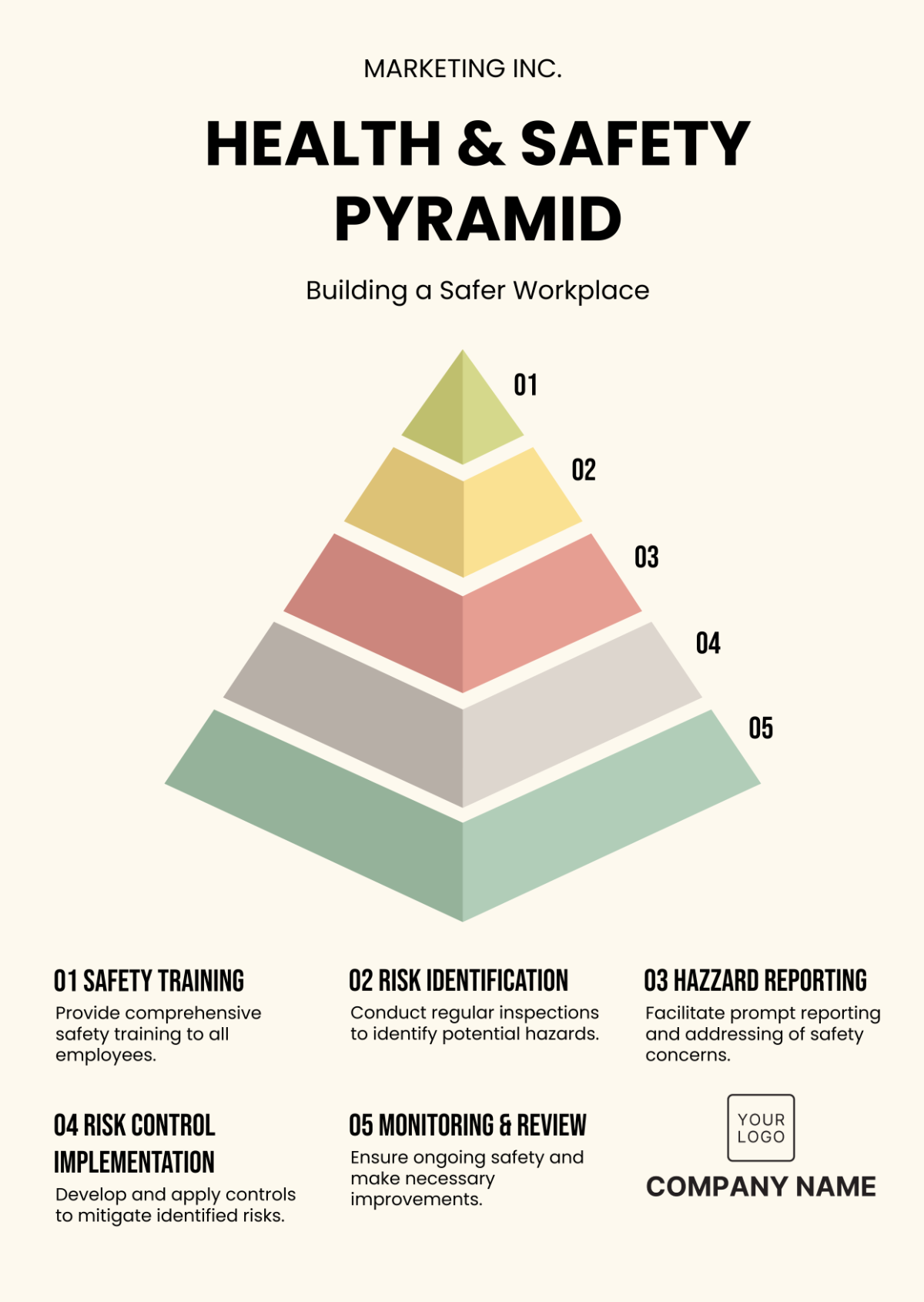
Professional Grocery Store Safety Protocols Guideline
I. Introduction
A. Purpose of the Guideline
The purpose of this comprehensive guideline is to establish a set of safety protocols and procedures that must be diligently followed to ensure a safe and healthy environment for employees, customers, and visitors at [Your Company Name]. Safety is a fundamental aspect of our operations, and this document provides a structured approach to identifying, mitigating, and managing various safety risks associated with grocery store operations. By adhering to these protocols, we aim to minimize hazards, prevent accidents, and comply with all relevant health and safety regulations. The ultimate goal is to foster a culture of safety that prioritizes the well-being of everyone who interacts with our store.
B. Scope of the Guideline
This guideline applies comprehensively to all individuals present on [Your Company Name] premises, including employees, contractors, vendors, and visitors. It encompasses a wide range of safety aspects, including personal safety, food safety, fire safety, and emergency response procedures. Each section of this document is designed to address specific safety concerns and provide clear instructions on how to handle potential risks. By implementing these protocols, we aim to create a secure and conducive environment for both work and shopping, ultimately enhancing the overall experience at [Your Company Name].
II. Personal Safety
A. Employee Safety
1. Training and Education
All employees must undergo a rigorous safety training program as part of their onboarding process. This training covers essential topics such as proper lifting techniques, the safe use of personal protective equipment (PPE), and emergency response procedures. Training sessions are designed to be interactive and engaging, ensuring that employees not only understand but also retain critical safety information. Regular refresher courses are mandatory to keep employees updated on the latest safety practices and regulations. This ongoing education helps employees stay vigilant and prepared to handle any safety challenges that may arise in the workplace.
2. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Employees are required to wear appropriate PPE, including gloves, aprons, and non-slip footwear, while performing their duties. PPE is essential for protecting employees from potential hazards such as sharp objects, hazardous chemicals, and slippery surfaces. [Your Company Name] provides all necessary PPE and ensures that it is of high quality and in good condition. Employees are responsible for properly wearing and maintaining their PPE. Any damaged or worn-out PPE should be reported immediately for replacement. Regular inspections of PPE are conducted to ensure that it meets safety standards and provides adequate protection.
3. Incident Reporting
It is crucial for all accidents, injuries, or near-misses to be reported immediately to a supervisor. Prompt reporting allows for a timely investigation of the incident and helps identify any underlying causes. An incident report form must be completed and submitted to the safety officer within 24 hours of the occurrence. This form should include details such as the date, time, location, and a description of the incident, as well as the names of any witnesses and the actions taken in response. The information collected is used to assess the incident, implement corrective measures, and prevent similar occurrences in the future.
B. Customer Safety
1. Store Layout and Signage
The store layout must be meticulously designed to ensure smooth traffic flow and minimize congestion. This includes organizing aisles, checkout areas, and product displays in a way that promotes safety and convenience. Clear and prominent signage should be placed throughout the store to guide customers and highlight potential hazards, such as wet floors, low-hanging displays, and restricted areas. Regular checks are conducted to ensure that all signs are visible, legible, and in good condition. The store layout is periodically reviewed and adjusted as needed to address any safety concerns and enhance the overall shopping experience.
2. Floor Maintenance
Maintaining clean and dry floors is essential for preventing slips, trips, and falls. Spills should be cleaned up immediately using appropriate cleaning agents and equipment. Wet floor signs should be prominently displayed to alert customers and employees to potential hazards. A regular floor inspection schedule is established to identify and address any potential trip hazards, such as loose tiles, uneven surfaces, or damaged carpets. Maintenance staff are trained to promptly report any floor issues and take corrective actions to ensure a safe environment.
3. Cart and Basket Safety
Shopping carts and baskets should be regularly inspected for damage to ensure they are safe for use. Any carts or baskets that are found to be damaged or defective should be removed from service immediately. Customers should be reminded to use carts and baskets safely, avoiding overloading them and using them for their intended purpose. Regular maintenance and repairs of carts and baskets are performed to prevent accidents and ensure their longevity. Clear guidelines on the proper use of carts and baskets are communicated to customers through signage and staff interactions.
III. Food Safety
A. Handling and Storage
1. Receiving Deliveries
Upon receiving deliveries, all items must be thoroughly inspected to ensure they meet quality and safety standards. This includes checking for visible damage, proper labeling, and correct temperatures. Perishable items must be inspected to ensure they are at the appropriate temperatures for safe storage. Any discrepancies or issues with the delivery should be reported immediately to the supplier for resolution. Documentation of the inspection process is maintained for record-keeping and quality assurance purposes.
2. Temperature Control
Maintaining proper temperature control is crucial for ensuring the safety of stored food items. Refrigerated items must be stored at or below 40°F (4°C), while frozen items must be kept at or below 0°F (-18°C). Regular temperature checks are conducted using calibrated thermometers, and the results are recorded to ensure compliance with safety standards. Any deviations from the required temperature range are addressed promptly to prevent potential spoilage or contamination. Temperature logs are reviewed regularly to identify any patterns or recurring issues.
3. Cross-Contamination Prevention
Preventing cross-contamination is essential for maintaining food safety. Raw and cooked foods must be stored separately to avoid contamination. Different utensils, cutting boards, and food preparation surfaces should be used for raw and cooked foods. Employees must wash their hands thoroughly after handling raw food and before touching cooked or ready-to-eat items. A color-coded system for cutting boards and utensils is implemented to further reduce the risk of cross-contamination. Regular training on cross-contamination prevention is provided to all employees.
B. Hygiene Practices
1. Employee Hygiene
Strict personal hygiene practices are mandatory for all employees. This includes regular hand washing with soap and water, wearing clean uniforms, and keeping hair restrained using appropriate hair coverings. Employees who are ill or exhibit symptoms of illness, such as coughing or sneezing, should refrain from handling food and must report their condition to a supervisor. Proper hygiene practices help prevent the spread of illness and maintain a clean environment for food preparation and service.
2. Sanitation Procedures
Effective sanitation procedures are critical for maintaining a hygienic environment. All food contact surfaces, equipment, and utensils must be cleaned and sanitized regularly. A detailed cleaning schedule is established, outlining daily, weekly, and monthly cleaning tasks. Cleaning solutions and sanitizers must be used according to manufacturer instructions to ensure they are effective against pathogens. Regular audits of sanitation procedures are conducted to ensure compliance and identify any areas for improvement.
3. Pest Control
A comprehensive pest control program is essential for preventing infestations and maintaining a clean environment. Regular inspections are conducted to identify any signs of pest activity, such as droppings or gnaw marks. Any signs of pest activity are addressed immediately, and professional pest control services are utilized as needed. Pest control measures include sealing entry points, maintaining cleanliness, and using approved pest control products. Records of pest control activities and inspections are maintained for reference.
IV. Fire Safety
A. Fire Prevention
1. Electrical Safety
Ensuring electrical safety is a key aspect of fire prevention. All electrical equipment, including wiring, outlets, and appliances, must be regularly inspected and maintained to prevent electrical hazards. Employees should be trained to recognize potential electrical hazards, such as frayed cords or overloaded circuits, and report them promptly. Regular inspections and maintenance help prevent electrical fires and ensure the safe operation of electrical systems.
2. Flammable Materials
Flammable materials, such as cleaning supplies, cooking oils, and paper products, must be stored in designated areas away from heat sources and open flames. Proper labeling and handling procedures should be followed to minimize the risk of fire. Storage containers for flammable materials should be approved for their intended use and kept closed when not in use. Employees should be trained on the safe handling and storage of flammable materials to prevent accidents.
3. Smoking Policy
Smoking is strictly prohibited within the store premises to prevent fire hazards and maintain a clean environment. Designated smoking areas should be provided outside the building, equipped with proper disposal containers for cigarette butts. These areas should be monitored to ensure compliance with the smoking policy. Signage should be posted to inform employees and customers of the smoking policy and designated smoking areas.
B. Fire Response
1. Fire Extinguishers
Fire extinguishers must be strategically placed throughout the store to ensure they are easily accessible in case of a fire. Regular inspections are conducted to ensure that fire extinguishers are fully charged and in good working condition. Employees should be trained on the proper use of fire extinguishers, including understanding the different types of extinguishers and their applications. Fire extinguisher training includes hands-on demonstrations and practice to ensure employees are prepared to use them effectively in an emergency.
2. Evacuation Plan
An evacuation plan must be developed, clearly communicated to all employees, and practiced regularly through fire drills. The plan should include specific evacuation routes, assembly points, and procedures for assisting individuals with disabilities. Emergency exits should be clearly marked, unobstructed, and easily accessible. Fire drills should be conducted at least quarterly to ensure that employees are familiar with the evacuation procedures and can evacuate the building quickly and safely.
3. Alarm Systems
Fire alarm systems must be installed and maintained to provide early warning in case of a fire. Regular tests are conducted to ensure that the alarm systems are functioning correctly and that alarms are audible throughout the store. Employees should be trained on how to respond when the alarm sounds, including initiating evacuation procedures and contacting emergency services. Maintenance records for fire alarm systems should be kept to track inspection and testing activities.
V. Emergency Response
A. Medical Emergencies
1. First Aid Kits
First aid kits must be readily available and fully stocked at all times. Kits should contain essential items such as bandages, antiseptics, gloves, and other medical supplies. Regular checks are conducted to ensure that the contents of the first aid kits are complete and within their expiration dates. Employees should be trained in basic first aid procedures, including how to use the items in the kit and provide initial care for injuries or medical conditions.
2. Emergency Contacts
A comprehensive list of emergency contacts should be prominently displayed in the store. This list should include contact information for local hospitals, emergency services, poison control, and other relevant agencies. Employees should know how to quickly access this information in case of an emergency. The emergency contact list should be updated regularly to ensure that the contact information remains current and accurate.
3. Incident Response
In the event of a medical emergency, employees should remain calm and follow the established response procedures. This includes assessing the situation, providing first aid if trained to do so, and contacting medical assistance as needed. Employees should ensure that the affected individual is kept safe and comfortable until help arrives. Proper documentation of the incident and the actions taken should be completed to provide a record for future reference and potential follow-up.
B. Natural Disasters
1. Preparedness Planning
A preparedness plan should be developed to address potential natural disasters, such as earthquakes, hurricanes, or tornadoes. The plan should outline specific actions to take before, during, and after a disaster, including securing the store and ensuring the safety of employees and customers. The preparedness plan should be reviewed and updated regularly to reflect any changes in the store’s layout, procedures, or external environment. Employees should be trained on the plan and familiarized with their roles and responsibilities during a natural disaster.
2. Communication Procedures
Clear communication procedures must be established to relay important information to employees and customers during a natural disaster. This includes using public address systems, social media, and other communication tools to provide timely updates and instructions. Designated communication channels should be identified, and employees should be trained on how to use them effectively. Regular drills and simulations should be conducted to test the communication procedures and ensure that they are effective.
3. Shelter and Evacuation
Designated shelter areas and evacuation routes should be clearly identified and marked throughout the store. Employees should be trained to guide customers to these areas and ensure their safety during a natural disaster. Shelter areas should be equipped with necessary supplies, such as first aid kits, water, and emergency food rations, to support individuals during extended periods of sheltering. Regular reviews of shelter and evacuation procedures should be conducted to ensure they remain effective and up-to-date.
VI. Security Measures
A. Theft Prevention
1. Surveillance Systems
Surveillance cameras should be installed in strategic locations throughout the store to monitor activity and deter theft. Cameras should cover key areas such as entrances, exits, and high-value merchandise sections. Regular maintenance and calibration of the surveillance systems are necessary to ensure they are functioning correctly and providing clear footage. Security footage should be reviewed periodically to identify any suspicious activity and address potential security concerns.
2. Employee Training
Employees should be trained to recognize and respond to suspicious behavior effectively. This training includes identifying potential thefts, approaching suspicious individuals in a non-confrontational manner, and reporting incidents to store security or management. Regular refresher training sessions should be conducted to reinforce theft prevention techniques and ensure employees remain vigilant.
3. Inventory Control
Implementing an effective inventory control system helps track products and reduce the risk of theft. Regular inventory checks should be conducted to identify any discrepancies and address potential issues. Inventory records should be maintained and reviewed to monitor product movement and detect any irregularities. Security measures, such as electronic article surveillance (EAS) tags and alarms, should be used to protect high-value items.
B. Customer Safety
1. Customer Service
Providing excellent customer service can help deter theft and create a safe shopping environment. Employees should be approachable, attentive, and ready to assist customers with their needs. Training on effective customer service techniques, including maintaining a visible presence on the sales floor and engaging with customers, can help reduce the likelihood of theft and create a positive shopping experience.
2. Incident Reporting
Customers should be encouraged to report any suspicious activity or security concerns to store employees. A clear process for reporting incidents should be communicated to both customers and employees, including how to use store communication channels or contact security personnel. A customer feedback system should be in place to address any concerns and provide follow-up as needed.
3. Security Personnel
If necessary, trained security personnel should be employed to patrol the store and respond to security incidents. Security staff should be easily identifiable, such as by wearing uniforms or badges, and trained to handle various security situations professionally. Security personnel should work closely with store management to address any security concerns and ensure a safe environment for customers and employees.
VII. Regular Audits and Inspections
A. Internal Audits
1. Safety Audits
Regular internal safety audits should be conducted to identify potential hazards and ensure compliance with safety protocols. These audits should cover all aspects of store safety, including personal safety, food safety, fire safety, and emergency response procedures. Auditors should use a detailed checklist to evaluate safety practices and procedures, and findings should be documented and reviewed by management. Corrective actions should be implemented based on audit results to address any identified issues.
2. Compliance Checks
Compliance checks should be performed to ensure adherence to local, state, and federal safety regulations. These checks involve reviewing store practices and procedures to verify that they meet regulatory requirements. Non-compliance issues should be addressed promptly, and any necessary changes to procedures or practices should be implemented to maintain compliance and avoid penalties.
B. External Inspections
1. Health Department Inspections
Routine inspections by health department officials should be welcomed and facilitated to ensure that food safety standards are met. Health department inspectors will review food handling, storage practices, and sanitation procedures to assess compliance with regulations. Any recommendations or corrective actions provided by the health department should be implemented promptly to maintain a high standard of food safety.
2. Fire Department Inspections
The local fire department should conduct regular inspections to ensure that fire safety measures are in place and functioning correctly. These inspections involve evaluating fire prevention systems, such as fire extinguishers, alarms, and sprinkler systems. Recommendations from the fire department should be addressed promptly, and any necessary improvements should be made to ensure compliance with fire safety standards.
3. Third-Party Audits
Engaging third-party auditors can provide an objective assessment of the store’s safety protocols and practices. Third-party audits offer valuable insights and recommendations for enhancing safety measures. Auditors will review safety procedures, conduct interviews with employees, and evaluate compliance with industry standards. The results of the audit should be used to inform ongoing safety improvements and address any identified areas for enhancement.
VIII. Continuous Improvement
A. Feedback and Suggestions
1. Employee Feedback
Employees are encouraged to provide feedback and suggestions for improving safety protocols. Regular meetings, surveys, and suggestion boxes provide opportunities for employees to share their input and raise any concerns. Feedback is reviewed by management, and actionable suggestions are implemented to enhance safety practices. Creating a culture of open communication helps ensure that safety concerns are addressed and improvements are continuously made.
2. Customer Feedback
Customer feedback is a valuable source of information for identifying areas where safety can be improved. Customers should be provided with easy-to-use feedback channels, such as comment cards, online surveys, and direct communication with store staff. Feedback should be reviewed and analyzed to identify trends and areas for improvement. Addressing customer concerns helps improve the overall safety and shopping experience.
B. Ongoing Training
1. Training Updates
Safety training programs should be updated regularly to reflect the latest best practices and regulatory requirements. Training materials should be reviewed and revised as needed to incorporate new information and address emerging safety issues. Ongoing training ensures that employees remain knowledgeable about safety protocols and are prepared to handle any changes in safety practices.
2. Cross-Training
Cross-training employees in various safety-related tasks enhances overall safety and ensures that employees can provide support in different areas. Employees who are familiar with multiple aspects of store safety can respond more effectively in emergencies and assist with safety procedures. Cross-training also helps improve team cohesion and ensures that there are multiple personnel available to address safety concerns.
C. Technology and Innovation
1. Safety Technologies
Investing in new safety technologies can significantly enhance store safety and improve overall efficiency. Technologies such as advanced surveillance systems, automated temperature monitoring, and smart fire detection systems can provide real-time data and alerts. Regularly evaluating and adopting new technologies helps keep the store’s safety measures up-to-date and effective.
2. Process Improvement
Continuous improvement of safety processes is essential for maintaining a safe environment. Regular reviews of safety protocols, risk assessments, and the implementation of new strategies help address identified risks and enhance safety measures. A proactive approach to process improvement ensures that the store remains compliant with safety standards and adapts to changing conditions.
IX. Conclusion
A. Commitment to Safety
[Your Company Name] is unwavering in its commitment to providing a safe and healthy environment for all employees, customers, and visitors. By adhering to the safety protocols outlined in this guideline, we aim to create a secure environment where everyone can thrive. Safety is not a one-time effort but an ongoing commitment that requires the active participation of all individuals involved.
B. Ongoing Efforts
Safety is an ongoing effort that demands continuous attention and improvement. Regularly reviewing and updating safety protocols, conducting training sessions, and incorporating feedback are essential for maintaining and enhancing safety standards. By fostering a culture of safety and ensuring that safety measures are consistently applied, we can create a safe and positive environment for all.
C. Final Remarks
The safety of our employees and customers is our top priority. At [Your Company Name], we are dedicated to continuously improving our safety measures and ensuring that our store remains a safe and welcoming place. We appreciate the efforts of all individuals in adhering to these protocols and contributing to a safe and secure shopping experience.