Grocery Store Quality Control Guideline
I. Introduction
The purpose of this Grocery Store Quality Control Guideline is to outline key procedures and best practices for maintaining high-quality standards in [Your Company Name]. Effective quality control ensures that our products meet customer expectations and comply with regulatory requirements.
A. Purpose
Ensure Consistency: Establish standards to ensure product consistency across all [Your Company Name] locations. Consistent quality helps build customer trust and brand loyalty.
Customer Satisfaction: Enhance customer satisfaction by providing high-quality products. Satisfied customers are more likely to return and recommend our store.
Compliance: Ensure compliance with food safety regulations and industry standards. Compliance helps avoid legal issues and potential fines.
Continuous Improvement: Promote a culture of continuous improvement in quality control processes. Continuous improvement leads to better efficiency and product quality.
B. Scope
Product Categories: This guideline applies to all product categories, including fresh produce, packaged goods, and deli items. Comprehensive coverage ensures quality across the board.
Store Locations: All [Your Company Name] locations must adhere to these quality control guidelines. Uniform standards help maintain a consistent customer experience.
Suppliers: Includes guidelines for evaluating and managing suppliers. Effective supplier management is crucial for maintaining product quality.
Staff Roles: Outlines the roles and responsibilities of staff involved in quality control. Clear roles help ensure accountability and effective implementation.
C. Target Audience
Managers: Responsible for overseeing the implementation of quality control measures. Managers ensure that staff follow the guidelines.
Quality Control Team: Dedicated team focused on monitoring and enforcing quality standards. The team plays a key role in identifying and addressing quality issues.
Employees: All employees must be aware of and adhere to quality control procedures. Employee involvement is essential for maintaining high standards.
Suppliers: Suppliers must understand and comply with our quality expectations. Supplier compliance is critical for ensuring product quality.
II. Quality Standards
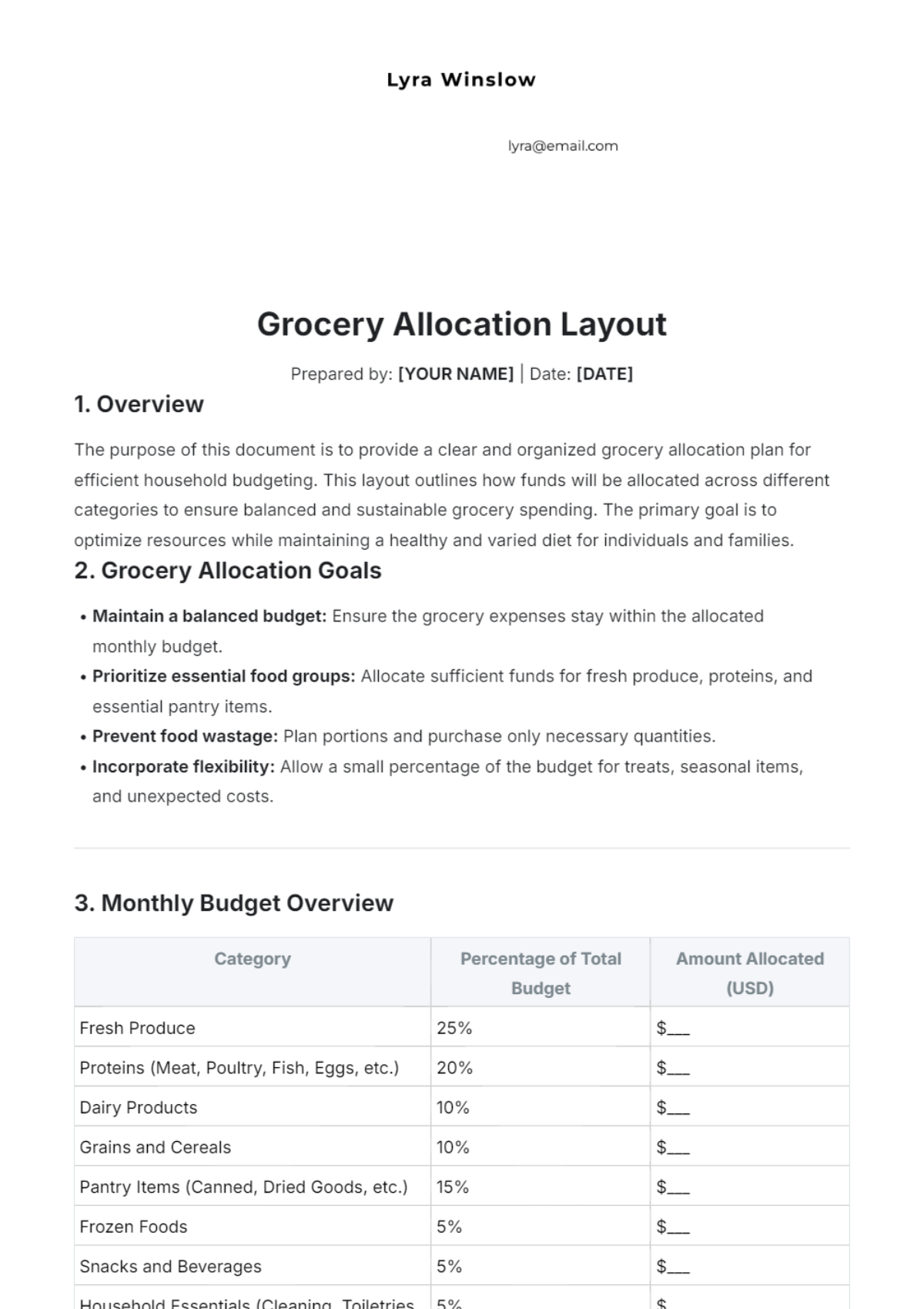
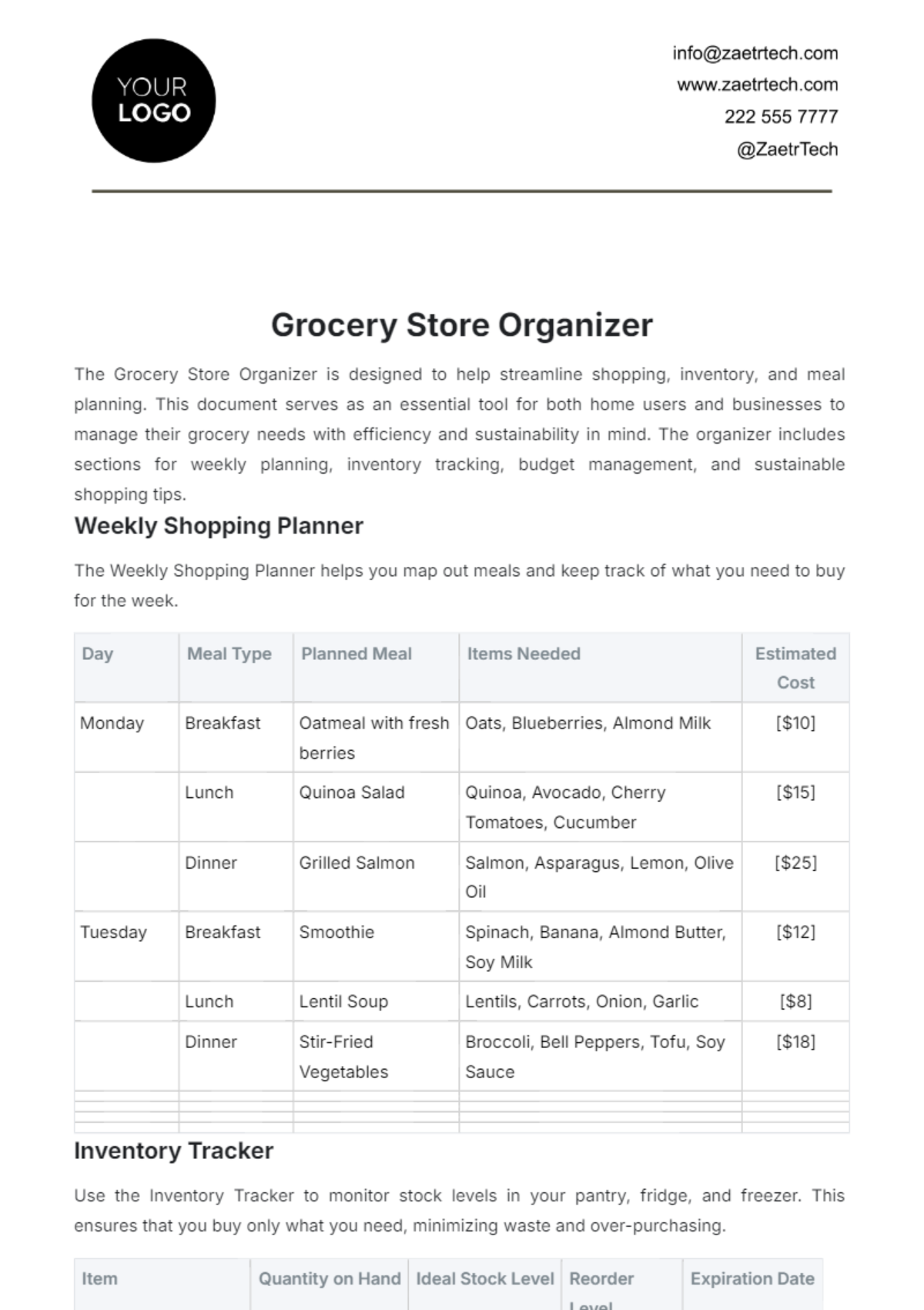
Maintaining high-quality standards is essential for customer satisfaction and regulatory compliance. The following table outlines the key quality standards for various product categories:
No. | Product Category | Quality Standards |
|---|---|---|
1 | Fresh Produce | Fresh, unblemished, and free from contamination. |
2 | Packaged Goods | Properly sealed, labeled, and within expiration date. |
3 | Deli Items | Freshly prepared, correctly stored, and appropriately labeled. |
4 | Dairy Products | Properly refrigerated, within expiration date, and free from spoilage. |
5 | Bakery Items | Freshly baked, properly packaged, and free from defects. |
A. Fresh Produce
Inspection Criteria: Inspect produce for freshness and signs of spoilage. Fresh produce should be free from bruises, mold, and other defects.
Storage Conditions: Store produce at the appropriate temperature and humidity levels. Proper storage helps extend shelf life and maintain quality.
Rotation Policy: Implement a first-in, first-out (FIFO) policy. FIFO ensures that older items are sold first, reducing waste and spoilage.
Supplier Standards: Set clear quality standards for suppliers. Supplier standards ensure that produce meets our quality requirements before it reaches the store.
Customer Feedback: Regularly collect and review customer feedback on produce quality. Feedback helps identify areas for improvement and address issues promptly.
B. Packaged Goods
Packaging Integrity: Ensure that all packaged goods are properly sealed and free from damage. Intact packaging protects products from contamination and spoilage.
Label Accuracy: Verify that product labels are accurate and comply with regulatory requirements. Accurate labeling provides essential information to customers.
Expiration Monitoring: Regularly check the expiration dates of packaged goods. Products near expiration should be removed from shelves to maintain quality.
Stock Rotation: Implement a stock rotation policy to ensure older products are sold first. Stock rotation helps reduce waste and maintain product freshness.
C. Deli Items
Preparation Standards: Ensure that all deli items are prepared according to strict hygiene and safety standards. Proper preparation reduces the risk of contamination.
Storage Requirements: Store deli items at the appropriate temperature to prevent spoilage. Proper storage helps maintain freshness and quality.
Labeling Practices: Accurately label all deli items with preparation dates and ingredient information. Clear labeling helps customers make informed choices.
Shelf Life Management: Monitor the shelf life of deli items and remove any expired products. Managing shelf life helps ensure that only fresh items are sold.
Customer Education: Provide customers with information on how to store and handle deli items. Educated customers are more likely to maintain product quality at home.
D. Dairy Products
Temperature Control: Maintain proper refrigeration for all dairy products. Consistent temperature control prevents spoilage and extends shelf life.
Expiration Checks: Regularly check the expiration dates of dairy products. Expired items should be promptly removed from shelves.
Supplier Compliance: Ensure that suppliers adhere to our quality standards for dairy products. Supplier compliance helps maintain product consistency and safety.
Quality Audits: Conduct regular quality audits to verify that dairy products meet our standards. Audits help identify and address potential issues.
Customer Communication: Educate customers on the importance of proper refrigeration at home. Effective communication helps ensure product quality after purchase.
E. Bakery Items
Baking Standards: Follow strict baking standards to ensure product quality and consistency. Proper baking techniques result in high-quality baked goods.
Packaging Practices: Properly package bakery items to protect them from contamination and damage. Effective packaging helps maintain freshness.
Shelf Life Monitoring: Monitor the shelf life of bakery items and remove any expired products. Shelf life management helps ensure that only fresh items are available.
Product Rotation: Implement a product rotation policy to ensure that older items are sold first. Rotation helps reduce waste and maintain quality.
Customer Feedback: Collect and review customer feedback on bakery items. Feedback helps identify areas for improvement and enhance product quality.
Maintaining high-quality standards across all product categories is crucial for customer satisfaction and compliance with regulations. By adhering to these guidelines, we can ensure that our products meet the highest quality standards.
III. Supplier Management
Effective supplier management is essential for ensuring that our products meet quality standards. The following table outlines key supplier management activities:
No. | Activity | Description |
|---|---|---|
1 | Supplier Selection | Evaluate and select suppliers based on quality criteria. |
2 | Supplier Audits | Conduct regular audits to ensure compliance. |
3 | Supplier Performance Review | Monitor and review supplier performance regularly. |
4 | Supplier Communication | Maintain open and transparent communication. |
5 | Supplier Improvement Plans | Develop and implement plans for continuous improvement. |
A. Supplier Selection
Evaluation Criteria: Develop clear criteria for evaluating potential suppliers. Criteria should include quality standards, reliability, and cost.
Supplier Assessment: Conduct thorough assessments of potential suppliers. Assessments should include site visits, product testing, and reference checks.
Approval Process: Establish a formal process for approving new suppliers. The approval process ensures that all selected suppliers meet our standards.
Contractual Agreements: Develop detailed contracts with suppliers outlining quality expectations. Contracts provide a legal framework for managing supplier relationships.
Initial Audits: Conduct initial audits of new suppliers to verify compliance with our standards. Initial audits help identify potential issues early on.
B. Supplier Audits
Audit Schedule: Develop a regular schedule for supplier audits. Regular audits help ensure ongoing compliance with our quality standards.
Audit Criteria: Establish clear criteria for conducting supplier audits. Criteria should include product quality, process control, and regulatory compliance.
Audit Reporting: Document audit findings and share them with suppliers. Reports provide a basis for developing improvement plans.
Corrective Actions: Work with suppliers to develop corrective actions for any identified issues. Corrective actions help improve supplier performance.
C. Supplier Performance Review
Performance Metrics: Develop key performance metrics for evaluating suppliers. Metrics should include delivery performance, product quality, and compliance.
Regular Reviews: Conduct regular performance reviews with suppliers. Reviews help identify trends and areas for improvement.
Feedback Mechanisms: Establish mechanisms for providing feedback to suppliers. Feedback helps suppliers understand our expectations and improve performance.
Continuous Improvement: Develop plans for continuous improvement based on performance reviews. Improvement plans help drive long-term success.
Recognition Programs: Implement programs to recognize top-performing suppliers. Recognition helps motivate suppliers to maintain high standards.
D. Supplier Communication
Communication Channels: Establish clear communication channels with suppliers. Effective communication helps ensure that issues are addressed promptly.
Regular Meetings: Schedule regular meetings with key suppliers. Meetings provide an opportunity to discuss performance, address issues, and plan improvements.
Information Sharing: Share relevant information with suppliers to support quality improvement. Information sharing helps build strong partnerships.
Conflict Resolution: Develop a process for resolving conflicts with suppliers. Effective conflict resolution helps maintain positive relationships.
E. Supplier Improvement Plans
Improvement Objectives: Develop clear objectives for supplier improvement plans. Objectives should be specific, measurable, and achievable.
Collaborative Approach: Work collaboratively with suppliers to develop improvement plans. Collaboration helps ensure buy-in and effective implementation.
Monitoring Progress: Regularly monitor progress on improvement plans. Monitoring helps ensure that objectives are being met.
Review and Adjustment: Regularly review and adjust improvement plans as needed. Regular review helps ensure continuous improvement.
Effective supplier management helps ensure that our products meet high-quality standards and comply with regulatory requirements. By working closely with our suppliers, we can drive continuous improvement and maintain strong partnerships.
IV. Product Inspection and Testing
Regular product inspection and testing are essential for ensuring product quality and compliance with standards. The following table outlines key inspection and testing activities:
No. | Activity | Description |
|---|---|---|
1 | Incoming Inspections | Inspect products upon receipt to ensure quality. |
2 | In-Process Inspections | Conduct inspections during production. |
3 | Final Inspections | Perform final inspections before products are shelved. |
4 | Random Sampling | Conduct random sampling for quality verification. |
5 | Laboratory Testing | Perform laboratory testing for specific quality attributes. |
A. Incoming Inspections
Inspection Criteria: Develop criteria for inspecting incoming products. Criteria should include product condition, packaging integrity, and labeling accuracy.
Inspection Process: Establish a process for conducting incoming inspections. The process should include visual inspection, sampling, and documentation.
Rejection Policy: Develop a policy for rejecting products that do not meet quality standards. The rejection policy helps ensure that only high-quality products are accepted.
Supplier Notification: Notify suppliers of any issues identified during incoming inspections. Supplier notification helps address issues promptly.
Documentation: Maintain detailed records of incoming inspections. Documentation provides a basis for tracking and addressing quality issues.
B. In-Process Inspections
Inspection Points: Identify key points in the production process for inspections. Inspection points should be chosen based on critical quality attributes.
Inspection Procedures: Develop procedures for conducting in-process inspections. Procedures should include criteria, methods, and documentation requirements.
Corrective Actions: Implement corrective actions for any issues identified during in-process inspections. Corrective actions help prevent defects and improve quality.
Process Monitoring: Regularly monitor and review the effectiveness of in-process inspections. Monitoring helps identify trends and areas for improvement.
C. Final Inspections
Inspection Criteria: Develop criteria for final product inspections. Criteria should include product appearance, packaging, and labeling.
Inspection Procedures: Establish procedures for conducting final inspections. Procedures should include methods, criteria, and documentation requirements.
Acceptance Criteria: Define acceptance criteria for final products. Acceptance criteria help ensure that only high-quality products are shelved.
Documentation: Maintain detailed records of final inspections. Documentation provides a basis for tracking quality issues and ensuring compliance.
D. Random Sampling
Sampling Plan: Develop a plan for random sampling of products. The sampling plan should include criteria for selecting samples and sample sizes.
Sampling Procedures: Establish procedures for conducting random sampling. Procedures should include methods, criteria, and documentation requirements.
Quality Verification: Use random sampling to verify product quality. Quality verification helps ensure that products meet our standards.
Corrective Actions: Implement corrective actions for any issues identified through random sampling. Corrective actions help improve overall quality.
E. Laboratory Testing
Testing Criteria: Develop criteria for laboratory testing of products. Criteria should include specific quality attributes to be tested.
Testing Procedures: Establish procedures for conducting laboratory testing. Procedures should include methods, criteria, and documentation requirements.
Test Results: Review and analyze laboratory test results. Test results provide a basis for quality verification and improvement.
Corrective Actions: Implement corrective actions for any issues identified through laboratory testing. Corrective actions help improve product quality.
Regular product inspection and testing help ensure that our products meet high-quality standards and comply with regulatory requirements. By adhering to these guidelines, we can maintain customer satisfaction and drive continuous improvement.
V. Handling and Storage
Proper handling and storage are essential for maintaining product quality and safety. The following table outlines key handling and storage activities:
No. | Activity | Description |
|---|---|---|
1 | Temperature Control | Maintain appropriate temperatures for different products. |
2 | Humidity Control | Manage humidity levels to prevent spoilage. |
3 | Stock Rotation | Implement a stock rotation policy to ensure freshness. |
4 | Cleanliness and Hygiene | Ensure cleanliness and hygiene in storage areas. |
5 | Pest Control | Implement pest control measures to protect products. |
A. Temperature Control
Refrigeration Units: Regularly monitor and maintain refrigeration units. Proper maintenance helps ensure consistent temperature control.
Temperature Monitoring: Implement a system for continuous temperature monitoring. Monitoring helps identify and address temperature fluctuations promptly.
Temperature Logs: Maintain detailed temperature logs for all refrigerated products. Logs provide a record for compliance and quality verification.
Emergency Procedures: Develop emergency procedures for handling temperature deviations. Emergency procedures help prevent product spoilage during equipment failures.
B. Humidity Control
Humidity Monitoring: Regularly monitor humidity levels in storage areas. Proper monitoring helps prevent spoilage and maintain product quality.
Humidity Control Equipment: Use appropriate equipment to control humidity levels. Equipment should be regularly maintained and calibrated.
Storage Guidelines: Develop guidelines for storing products based on humidity requirements. Guidelines help ensure that products are stored in optimal conditions.
Documentation: Maintain records of humidity levels and control measures. Documentation provides a basis for compliance and quality verification.
C. Stock Rotation
FIFO Policy: Implement a First-in, First-out (FIFO) stock rotation policy. FIFO helps ensure that older products are sold first, reducing waste and spoilage.
Shelf Life Monitoring: Regularly monitor the shelf life of all products. Monitoring helps ensure that products are sold within their optimal freshness period.
Rotation Procedures: Develop procedures for rotating stock effectively. Procedures should include guidelines for identifying and rotating older stock.
Training: Provide training to staff on stock rotation procedures. Training helps ensure that staff understand and follow rotation guidelines.
D. Cleanliness and Hygiene
Cleaning Schedule: Develop a regular cleaning schedule for storage areas. A consistent cleaning schedule helps maintain cleanliness and hygiene.
Sanitation Procedures: Implement sanitation procedures for handling products. Proper sanitation helps prevent contamination and maintain product quality.
Hygiene Standards: Establish hygiene standards for staff working in storage areas. Hygiene standards help ensure that staff practices do not compromise product quality.
Audit and Inspection: Conduct regular audits and inspections of storage areas. Audits help identify areas for improvement and ensure compliance.
E. Pest Control
Pest Control Plan: Develop a comprehensive pest control plan. The plan should include measures for preventing and addressing pest infestations.
Regular Inspections: Conduct regular inspections for signs of pests. Regular inspections help identify and address issues promptly.
Pest Control Measures: Implement appropriate pest control measures. Measures should be safe, effective, and comply with regulatory requirements.
Documentation: Maintain detailed records of pest control activities. Documentation provides a basis for compliance and quality verification.
Proper handling and storage are crucial for maintaining product quality and safety. By adhering to these guidelines, we can ensure that our products meet high standards and provide a safe and satisfying experience for our customers.
VI. Quality Control Training
Effective quality control training is essential for ensuring that staff understand and follow quality guidelines. The following table outlines key training activities:
No. | Activity | Description |
|---|---|---|
1 | Initial Training | Provide initial training for new employees. |
2 | Ongoing Training | Conduct ongoing training sessions for all staff. |
3 | Specialized Training | Offer specialized training for specific roles. |
4 | Training Materials | Develop comprehensive training materials. |
5 | Training Evaluation | Evaluate the effectiveness of training programs. |
A. Initial Training
Training Content: Develop comprehensive training content for new employees. Content should cover quality standards, procedures, and expectations.
Training Schedule: Establish a regular schedule for initial training sessions. A consistent schedule helps ensure that all new employees receive timely training.
Hands-On Training: Include hands-on training components to reinforce learning. Hands-on training helps employees apply what they have learned.
Assessment: Conduct assessments to evaluate new employees' understanding of quality guidelines. Assessments help ensure that training objectives are met.
B. Ongoing Training
Regular Sessions: Schedule regular ongoing training sessions for all staff. Regular training helps reinforce quality standards and procedures.
Updated Content: Continuously update training content to reflect changes in quality guidelines. Updated content ensures that staff have the latest information.
Interactive Training: Use interactive training methods to engage staff. Interactive methods, such as workshops and group discussions, enhance learning.
Feedback Mechanisms: Implement mechanisms for collecting feedback on training sessions. Feedback helps identify areas for improvement in training programs.
C. Specialized Training
Role-Specific Training: Develop specialized training programs for specific roles. Specialized training ensures that staff have the necessary skills for their roles.
Advanced Topics: Include advanced topics in specialized training programs. Advanced topics help staff develop expertise in quality control.
Certifications: Offer certifications for completing specialized training programs. Certifications provide recognition for staff expertise and commitment to quality.
Continuous Learning: Encourage continuous learning and development. Continuous learning helps staff stay current with industry trends and best practices.
Mentorship Programs: Implement mentorship programs to support specialized training. Mentorship programs provide guidance and support for staff development.
D. Training Materials
Comprehensive Materials: Develop comprehensive training materials that cover all aspects of quality control. Comprehensive materials provide a solid foundation for learning.
Accessible Formats: Ensure that training materials are available in accessible formats. Accessible formats help accommodate different learning styles and needs.
Regular Updates: Regularly update training materials to reflect changes in quality guidelines. Updated materials ensure that staff have the latest information.
Digital Resources: Provide digital resources, such as online training modules and videos. Digital resources offer flexibility and convenience for staff training.
E. Training Evaluation
Evaluation Methods: Develop methods for evaluating the effectiveness of training programs. Evaluation methods should include assessments, feedback, and performance reviews.
Regular Assessments: Conduct regular assessments to evaluate staff understanding of quality guidelines. Assessments help identify areas for improvement.
Feedback Collection: Collect feedback from staff on training programs. Feedback provides valuable insights for improving training programs.
Continuous Improvement: Use evaluation results to continuously improve training programs. Continuous improvement helps ensure that training programs remain effective.
Effective quality control training helps ensure that staff understand and follow quality guidelines. By providing comprehensive and ongoing training, we can maintain high-quality standards and drive continuous improvement.
VII. Customer Feedback and Complaints
A. Feedback Collection
Feedback Channels: Establish multiple channels for collecting customer feedback. Channels should include in-store surveys, online forms, and social media.
Incentives: Offer incentives to encourage customers to provide feedback. Incentives, such as discounts or loyalty points, can increase response rates.
Feedback Forms: Develop easy-to-use feedback forms for customers. Forms should be simple, straightforward, and accessible.
Regular Collection: Regularly collect feedback to ensure ongoing insights. Consistent feedback collection helps identify trends and areas for improvement.
Feedback Documentation: Maintain detailed records of customer feedback. Documentation provides a basis for analysis and action.
B. Complaint Handling
Complaint Procedures: Develop clear procedures for handling customer complaints. Procedures should include steps for logging, investigating, and resolving complaints.
Timely Response: Ensure timely responses to customer complaints. Prompt responses help maintain customer trust and satisfaction.
Resolution Tracking: Track the resolution of customer complaints. Tracking helps ensure that all complaints are addressed and resolved.
Staff Training: Train staff on complaint handling procedures. Training helps ensure that staff can effectively manage customer complaints.
C. Feedback Analysis
Data Analysis: Analyze customer feedback data to identify trends and issues. Data analysis helps uncover patterns and areas for improvement.
Root Cause Analysis: Conduct root cause analysis for recurring issues. Root cause analysis helps identify underlying problems and develop effective solutions.
Action Plans: Develop action plans based on feedback analysis. Action plans should include specific steps for addressing identified issues.
Performance Metrics: Establish metrics for evaluating the effectiveness of actions taken. Metrics help track progress and measure success.
Regular Reviews: Regularly review feedback analysis and action plans. Reviews help ensure continuous improvement and effectiveness.
D. Corrective Actions
Immediate Actions: Implement immediate actions to address urgent issues. Immediate actions help prevent further customer dissatisfaction.
Long-Term Solutions: Develop long-term solutions for recurring issues. Long-term solutions help address root causes and improve overall quality.
Monitoring Progress: Monitor the progress of corrective actions. Monitoring helps ensure that actions are effective and issues are resolved.
Continuous Improvement: Use customer feedback to drive continuous improvement. Continuous improvement helps enhance product quality and customer satisfaction.
E. Customer Communication
Transparency: Maintain transparency with customers about actions taken. Transparency helps build trust and credibility.
Regular Updates: Provide regular updates to customers on the status of their feedback or complaints. Regular updates help keep customers informed and engaged.
Thank You Messages: Send thank you messages to customers who provide feedback. Thank you messages show appreciation and encourage future feedback.
Feedback Loop: Establish a feedback loop to keep customers informed of changes made based on their input. A feedback loop helps demonstrate that customer feedback is valued and acted upon.
Effectively managing customer feedback and complaints helps us improve product quality and customer satisfaction. By actively seeking and addressing feedback, we can drive continuous improvement and maintain high standards.
VIII. Quality Control Documentation
A. Document Creation
Standard Operating Procedures: Develop Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) for quality control activities. SOPs provide clear guidelines for staff.
Quality Manuals: Create quality manuals that outline quality standards and procedures. Quality manuals serve as comprehensive references for staff.
Forms and Templates: Develop forms and templates for quality control activities. Forms and templates help ensure consistency and accuracy.
Record Keeping: Establish procedures for keeping detailed records of quality control activities. Record keeping provides a basis for tracking and verification.
B. Document Storage
Digital Storage: Implement digital storage solutions for quality control documents. Digital storage provides easy access and security.
Physical Storage: Ensure secure physical storage for important quality control documents. Physical storage helps protect documents from damage and loss.
Backup Systems: Develop backup systems for digital documents. Backups help prevent data loss in case of system failures.
Storage Organization: Organize storage systems for easy retrieval of documents. Proper organization helps ensure that documents are readily available when needed.
C. Document Review
Regular Reviews: Schedule regular reviews of quality control documents. Regular reviews help ensure that documents remain current and accurate.
Review Procedures: Develop procedures for reviewing and updating documents. Review procedures should include criteria, methods, and documentation requirements.
Stakeholder Involvement: Involve relevant stakeholders in the document review process. Stakeholder involvement helps ensure that documents meet all requirements.
Revision Tracking: Implement a system for tracking document revisions. Revision tracking helps maintain a history of changes and updates.
Approval Process: Establish an approval process for updated documents. The approval process ensures that all changes are reviewed and approved by appropriate personnel.
D. Document Access
Access Control: Implement access control measures for quality control documents. Access control helps ensure that only authorized personnel can access sensitive documents.
Access Procedures: Develop procedures for requesting and granting access to documents. Access procedures help ensure that access is properly managed.
Training: Provide training to staff on document access procedures. Training helps ensure that staff understand how to access and use quality control documents.
Monitoring Access: Regularly monitor access to quality control documents. Monitoring helps ensure that access is properly controlled and managed.
E. Document Compliance
Regulatory Requirements: Ensure that quality control documents comply with regulatory requirements. Compliance helps avoid legal issues and potential fines.
Compliance Audits: Conduct regular compliance audits to verify that documents meet all requirements. Audits help identify and address any compliance issues.
Document Updates: Regularly update documents to reflect changes in regulatory requirements. Updates help ensure that documents remain compliant.
Compliance Training: Provide training to staff on regulatory requirements and document compliance. Training helps ensure that staff understand and follow compliance guidelines.
Proper documentation is essential for maintaining quality control standards and ensuring compliance. By adhering to these guidelines, we can ensure that our documentation practices support our quality control efforts.
IX. Review and Update
A. Annual Review
Scheduled Reviews: The management schedules an annual review of the quality control guideline. Regular reviews help ensure that the guideline remains relevant and effective.
Assessment of Effectiveness: Assess the effectiveness of the current guideline. Assessments help identify areas for improvement and necessary updates.
Documentation of Findings: Document findings and recommendations from the annual review. Documentation provides a basis for making informed changes.
Action Plans: Develop action plans for implementing recommended changes. Action plans help ensure that updates are executed effectively.
B. Stakeholder Involvement
Engagement of Stakeholders: The review process involves relevant stakeholders. Stakeholder engagement helps ensure that all perspectives are considered.
Feedback Collection: Collect feedback from stakeholders on the current guideline. Feedback provides valuable insights for improving the guideline.
Discussion Forums: Organize discussion forums for stakeholders to share their perspectives. Discussion forums encourage open communication and collaboration.
Consensus Building: Work towards building consensus among stakeholders on necessary changes. Consensus helps ensure that changes are supported and accepted.
C. Update Procedures
Documented Changes: We will maintain documentation of all changes made to the guideline. Documentation helps maintain a record of updates for future reference.
Version Control: Implement version control for the quality control guideline. Version control helps ensure that all staff are using the most current version.
Review of Updates: Regularly review updates to ensure that they remain relevant and effective. Regular reviews help maintain the integrity of the guideline.
D. Communication of Changes
Internal Communication: Changes will be communicated to all relevant staff in a timely manner. Timely communication helps ensure that all staff are aware of updates.
Training on Changes: Provide training on significant changes to the guideline. Training helps ensure that staff understand and implement updates effectively.
Documentation of Communication: Maintain records of communications regarding changes to the guideline. Documentation helps track the dissemination of information.
Feedback on Changes: Collect feedback from staff on changes made to the guideline. Feedback helps assess the impact of updates and identify areas for improvement.
E. Implementation Monitoring
Monitoring Progress: The management will monitor the implementation of changes to the guideline. Monitoring helps ensure that updates are being executed effectively.
Performance Metrics: Establish metrics for evaluating the effectiveness of changes. Metrics help track progress and measure success.
Regular Reviews: Conduct regular reviews to assess the effectiveness of changes. Regular reviews help identify areas for further improvement.
Continuous Improvement: Use implementation monitoring results to drive continuous improvement. Continuous improvement helps ensure that the guideline remains relevant and effective.
Regular review and update of this Grocery Store Quality Control Guideline ensures that it remains current and effective. By adhering to these guidelines, we can maintain high-quality standards and drive continuous improvement.